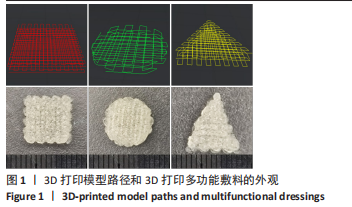
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1562-1567.doi: 10.12307/2024.371
• 功能性生物材料Functional biomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印多功能敷料治疗放创复合伤
焦文成1,2,代 晶3,严文锐2,4,沈锦涛2,胡静璐2,5,金义光2,4,杜丽娜1,2,4,5
- 1河北大学,河北省保定市 071002;2中国人民解放军军事医学研究院辐射医学研究所,北京市 100850;3中国人民解放军西部战区总医院,四川省成都市 610083;4广东药科大学,广东省广州市 510006;5河南大学,河南省开封市 475004
3D-printed multifunctional wound dressing for combined radiation and wound injury
Jiao Wencheng1, 2, Dai Jing3, Yan Wenrui2, 4, Shen Jintao2, Hu Jinglu2, 5, Jin Yiguang2, 4, Du Lina1, 2, 4, 5
- 1Hebei University, Baoding 071002, Hebei Province, China; 2Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine, Beijing 100850, China; 3General Hospital of Western War Zone, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China; 4Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 5Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, Henan Province, China
摘要:
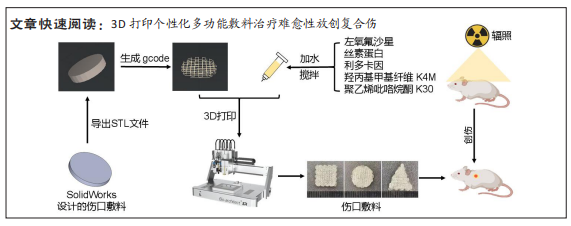
文题释义:
3D打印:是一种将数字模型文件分层处理、逐层添加材料并逐层叠加,最终获得实物的快速成型技术。3D打印工艺分为3个步骤:首先是数据处理,即对模型进行处理;其次是材料选择,将处理后的数据通过逐层叠加的方式制作实物;最后是成型处理,即将所选的材料逐层添加到实体模型中。在打印过程中,电脑会根据扫描获得的三维数据来控制激光发生器、喷头和材料,从而将模型分层、切片并逐层打印出来。放创复合伤:是由辐射损伤复合机械损伤引起的皮肤损伤,主要表现为辐射破坏了修复机制,导致创面愈合延迟或经久不愈,易反复发作。此外,辐射还会导致皮肤表面产生大量自由基,细胞因子与生长因子表达降低,而相关凋亡基因表达增高,受照皮肤局部成纤维细胞数量减少、形态受损、功能下降、肉芽组织生长缓慢等。
背景:放创复合伤主要发生在肿瘤放疗和核辐射事故患者中,由于辐射破坏修复机制导致伤口愈合延迟或延长,目前仍缺乏有效的治疗策略。
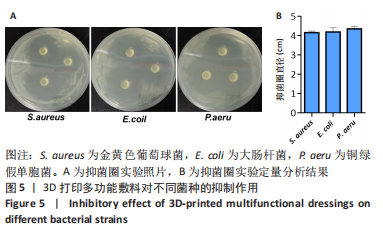
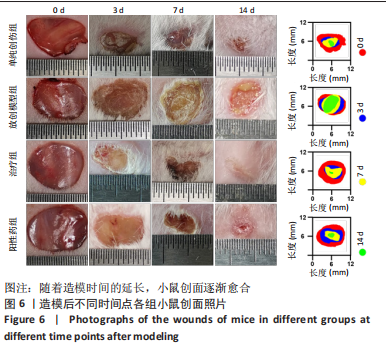
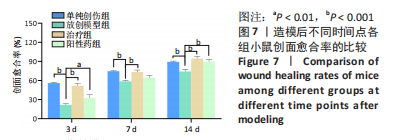
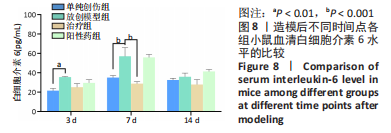
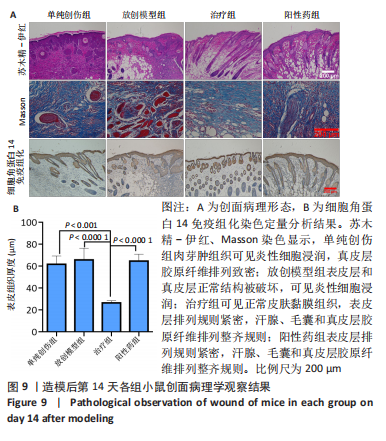
目的:针对放创复合伤的多种临床症状,制备抗菌、加速愈合和局部麻醉的多功能敷料。方法:以左氧氟沙星、丝素蛋白和盐酸利多卡因为原料,应用3D生物打印技术制备多功能创面敷料。①将多功能敷料分别放置于表面涂有金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌与铜绿假单胞菌的固定培养板上,37 ℃孵育过夜,检测抑菌圈直径。②将40只昆明种小鼠随机分单纯创伤组、放创模型组、治疗组、阳性药组,每组10只。放创模型组、治疗组、阳性药组小鼠全身接受60Co γ射线照射,辐射1 h后,在4组小鼠背部各制作1个直径1 cm的全层皮肤缺损创面,单纯创伤组、放创模型组创面涂抹生理盐水,阳性药组创面涂抹三乙醇胺乳膏,治疗组创面覆盖多功能敷料,每隔1 d更换敷料或换药,连续治疗14 d。创面造模后3,7,14 d,检测创面愈合率与血清白细胞介素6水平;创面造模后14 d,获取创面处皮肤组织,进行苏木精-伊红、Masson染色及细胞角蛋白14免疫组化染色。
结果与结论:①3D打印多功能创面敷料具有良好的抗菌活性,对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌与铜绿假单胞菌的抑菌圈直径分别为(4.15±0.09),(4.18±0.23),(4.35±0.13) cm。②随着造模时间的延长,小鼠创面逐渐愈合,治疗组、阳性药组造模后3,7,14 d的创面愈合率均高于放创模型组(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),并且治疗组创面愈合率高于阳性药组。随着造模时间的延长,小鼠血清白细胞介素水平呈先升高后降低的趋势,治疗组造模后3,7,14 d的血清白细胞介素水平均低于放创模型组。苏木精-伊红、Masson染色显示,单纯创伤组肉芽肿组织可见炎性细胞浸润,真皮层胶原纤维排列致密;放创模型组表皮层和真皮层正常结构被破坏,可见炎性细胞浸润;治疗组可见正常皮肤黏膜组织,表皮层排列规则紧密,汗腺、毛囊和真皮层胶原纤维排列整齐规则;阳性药组表皮层排列规则紧密,汗腺、毛囊和真皮层胶原纤维排列整齐规则。细胞角蛋白14免疫组化染色显示,治疗组表皮组织厚度低于其他3组(P < 0.01,P < 0.001)。③结果表明,3D打印多功能敷料具有局部麻醉、抗感染、促愈合多重功能。
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-9507-8360(焦文成)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: