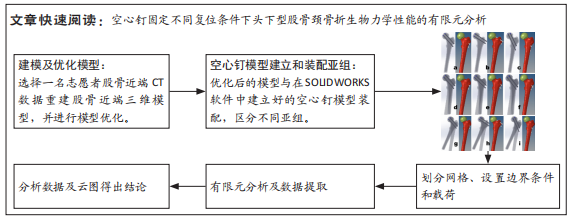
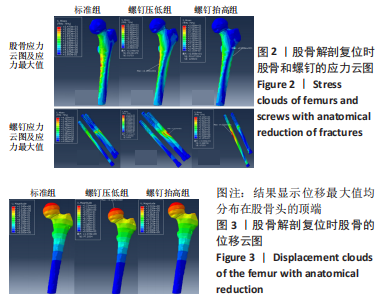
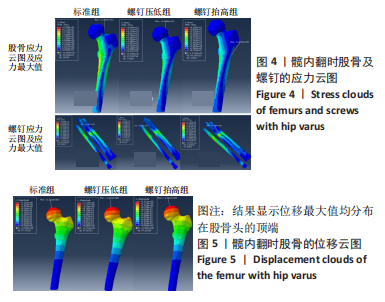
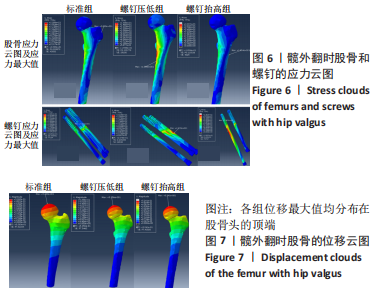
[1] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence, mortality and disability associated with hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(11):897-902.
[2] ABRAHAMSEN B, VAN STAA T, ARIELY R, et al. Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(10):1633-1650.
[3] 张长青, 黄轶刚. 股骨颈骨折的治疗理念与新技术[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016,18(8):645-646.
[4] XU JL, LIANG ZR, XIONG BL, et al. Risk factors associated with osteonecrosis of femoral head after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture:a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):632.
[5] HAUBRUCK P, HELLER RA, TANNER MC. Femoral neck fractures: Current evidence, controversies and arising challenges. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(4): 597-600.
[6] STOEN RO, NORDSLETTEN L, MEYER HE, et al. Hip fracture incidence is decreasing in the high incidence area of Oslo, Norway. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(10):2527-2534.
[7] THORNGREN KG, HOMMEL A, NORRMAN PO, et al. Epidemiology of femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2002;33 (Suppl 3):C1-C7.
[8] CHEN Y, ZHANG X, GUO H, et al. Poor outcomes of children and adolescents with femoral neck fractures: a Meta-analysis based on clinical studies. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):639-644.
[9] VAN AUDEKERCKE RV, MARTENS M, MULIER JC, et al. Experimental study on internal fixation of femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;(141):203.
[10] Wang XD, Lan H, Li KN. Treatment of femoral neck fractures with cannulated screw invasive internal fixation assisted by orthopaedic surgery robot positioning system. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):864-872.
[11] 孙勇, 龚春柱, 王常德, 等. 改良空心钉内固定方式治疗青中年股骨颈骨折的近期疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(6):588-590.
[12] 徐刚. 不同角度螺钉固定内收型股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):173-176.
[13] 任文军. 三种不同内固定方式固定PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2020.
[14] 胥少汀, 葛宝丰, 卢世璧. 实用骨科学[M].4版修订本. 郑州:河南科学技术出版社,2019:932.
[15] 王颖, 刘志朋, 殷涛,等. 利用有限元探究内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2019,25(1):56-61.
[16] SHARMA A, SHANTHAPPA AH, AGARAWAL S. Is emergency surgery an indicator of good functional outcomes in neck of femur fractures among adults: a prospective clinical study. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e23074.
[17] 陈新疆. 不同时机切开复位内固定术对股骨颈骨折患者的影响[J]. 中外医学研究,2022,20(33):110-114.
[18] ZHOU L, LIN J, HUANG A, et al. Modified cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;74:103-110.
[19] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimum Configuration of Cannulated Compression Screws for the Fixation of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures: Finite Element Analysis Evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:1271762.
[20] TIANYE L, PENG Y, JINGLI X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[21] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Finite element analysis of different screw constructs in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2020;51(4):995-1003.
[22] 王照东, 官建中, 吴敏,等. 两种空心螺钉构型治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3):318-322.
[23] DUFFIN M, PILSON HT. Technologies for Young Femoral Neck Fracture Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33:S20-S26.
[24] SHU DP, XIAO YP, BEI MJ, et al. Dynamic compression locking system versus multiple cannulated compression screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures: a comparative study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):230.
[25] JU FX, HOU RX, XIONG J, et al. Outcomes of femoral neck fractures treated with cannulated internal fixation in elderly patients: a long-term follow-up study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):809-818.
[26] FILIPOV O. Biplane double-supported screw fixation (F-technique): a method of screw fixation at osteoporotic fractures of the femoral neck. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2011;21(7):539-543.
[27] 陈方,刘修其,邓钰泓,等. 空心拉力螺钉”F”形固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(10):954-957.
[28] LIN TY, YANG P, XU JL, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[29] SU Z, LIANG L, HAO Y. Medial femoral plate with cannulated screw for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: A meta-analysis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(2):169-177.
[30] HUANG ZY, SU YH, HUANG ZP, et al. Medial buttress plate and allograft bone-assisted cannulated screw fixation for unstable femoral neck fracture with posteromedial comminution: a retrospective controlled study. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(5):911-918.
[31] 范智荣,苏海涛,周霖,等.新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2321-2328.
[32] 梁浩然,周新,杨彦飞,等.青壮年股骨颈骨折内固定后股骨头坏死的发病机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):456-460.
[33] Panteli M, Rodham P, Giannoudis PV. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the non-elderly. Injury. 2015;46(3):445-452.
|