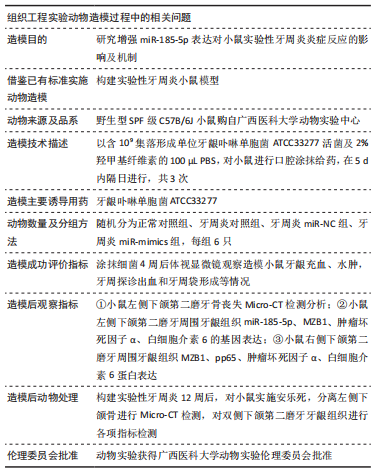
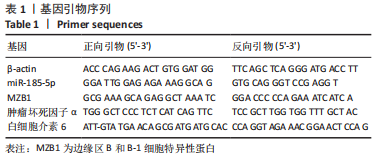
[1] ZHANG Q, LI Z, WANG C, et al. Prevalence and predictors for periodontitis among adults in China, 2010. Glob Health Action. 2014;7:24503.
[2] WESSELING H, XU B, WANT EJ, et al. System-based proteomic and metabonomic analysis of the Df(16)A+/− mouse identifies potential miR-185 targets and molecular pathway alterations. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):384-395.
[3] HUANG A, JI L, HUANG Y, et al. miR-185-5p alleviates CCI-induced neuropathic pain by repressing NLRP3 inflammasome through dual targeting MyD88 and CXCR4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;104:108508.
[4] MA X, LIU H, ZHU J, et al. miR-185-5p Regulates Inflammation and Phagocytosis through CDC42/JNK Pathway in Macrophages. Genes. 2022;13(3):468.
[5] PERRI R, NARES S, ZHANG S, et al. MicroRNA modulation in obesity and periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2012;91(1):33-38.
[6] ZHANG C, XUE P, KE J, et al. Development of Ferroptosis-Associated ceRNA Network in Periodontitis. Int Dent J. 2022:S0020-6539(22)00106-X.
[7] VAN ANKEN E, PENA F, HAFKEMEIJER N, et al. Efficient IgM assembly and secretion require the plasma cell induced endoplasmic reticulum protein pERp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S. 2009;106(40):17019-17024.
[8] SOWA ST, MOILANEN A, BITEROVA E, et al. High-resolution Crystal Structure of Human pERp1, A Saposin-like Protein Involved in IgA, IgM and Integrin Maturation in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J Mol Biol. 2021;433(5):166826.
[9] SCHILDKNEGT D, LODDER N, PANDEY A, et al. Characterization of CNPY5 and its family members. Protein Sci. 2019;28(7):1276-1289.
[10] GUZELDEMIR-AKCAKANAT E, SUNNETCI-AKKOYUNLU D, ORUCGUNEY B, et al. Gene-Expression Profiles in Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: A Gene Network-Based Microarray Analysis. J Periodontol. 2016;87(1):58-65.
[11] GUZELDEMIR-AKCAKANAT E, ALKAN B, SUNNETCI-AKKOYUNLU D, et al. Molecular signatures of chronic periodontitis in gingiva: A genomic and proteomic analysis. J Periodontol. 2019;90(6):663-673.
[12] KEBSCHULL M, GUARNIERI P, DEMMER RT, et al. Molecular differences between chronic and aggressive periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2013;92(12):1081-1088.
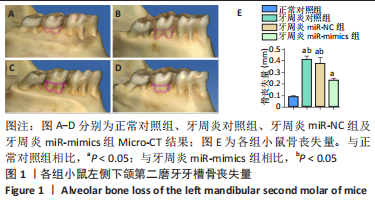
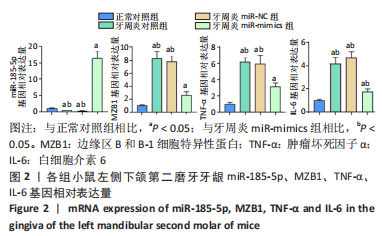
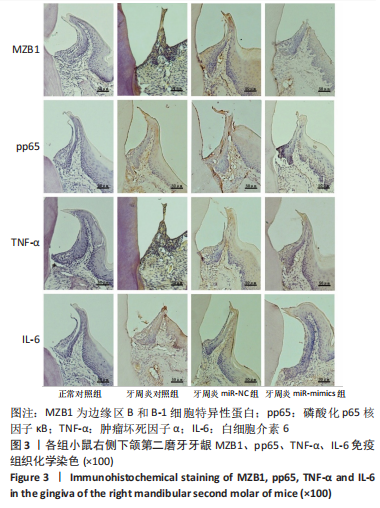
[13] LI D, ZHU Y, ZHANG L, et al. MZB1 targeted by miR-185-5p inhibits the migration of human periodontal ligament cells through NF-κB signaling and promotes alveolar bone loss. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(4):811-823.
[14] BELKAYA S, MURRAY SE, EITSON JL, et al. Transgenic Expression of MicroRNA-185 Causes a Developmental Arrest of T Cells by Targeting Multiple Genes Including Mzb1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(42):30752-30762.
[15] 李丁一. MZB1在牙周炎进程中的作用及机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2022.
[16] FRANCIS M, GOPINATHAN G, SALAPATAS A, et al. SETD1 and NF-κB Regulate Periodontal Inflammation through H3K4 Trimethylation. J Dent Res. 2020;99(13): 1486-1493.
[17] KINANE DF, STATHOPOULOU PG, PAPAPANOU PN. Periodontal diseases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3(1):17038.
[18] LUAN X, ZHOU X, NAQVI A, et al. MicroRNAs and immunity in periodontal health and disease. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(3):24.
[19] WANG W, QIAO SC, WU XB, et al. Circ_0008542 in osteoblast exosomes promotes osteoclast-induced bone resorption through m6A methylation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(7):628.
[20] WANG J, XUE Y, ZHOU L. Comparison of immune cells and diagnostic markers between spondyloarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatics analysis. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):196.
[21] WILDSCHÜTZ L, ACKERMANN D, WITTEN A, et al. Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of iris tissue and aqueous humor in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis. J Autoimmun. 2019;100:75-83.
[22] HASLBAUER JD, MATTER MS, STALDER AK, et al. Histomorphological patterns of regional lymph nodes in COVID-19 lungs. Pathologe. 2021;42(Suppl 1):89-97.
[23] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. NF-κB in immunobiology. Cell Res. 2011;21(2):223-244.
[24] 王晓晨, 吉爱国. NF-κB信号通路与炎症反应[J]. 生理科学进展,2014,45(1): 68-71.
[25] KESAVALU L, CHANDRASEKAR B, EBERSOLE JL. In vivo induction of proinflammatory cytokines in mouse tissue by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002;17(3):177-180.
[26] HONG Q, LING L, HUANG W, et al. LncRNA RNCR3 promotes endothelial cell proliferation and inflammatory cytokine secretion via regulating miR-185-5p/cyclin D2 axis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021;28(21):27025-27032.
|