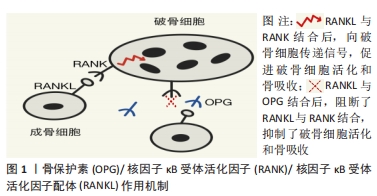
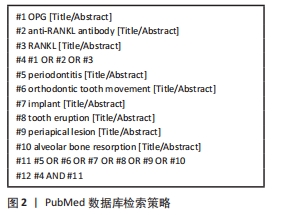
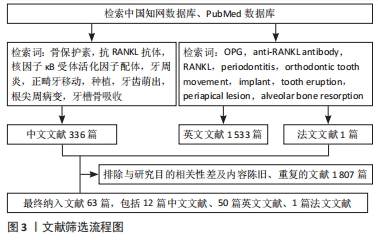
[1] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371.
[2] TAKEGAHARA N, KIM H, CHOI Y. RANKL biology. Bone. 2022;159:116353.
[3] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26.
[4] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):2-11.
[5] KAPASA ER, GIANNOUDIS PV, JIA X, et al. The Effect of RANKL/OPG Balance on Reducing Implant Complications. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(4):42.
[6] YASUDA H. OPG, anti-rANKL antibody. Nihon Rinsho. 2005;63(9):1647-1653.
[7] TEODORESCU AC, MARTU I, TESLARU S, et al. Assessment of Salivary Levels of RANKL and OPG in Aggressive versus Chronic Periodontitis. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:6195258.
[8] BELIBASAKIS GN, BOSTANCI N. The RANKL-OPG system in clinical periodontology. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(3):239-248.
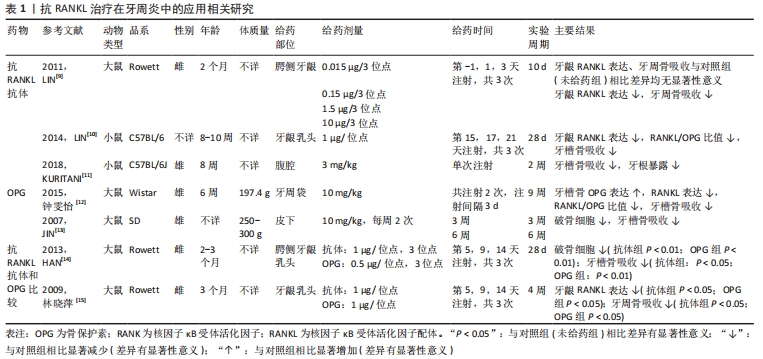
[9] LIN X, HAN X, KAWAI T, et al. Antibody to receptor activator of NF-κB ligand ameliorates T cell-mediated periodontal bone resorption. Infect Immun. 2011;79(2):911-917.
[10] LIN J, BI L, YU X, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbates ligature-induced, RANKL-dependent alveolar bone resorption via differential regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4. Infect Immun. 2014;82(10):4127-4134.
[11] KURITANI M, SAKAI N, KARAKAWA A, et al. Anti-mouse RANKL Antibodies Inhibit Alveolar Bone Destruction in Periodontitis Model Mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(4):637-643.
[12] 钟雯怡,武岐山,高丽,等.重组人骨保护素对牙周炎大鼠牙槽骨RANKL、OPG蛋白表达的影响[J].重庆医学,2015,44(14):1879-1881.
[13] JIN Q, CIRELLI JA, PARK CH, et al. RANKL inhibition through osteoprotegerin blocks bone loss in experimental periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2007;78(7):1300-1308.
[14] HAN X, LIN X, YU X, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection-associated periodontal bone resorption is dependent on receptor activator of NF-κB ligand. Infect Immun. 2013;81(5):1502-1509.
[15] 林晓萍,韩晓哲,魏巍,等.抗RANKL多克隆抗体对P.gingivalis感染的大鼠牙周骨吸收的抑制作用[J].解剖科学进展,2009,15(3):269-272.
[16] SYDORAK I, DANG M, BAXTER SJ, et al. Microsphere controlled drug delivery for local control of tooth movement. Eur J Orthod. 2019;41(1):1-8.
[17] YOSHIMATSU M, KITAURA H, MORITA Y, et al. Effects of anti-mouse RANKL antibody on orthodontic tooth movement in mice. J Dent Sci. 2022;17(3):1087-1095.
[18] KELES A, GRUNES B, DIFURIA C, et al. Inhibition of tooth movement by osteoprotegerin vs. pamidronate under conditions of constant orthodontic force. Eur J Oral Sci. 2007; 115(2):131-136.
[19] 娄颖,马欣.骨保护素对大鼠正畸牙齿移动过程中破骨细胞分化和p38-MAPK信号通路的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,46(6):1221-1226,1350.
[20] FERNÁNDEZ-GONZÁLEZ FJ, CAÑIGRAL A, LÓPEZ-CABALLO JL, et al. Recombinant osteoprotegerin effects during orthodontic movement in a rat model. Eur J Orthod. 2016;38(4):379-385.
[21] 周建萍,陈雁南,任嫒姝,等.局部应用骨保护素对鼠正畸牙移动影响的实验研究[J].重庆医学,2009,38(15):1915-1917,1920.
[22] 陈雁南,裴帆,李晓智,等.局部注射骨保护素与二磷酸盐对大鼠正畸牙移动的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(11):1200-1202,1206.
[23] 陈雁南,裴帆,李晓智,等.局部注射不同浓度骨保护素对大鼠正畸牙移动影响的研究[J].激光杂志,2011,32(5):89-90,92.
[24] 陈雁南. OPG对实验大鼠正畸牙移动的影响[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2012.
[25] DUNN MD, PARK CH, KOSTENUIK PJ, et al. Local delivery of osteoprotegerin inhibits mechanically mediated bone modeling in orthodontic tooth movement. Bone. 2007; 41(3):446-455.
[26] HUDSON JB, HATCH N, HAYAMI T, et al. Local delivery of recombinant osteoprotegerin enhances postorthodontic tooth stability. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(4):330-342.
[27] SCHNEIDER DA, SMITH SM, CAMPBELL C, et al. Locally limited inhibition of bone resorption and orthodontic relapse by recombinant osteoprotegerin protein. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2015;18 Suppl 1:187-195.
[28] 李静,陈争晖,凯迪丽娅·亚力坤,等.微渠多孔羟基磷灰石支架修复犬下颌骨大面积缺损后与种植体的骨结合[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(12):1920-1926.
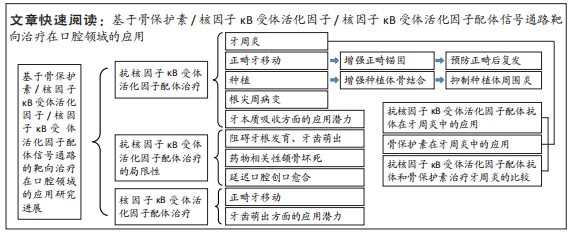
[29] 高鑫,曾融生.骨保护素在口腔领域的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2019,46(3): 316-319.
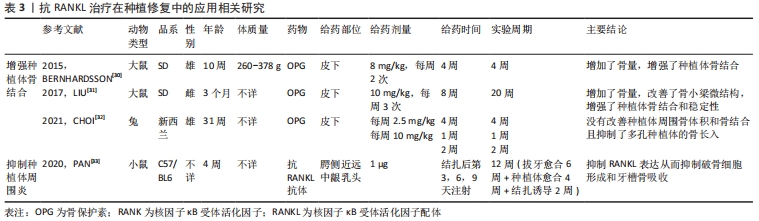
[30] BERNHARDSSON M, SANDBERG O, ASPENBERG P. Anti-RANKL treatment improves screw fixation in cancellous bone in rats. Injury. 2015;46(6):990-995.
[31] LIU Y, HU J, LIU B, et al. The effect of osteoprotegerin on implant osseointegration in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Sci. 2017;13(2):489-495.
[32] CHOI JH, WANG Z, ROSS FP, et al. Systemic osteoprotegerin does not improve peri-implant bone volume or osseointegration in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(8):1611-1621.
[33] PAN K, HU Y, WANG Y, et al. RANKL blockade alleviates peri-implant bone loss and is enhanced by anti-inflammatory microRNA-146a through TLR2/4 signaling. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):15.
[34] LIU L, ZHANG C, HU Y, et al. Protective effect of metformin on periapical lesions in rats by decreasing the ratio of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin. J Endod. 2012;38(7):943-947.
[35] IKEDA M, KARAKAWA A, TAKIZAWA H, et al. Effects of Anti-Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand Antibody and Zoledronic Acid on Periapical Lesion Development in Mice. J Endod. 2022;48(5):632-640.
[36] FUKUSHIMA H, KAJIYA H, TAKADA K, et al. Expression and role of RANKL in periodontal ligament cells during physiological root-resorption in human deciduous teeth. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111(4):346-352.
[37] ZHENG Y, CHEN M, HE L, et al. Mesenchymal dental pulp cells attenuate dentin resorption in homeostasis. J Dent Res. 2015;94(6):821-827.
[38] CHEN MY, CHEN KL, CHEN CA, et al. Responses of immature permanent teeth with infected necrotic pulp tissue and apical periodontitis/abscess to revascularization procedures. Int Endod J. 2012;45(3):294-305.
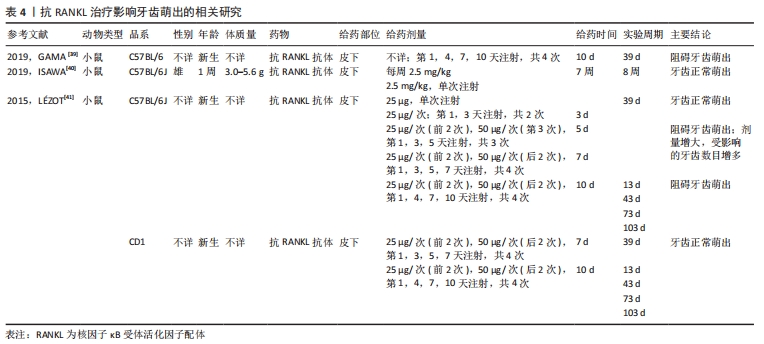
[39] GAMA A, PEREA L, YEPES C, et al. Effects of post-natal inhibition of RANKL on molar eruption and root formation in C57BL/6 mice. Orthod Fr. 2019;90(1):55-63.
[40] ISAWA M, KARAKAWA A, SAKAI N, et al. Biological Effects of Anti-RANKL Antibody and Zoledronic Acid on Growth and Tooth Eruption in Growing Mice. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1): 19895.
[41] LÉZOT F, CHESNEAU J, NAVET B, et al. Skeletal consequences of RANKL-blocking antibody (IK22-5) injections during growth: mouse strain disparities and synergic effect with zoledronic acid. Bone. 2015;73:51-59.
[42] 冯志强,安金刚,张益等.晚期药物相关性颌骨坏死的手术治疗[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2023,41(1):43-51.
[43] 戢晓,朱桂全.维生素D与药物相关性颌骨坏死关系的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(4):441-447.
[44] BETH-TASDOGAN NH, MAYER B, HUSSEIN H, et al. Interventions for managing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;7(7): CD012432.
[45] SOUNDIA A, HADAYA D, ESFANDI N, et al. Osteonecrosis of the jaws (ONJ) in mice after extraction of teeth with periradicular disease. Bone. 2016;90:133-141.
[46] DE MOLON RS, SHIMAMOTO H, BEZOUGLAIA O, et al. OPG-Fc but Not Zoledronic Acid Discontinuation Reverses Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (ONJ) in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(9):1627-1640.
[47] AGHALOO TL, CHEONG S, BEZOUGLAIA O, et al. RANKL inhibitors induce osteonecrosis of the jaw in mice with periapical disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(4):843-854.
[48] WILLIAMS DW, LEE C, KIM T, et al. Impaired bone resorption and woven bone formation are associated with development of osteonecrosis of the jaw-like lesions by bisphosphonate and anti-receptor activator of NF-κB ligand antibody in mice. Am J Pathol. 2014;184(11):3084-3093.
[49] 潘剑,刘济远.药物相关性颌骨坏死的发病机制及其防治[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2021,39(3):245-254.
[50] ALROWIS R, ALDAWOOD A, ALOTAIBI M, et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): A Review of Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, Preventive Measures and Treatment Strategies. Saudi Dent J. 2022;34(3):202-210.
[51] KAWAHARA M, KUROSHIMA S, SAWASE T. Clinical considerations for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a comprehensive literature review. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):47.
[52] KUROSHIMA S, AL-SALIHI Z, YAMASHITA J. Mouse anti-RANKL antibody delays oral wound healing and increases TRAP-positive mononuclear cells in bone marrow. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(4):727-736.
[53] TSICHLAKI A, CHIN SY, PANDIS N, et al. How long does treatment with fixed orthodontic appliances last? A systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016;149(3): 308-318.
[54] KHLEF HN, HAJEER MY, AJAJ MA, et al. The effectiveness of traditional corticotomy vs flapless corticotomy in miniscrew-supported en-masse retraction of maxillary anterior teeth in patients with Class II Division 1 malocclusion: A single-centered, randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;158(6):e111-e120.
[55] SIRRI MR, BURHAN AS, HAJEER MY, et al. Evaluation of Perceived Pain, Discomfort, Functional Impairments, and Satisfaction When Relieving Crowded Lower Anterior Teeth in Young Adult Patients Using Corticision-Assisted Fixed Orthodontic Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e26489.
[56] AL-IBRAHIM HM, HAJEER MY, BURHAN AS, et al. Evaluation of Patient-Centered Outcomes Associated With the Acceleration of Upper Incisor Decrowding Using Self-Ligating Brackets With or Without Piezocision in Comparison With Traditional Brackets: A Three-Arm Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus. 2022;14(6):e26467.
[57] ALFAILANY DT, HAJEER MY, ALJABBAN O, et al. The Effectiveness of Repetition or Multiplicity of Different Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures Compared to a Single Procedure Application in Accelerating Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e23105.
[58] CHANG JH, CHEN PJ, ARUL MR, et al. Injectable RANKL sustained release formulations to accelerate orthodontic tooth movement. Eur J Orthod. 2020;42(3):317-325.
[59] KANZAKI H, CHIBA M, ARAI K, et al. Local RANKL gene transfer to the periodontal tissue accelerates orthodontic tooth movement. Gene Ther. 2006;13(8):678-685.
[60] IGLESIAS-LINARES A, MORENO-FERNANDEZ AM, YAÑEZ-VICO R, et al. The use of gene therapy vs. corticotomy surgery in accelerating orthodontic tooth movement. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2011;14(3):138-148.
[61] GAMA A, VARGAS-FRANCO JW, SÁNCHEZ MESA DC, et al. Origins of Alterations to Rankl Null Mutant Mouse Dental Root Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2201.
[62] HUANG H, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Bone resorption deficiency affects tooth root development in RANKL mutant mice due to attenuated IGF-1 signaling in radicular odontoblasts. Bone. 2018;114:161-171.
[63] VARGAS-FRANCO JW, CASTANEDA B, GAMA A, et al. Genetically-achieved disturbances to the expression levels of TNFSF11 receptors modulate the effects of zoledronic acid on growing mouse skeletons. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;168:133-148. |