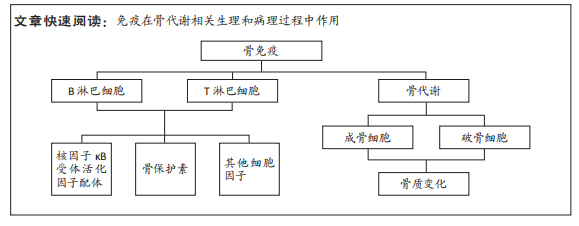
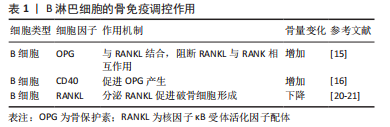
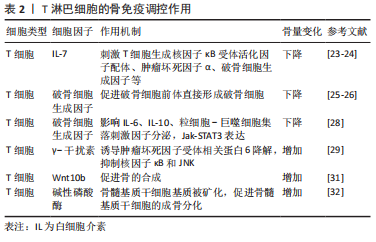
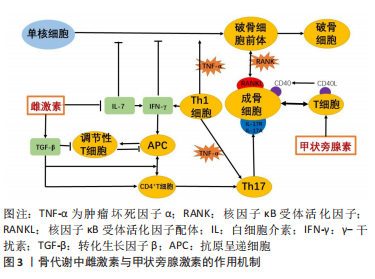
[1] WEITZMANN MN. Bone and the Immune System. Toxicol Pathol. 2017; 45(7):911-924.
[2] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812): 535-536.
[3] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019; 19(10):626-642.
[4] ZHANG W, DANG K, HUAI Y, et al. Osteoimmunology: The Regulatory Roles of T Lymphocytes in Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:465.
[5] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):2-11.
[6] WANG YN, LIU S, JIA T, et al. T Cell Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase in Osteoimmunology. Front Immunol. 2021;12:620333.
[7] 钱治, 仲泽远, 崔元斌, 等. T细胞与骨代谢[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2021, 37(11):1404-1410.
[8] VILACA T, EASTELL R, SCHINI M. Osteoporosis in men. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(4):273-283.
[9] TITANJI K, OFOTOKUN I, WEITZMANN MN. Immature/transitional B-cell expansion is associated with bone loss in HIV-infected individuals with severe CD4+ T-cell lymphopenia. Aids. 2020;34(10):1475-1483.
[10] 谭敏, 杨颜瑜, 熊琴, 等. OPG/RANKLlRANK信号通路在骨质疏松症患者骨重建中作用机制的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2018,58(43):111-114.
[11] LI Y, TORALDO G, LI A, et al. B cells and T cells are critical for the preservation of bone homeostasis and attainment of peak bone mass in vivo. Blood. 2007;109(9):3839-3848.
[12] WU D, CLINE-SMITH A, SHASHKOVA E, et al. T-Cell Mediated Inflammation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687551.
[13] JIANG TJ, CAO XL, LUAN S, et al. Percentage and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with hyperthyroidism. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17(2):2137-2144.
[14] MALLON PW. Aging with HIV: osteoporosis and fractures. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014;9(4):428-435.
[15] LI S, LIU Q, WU D, et al. PKC-δ deficiency in B cells displays osteopenia accompanied with upregulation of RANKL expression and osteoclast-osteoblast uncoupling. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):762.
[16] OLIVEIRA MC, PIETERS BCH, GUIMARÃES PB, et al. Bovine Milk Extracellular Vesicles Are Osteoprotective by Increasing Osteocyte Numbers and Targeting RANKL/OPG System in Experimental Models of Bone Loss. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:891.
[17] HABIBIE H, ADHYATMIKA A, SCHAAFSMA D, et al. The role of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in fibrosis: its potential as a biomarker and/or biological target for the treatment of fibrotic diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;228:107941.
[18] NAIK S, SAHU S, BANDYOPADHYAY D, et al. Serum levels of osteoprotegerin, RANK-L & vitamin D in different stages of osteoarthritis of the knee. Indian J Med Res. 2021;154(3):491-496.
[19] OTA Y, NIIRO H, OTA S, et al. Generation mechanism of RANKL(+) effector memory B cells: relevance to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:67.
[20] BRUNETTI G, FAIENZA MF, COLAIANNI G, et al. Impairment of Bone Remodeling in LIGHT/TNFSF14-Deficient Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018; 33(4):704-719.
[21] ZENG W, LIU G, LUAN Q, et al. B-Cell Deficiency Exacerbates Inflammation and Bone Loss in Ligature-Induced Experimental Periodontitis in Mice. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:5367-5380.
[22] RANA AK, LI Y, DANG Q, et al. Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:348-359.
[23] KOMATSU N, WIN S, YAN M, et al. Plasma cells promote osteoclastogenesis and periarticular bone loss in autoimmune arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2021; 131(6):e143060.
[24] RAJAKUMAR SA, PAPP E, LEE KK, et al. B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells mediate RANK-RANKL-dependent bone destruction. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(561):eaba5942.
[25] WEITZMANN MN. T-cells and B-cells in osteoporosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014;21(6):461-467.
[26] IHN HJ, KIM YS, LIM S, et al. PF-3845, a Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitor, Directly Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis through ERK and NF-κB Pathways In Vitro and Alveolar Bone Loss In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1915.
[27] ZHANG R, PENG S, ZHU G. The role of secreted osteoclastogenic factor of activated T cells in bone remodeling. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2022;58:227-232.
[28] RIFAS L, WEITZMANN MN. A novel T cell cytokine, secreted osteoclastogenic factor of activated T cells, induces osteoclast formation in a RANKL-independent manner. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(11):3324-3335.
[29] WEITZMANN MN, CENCI S, RIFAS L, et al. T cell activation induces human osteoclast formation via receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(2): 328-337.
[30] NAPIMOGA MH, DEMASI AP, JARRY CR, et al. In vitro evaluation of the biological effect of SOFAT on osteoblasts. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015; 26(2):378-383.
[31] TAKAYANAGI H, OGASAWARA K, HIDA S, et al. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 2000;408(6812):600-605.
[32] TSUMURA M, MIKI M, MIZOGUCHI Y, et al. Enhanced osteoclastogenesis in patients with MSMD due to impaired response to IFN-γ. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(1):252-261.e6.
[33] HSU MN, HUANG KL, YU FJ, et al. Coactivation of Endogenous Wnt10b and Foxc2 by CRISPR Activation Enhances BMSC Osteogenesis and Promotes Calvarial Bone Regeneration. Mol Ther. 2020;28(2):441-451.
[34] CROES M, ÖNER FC, VAN NEERVEN D, et al. Proinflammatory T cells and IL-17 stimulate osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2016;84:262-270.
[35] LEVESCOT A, CHANG MH, SCHNELL J, et al. IL-1β-driven osteoclastogenic Tregs accelerate bone erosion in arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(18): e141008.
[36] TOMINARI T, AKITA M, MATSUMOTO C, et al. Endosomal TLR3 signaling in stromal osteoblasts induces prostaglandin E(2)-mediated inflammatory periodontal bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(3):101603.
[37] JIMI E, NAKAMURA I, DUONG LT, et al. Interleukin 1 induces multinucleation and bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts in the absence of osteoblasts/stromal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1999;247(1):84-93.
[38] CHEN W, TANG P, FAN S, et al. A Novel Inhibitor INF 39 Promotes Osteogenesis via Blocking the NLRP3/IL-1β Axis. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:7250578.
[39] KUROZUMI A, NAKANO K, YAMAGATA K, et al. IL-6 and sIL-6R induces STAT3-dependent differentiation of human VSMCs into osteoblast-like cells through JMJD2B-mediated histone demethylation of RUNX2. Bone. 2019; 124:53-61.
[40] FUKUYO S, YAMAOKA K, SONOMOTO K, et al. IL-6-accelerated calcification by induction of ROR2 in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells is STAT3 dependent. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(7):1282-1290.
[41] LI N, LI X, ZHENG K, et al. Inhibition of Sirtuin 3 prevents titanium particle-induced bone resorption and osteoclastsogenesis via suppressing ERK and JNK signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(5):1382-1394.
[42] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8.
[43] SALVIO G, GIANFELICE C, FIRMANI F, et al. Bone Metabolism in SARS-CoV-2 Disease: Possible Osteoimmunology and Gender Implications. Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2020;18(4):51-57.
[44] MARAHLEH A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. TNF-α Directly Enhances Osteocyte RANKL Expression and Promotes Osteoclast Formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2925.
[45] CONSTANZE B, POPPER B, AGGARWAL BB, et al. Evidence that TNF-β suppresses osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and resveratrol reverses it through modulation of NF-κB, Sirt1 and Runx2. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;381(1):83-98.
[46] CORDEIRO PAS, ASSONE T, PRATES G, et al. The role of IFN-γ production during retroviral infections: an important cytokine involved in chronic inflammation and pathogenesis. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2022;64:e64.
[47] SHASHKOVA EV, TRIVEDI J, CLINE-SMITH AB, et al. Osteoclast-Primed Foxp3+ CD8 T Cells Induce T-bet, Eomesodermin, and IFN-γ To Regulate Bone Resorption. J Immunol. 2016;197(3):726-735.
[48] MARUHASHI T, KAIFU T, YABE R, et al. DCIR maintains bone homeostasis by regulating IFN-γ production in T cells. J Immunol. 2015;194(12):5681-5691.
[49] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):905.
[50] ZERBINI CAF, CLARK P, MENDEZ-SANCHEZ L, et al. Biologic therapies and bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int. 2017; 28(2): 429-446.
[51] WANG X, SUN L, HE N, et al. Increased expression of CXCL2 in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis and its role in osteoclastogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021;203(2):194-208.
[52] STEFFEN U, SCHETT G, BOZEC A. How Autoantibodies Regulate Osteoclast Induced Bone Loss in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1483.
[53] HECHT C, ENGLBRECHT M, RECH J, et al. Additive effect of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and rheumatoid factor on bone erosions in patients with RA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(12):2151-2156.
[54] PETROVSKÁ N, PRAJZLEROVÁ K, VENCOVSKÝ J, et al. The pre-clinical phase of rheumatoid arthritis: From risk factors to prevention of arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(5):102797.
[55] KELLER KK, THOMSEN JS, STENGAARD-PEDERSEN K, et al. Local bone loss in patients with anti-citrullinated peptide antibody and arthralgia, evaluated with high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(2):110-116.
[56] TEN BRINCK RM, TOES REM, Van Der Helm-Van Mil AHM. Inflammation functions as a key mediator in the link between ACPA and erosion development: an association study in Clinically Suspect Arthralgia. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):89.
[57] CECCARELLI F, PERRICONE C, COLASANTI T, et al. Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies as a new biomarker of erosive joint damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):126.
[58] O’NEIL LJ, OLIVEIRA CB, SANDOVAL-HEGLUND D, et al. Anti-Carbamylated LL37 Antibodies Promote Pathogenic Bone Resorption in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:715997.
[59] HAUSER B, HARRE U. The Role of Autoantibodies in Bone Metabolism and Bone Loss. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102(5):522-532.
[60] SRIVASTAVA S, TORALDO G, WEITZMANN MN, et al. Estrogen decreases osteoclast formation by down-regulating receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL)-induced JNK activation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(12): 8836-8840.
[61] UEHARA IA, SOLDI LR, SILVA MJB. Current perspectives of osteoclastogenesis through estrogen modulated immune cell cytokines. Life Sci. 2020;256: 117921.
[62] MANOLAGAS SC, O’BRIEN CA, ALMEIDA M. The role of estrogen and androgen receptors in bone health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013; 9(12):699-712.
[63] DRAKE MT, KHOSLA S. Hormonal and systemic regulation of sclerostin. Bone. 2017;96:8-17.
[64] HUANG T, FU X, WANG N, et al. Andrographolide prevents bone loss via targeting estrogen-related receptor-α-regulated metabolic adaption of osteoclastogenesis. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(21):4352-4367.
[65] TANG J, LIU T, WEN X, et al. Estrogen-related receptors: novel potential regulators of osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):5.
[66] CHENG CH, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. Osteoporosis Due to Hormone Imbalance: An Overview of the Effects of Estrogen Deficiency and Glucocorticoid Overuse on Bone Turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1376.
[67] STEPAN JJ, HRUSKOVA H, KVERKA M. Update on Menopausal Hormone Therapy for Fracture Prevention. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(6):465-473.
[68] 张晓红, 高艳丽, 袁征, 等. 免疫系统在绝经后骨质疏松症中的作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(10):1538-1541.
[69] SCHEFFLER JM, GRAHNEMO L, ENGDAHL C, et al. Interleukin 17A: a Janus-faced regulator of osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):5692.
[70] MOLNÁR I, BOHATY I, SOMOGYINÉ-VÁRI É. IL-17A-mediated sRANK ligand elevation involved in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2014; 25(2):783-786.
[71] EGHBALI-FATOURECHI G, KHOSLA S, SANYAL A, et al. Role of RANK ligand in mediating increased bone resorption in early postmenopausal women. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(8):1221-1230.
[72] DELPINO MV, QUARLERI J. Influence of HIV Infection and Antiretroviral Therapy on Bone Homeostasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:502.
[73] COTTER EJ, CHEW N, POWDERLY WG, et al. HIV type 1 alters mesenchymal stem cell differentiation potential and cell phenotype ex vivo. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2011;27(2):187-199.
[74] BEAUPERE C, GARCIA M, LARGHERO J, et al. The HIV proteins Tat and Nef promote human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell senescence and alter osteoblastic differentiation. Aging Cell. 2015;14(4):534-546.
[75] AGIDIGBI TS, KIM C. Reactive Oxygen Species in Osteoclast Differentiation and Possible Pharmaceutical Targets of ROS-Mediated Osteoclast Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(14):3576.
[76] MCCOMSEY GA, TEBAS P, SHANE E, et al. Bone disease in HIV infection: a practical review and recommendations for HIV care providers. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51(8):937-946.
[77] MATUSZEWSKA A, NOWAK B, NIŻAŃSKI W, et al. Long-Term Administration of Abacavir and Etravirine Impairs Semen Quality and Alters Redox System and Bone Metabolism in Growing Male Wistar Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5596090.
[78] CHISATI EM, CONSTANTINOU D, LAMPIAO F. Reduced bone mineral density among HIV infected patients on anti-retroviral therapy in Blantyre, Malawi: Prevalence and associated factors. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227893.
[79] CORMIER C, KOUMAKIS E. Bone and primary hyperparathyroidism. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(1):105129.
[80] PACIFICI R. Role of T cells in the modulation of PTH action: physiological and clinical significance. Endocrine. 2013;44(3):576-582.
[81] PACIFICI R. Role of Gut Microbiota in the Skeletal Response to PTH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(3):636-645. |