[1] BRANNAN CI, DEES EC, INGRAM RS, et al. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10(1):28-36.
[2] The FANTOM Consortium And The RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group Phase I & II Team*. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 2002;420(6915):563-573.
[3] 黄蕾,王雅洁,陈实.非编码RNA编辑技术研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(7):1036-1045.
[4] 李法君.长链非编码RNA及其生物学功能概述[J].生物学教学,2017,42(2):2-4.
[5] 李朋飞.电离辐射应答长链非编码RNA的研究[D].兰州:中国科学院研究生院(近代物理研究所),2015.
[6] 夏芳芳,胡明智,孙慧莹,等.LncRNA在自身免疫性疾病中的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(15):1907-1912.
[7] SCHAEFER AS, RICHTER GM, GROESSNER-SCHREIBER B, et al. Identification of a shared genetic susceptibility locus for coronary heart disease and periodontitis. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(2):e1000378.
[8] 屈茜,房付春,吴补领.长链非编码RNA在牙周炎和口腔肿瘤疾病中的作用[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(1):62-65.
[9] BOCHENEK G, HÄSLER R, EL MOKHTARI NE, et al. The large non-coding RNA ANRIL, which is associated with atherosclerosis, periodontitis and several forms of cancer, regulates ADIPOR1, VAMP3 and C11ORF10. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(22):4516-4527.
[10] ZOU Y, LI C, SHU F, et al. LncRNA expression signatures in periodontitis revealed by microarray: the potential role of lncRNA in periodontitis pathogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(4):640-647.
[11] 范琳媛,李红凌.长链非编码RNAs调控骨稳态研究进展[J].基础医学与临床,2020,40(1):115-119.
[12] ZHANG X, ZHAO Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Knockdown of DANCR reduces osteoclastogenesis and root resorption induced by compression force via jagged1. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(15):1759-1769.
[13] WANG Z, HUANG Y, TAN L. Downregulation of lncRNA DANCR promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. BMC Dev Biol. 2020;20(1):2.
[14] TANG Z, GONG Z, SUN X. LncRNA DANCR involved osteolysis after total hip arthroplasty by regulating foxo1 expression to inhibit osteoblast differentiation. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):4.
[15] 郭东光,陈明艳,王丰,等.长链非编码RNA对免疫功能的调控作用研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2021,42(7):90-95.
[16] ZHANG X, REN L, YAN X, et al. Identification of immune-related lncRNAs in periodontitis reveals regulation network of gene-lncRNA-pathway-immunocyte. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106600.
[17] WU D, ZHOU P, CAO F, et al. Expression Profiling and Cell Type Classification Analysis in Periodontitis Reveal Dysregulation of Multiple lncRNAs in Plasma Cells. Front. Genet. 2020;11:382.
[18] TANG H, YUAN S, CHEN T, et al. Development of an immune-related lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competing endogenous RNA in periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(11):1470-1479.
[19] YANG X, PAN Y, XU X, et al. Sialidase deficiency in porphyromonas gingivalis increases IL-12 secretion in stimulated macrophages through regulation of CR3, lncRNA GAS5 and miR-21. Front Cell Infect Mi. 2018;8:100.
[20] 胡安妮,苏俭生.LncRNA参与固有免疫及其在牙周炎症反应中的研究进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,31(1):52-55.
[21] LI J, WANG M, SONG L, et al. LncRNA MALAT 1 regulates inflammatory cytokine production in lipopolysaccharide‐stimulated human gingival fibroblasts through sponging miR‐20a and activating TLR 4 pathway. J Periodont Res. 2020;55(2):182-190.
[22] LIU W, ZHENG Y, CHEN B, et al. LncRNA papillary thyroid carcinoma susceptibility candidate 3 (PTCSC3) regulates the proliferation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression to improve periodontitis. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):108.
[23] ZHOU X, WANG Q, NIE L, et al.Metformin ameliorates the NLPP3 inflammasome mediated pyroptosis by inhibiting the expression of NEK7 in diabetic periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;116:104763.
[24] AARABI G, ZELLER T, HEYDECKE G, et al. Roles of the Chr.9p21.3 ANRIL Locus in Regulating Inflammation and Implications for Anti-Inflammatory Drug Target Identification. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:8.
[25] YANG Q, LIU P, HAN Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 alleviates the inflammatory response of human periodontal ligament stem cells by regulating the NF-κB signalling pathway. Eur J Orthodont. 2022;44(6):669-678.
[26] WANG L, WU F, SONG Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA related to periodontitis interacts with miR-182 to upregulate osteogenic differentiation in periodontal mesenchymal stem cells of periodontitis patients. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(8): e2327.
[27] CHEN H, LAN Z, LI Q, et al. Abnormal expression of long noncoding RNA FGD5-AS1 affects the development of periodontitis through regulating miR-142-3p/SOCS6/NF-κB pathway. Artif Cell Nanomed B. 2019;47(1):2098-2106.
[28] LIU N, SHI S, DENG M, et al. High levels of β-catenin signaling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in inflammatory microenvironments through inhibition of the noncanonical Wnt pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(9): 2082-2095.
[29] ZHANG L, LV H, CUI Y, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) in chronic periodontitis progression. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):2336-2345.
[30] LIU Y, ZENG X, MIAO J, et al. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(4):4617-4626.
[31] DONG Y, FENG S, DONG F. Maternally-Expressed Gene 3 (MEG3)/miR-143-3p Regulates Injury to Periodontal Ligament Cells by Mediating the AKT/Inhibitory κB Kinase (IKK) Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e922486.
[32] CHEN P, HUANG Y, WANG Y, et al. MALAT1 overexpression promotes the proliferation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by upregulating fibroblast growth factor 2. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(3):1627-1632.
[33] RUAN D, WU C, ZHANG Y, et al. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 inhibits proliferation of PDLSCs and downregulates IL-1β in periodontitis patients. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(2):324-331.
[34] WANG X, WANG Y. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 inhibits PDLCs’ proliferation in periodontitis and may bind with miR-21 precursor to upregulate PLAP-1. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(2):256-264.
[35] 胡琮佼,孙瑶.长链非编码RNA在干细胞成骨分化中作用机制的研究进展[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(3):205-210.
[36] DENG L, HONG H, ZHANG X, et al. Down-regulated lncRNA MEG3 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental follicle stem cells by epigenetically regulating Wnt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(3):2061-2067.
[37] LI Z, GUO X, WU S. Epigenetic silencing of KLF2 by long non-coding RNA SNHG1 inhibits periodontal ligament stem cell osteogenesis differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):435.
[38] DUAN R, DU W, GUO W. EZH2: a novel target for cancer treatment. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):104.
[39] 冯志国,孙海飚,韩晓强.长链非编码RNA对骨相关细胞增殖、分化、凋亡的调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):112-118.
[40] 李俊辉,蔡明详,孙瑶.长链非编码RNA Nron在牙周炎疾病中骨吸收的作用研究[C]//2019第九次全国口腔生物医学学术年会论文汇编. 中华口腔医学会口腔生物医学专业委员会,2019:24.
[41] 赵祥宇,张桂荣,郭传波,等.在牙周炎样本中长链非编码RNA linc00511表达增高并促进破骨细胞增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33):5360-5365.
[42] ZHANG C, PAN L, ZHANG H, et al.Osteoblasts-Derived Exosomal lncRNA-MALAT1 Promotes Osteoclastogenesis by Targeting the miR-124/NFATc1 Signaling Axis in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:781-795.
[43] GHOLAMI L, GHAFOURI-FARD S, MIRZAJANI S, et al. The lncRNA ANRIL is down-regulated in peripheral blood of patients with periodontitis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020;5(2):60-66.
[44] 赖文.LncRNA-tnfrsf13c对b细胞功能的调节作用和机制初探[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2020.
[45] WANG Y, SUN Y, ZHENG P, et al. Long non-coding RNAs mortal obligate RNA transcript regulates the proliferation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and affects the recurrence of periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;105:1-4.
[46] WANG X, MA F, JIA P. LncRNA AWPPH overexpression predicts the recurrence of periodontitis. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(7):BSR20190636.
[47] JIN SH, ZHOU RH, GUAN XY, et al. Identification of novel key lncRNAs involved in periodontitis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(1):96-106.
[48] ZHOU H, CHEN D, XIE G, et al. LncRNA-mediated ceRNA network was identified as a crucial determinant of differential effects in periodontitis and periimplantitis by high-throughput sequencing. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2020;22(3):424-450.
[49] 李艳平,徐明.NLRP3炎性小体激活机制及小分子抑制剂研究进展[J].广东化工,2020,47(19):83-86.
[50] HAN Y, HUANG Y, YANG Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 mediates periodontal inflammation through the NF-κB signalling pathway. J Clin Periodontol. 2022;49(10):1038-1051.
[51] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. The Lancet. 2004;364(9429):149-155.
[52] LIU Y, ZHENG Y, DING G, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cell-mediated treatment for periodontitis in miniature swine. Stem Cells. 2008;26(4):1065-1073.
[53] XU Y, QIN W, GUO D, et al. LncRNA-TWIST1 promoted osteogenic differentiation both in PPDLSCs and in hPDLSCs by inhibitingTWIST1 expression.Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:8735952.
[54] 贾搏.LncRNA-PCAT1对人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化调控机制的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018.
[55] 付秋月,兰兴明,徐溶蔚,等.不同信号通路对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(24):3910-3919.
[56] TU S, CHEN Y, FENG Y, et al. lncRNA CYTOR Facilitates Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Modulating SOX11 via Sponging miR-6512-3p. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:5671809.
[57] 施翔文,倪昊楠,李明军,等.长链非编码RNA在成骨分化相关信号通路中的调控作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(4):479-486.
[58] JIA Q, JIANG W, NI L.Down-regulated non-coding RNA (lncRNA-ANCR) promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(2):234-241.
[59] 王丽颖.LncRNA对炎症条件下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化调控作用的研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016.
[60] YANG Q, HAN Y, LIU P, et al. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 alleviates the inflammatory response of human periodontal ligament stem cells by regulating the NF-κB signalling pathway. Eur J Orthodont. 2020;11:701.
[61] QU Q, FANG F, WU B, et al. Potential role of long non-coding RNA in osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Periodontol. 2016; 87(7):e127-137.
[62] BIAN M, YU Y, LI Y, et al. Upregulating the Expression of LncRNA ANRIL Promotes Osteogenesis via the miR-7-5p/IGF-1R Axis in the Inflamed Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:604400.
[63] 塔西甫拉提迪丽达尔,牛雅琪,阿布都克依木热依沙,等.长链非编码RNA AWPPH通过调控notch信号通路对人牙周膜细胞增殖和成骨向分化的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2023,32(1):23-27.
[64] ZHAO Y, LI J, GUO W, et al. Periodontitis-level butyrate-induced ferroptosis in periodontal ligament fibroblasts by activation of ferritinophagy. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6(1):119.
[65] MAO H, ZHAO Y, LI H, et al. Ferroptosis as an emerging target in inflammatory diseases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020;155:20-28
[66] WANG H, QIAO X, ZHANG C, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00616 promotes ferroptosis of periodontal ligament stem cells via the microRNA-370 / transferrin receptor axis.Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13070-13081.
[67] ZHANG C, XUE P, KE J, et al. Development of Ferroptosis-Associated ceRNA Network in Periodontitis. Int Dent J. 2023;73(2):186-194.
[68] GUO R, HUANG Y, LIU H, et al.Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Participates in Periodontal Inflammation via Activation of Autophagy. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13: 635-646.
[69] Li X, Tian BM, Deng DK, et al.LncRNA GACAT2 binds with protein PKM1/2 to regulate cell mitochondrial function and cementogenesis in an inflammatory environment. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):29.
[70] Huang Y, Zhang Y, Li X, et al. The long non-coding RNA landscape of periodontal ligament stem cells subjected to compressive force. Eur J Orthod. 2019;41(4): 333-342.
[71] Huang Y, Liu H, Guo R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA FER1L4 Mediates the Autophagy of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Under Orthodontic Compressive Force via AKT/FOXO3 Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:631181.
[72] Qin Q, Yang H, Zhang C, et al.lncRNA HHIP-AS1 Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation Potential and Inhibits the Migration Ability of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:5595580.
[73] Zhang Z, He Q, Yang S, et al. Mechanical force-sensitive lncRNA SNHG8 inhibits osteogenic differentiation by regulating EZH2 in hPDLSCs. Cell Signal. 2022;93: 110285.
[74] 刘佳.静态牵张力作用下健康和牙周病微环境来源PDLSCs生物学功能及LncRNA表达谱的研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016.
[75] 孙唯夫,刘传宏,张校晨,等.静态牵张力通过下调linc01135/miR-106a-5p抑制PPDLSCs 成骨分化[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(4):195-199.
[76] 邹宛桦,秦文,徐悦蓉,等.长链非编码RNA linc-01135对静态牵张力作用下人炎症牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2018,34(2): 193-197.
[77] 秦文.长链非编码RNA linc00638在牵张力作用下影响炎症来源牙周膜干细胞成骨分化作用的研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2019.
[78] 邹宛桦,秦文,徐悦蓉,等.LncRNA nr_034015对静态牵张力作用下人炎症牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响[G]//2017年国际正畸大会暨第十六次全国口腔正畸学术会议论文汇编.中华口腔医学会口腔正畸专业委员会、中国国际科技交流中心,2017: 351-352.
[79] LIU J, ZHAO Y, NIU Q, et al. Long Noncoding RNA Expression Profiles of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells from the Periodontitis Microenvironment in Response to Static Mechanical Strain.Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6655526.
[80] 温静瑜,和红兵,任晓斌,等.抗氧化剂在牙周炎治疗中的应用研究[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(1):97-99.
[81] CHEN D, WU L, LIU L, et al. Comparison of HIF1A‑AS1 and HIF1A‑AS2 in regulating HIF‑1α and the osteogenic differentiation of PDLCs under hypoxia. Int J Mol Med,. 2017;40(5):1529-1536.
[82] ZHOU M, HU H, HAN Y, et al. Long non‐coding RNA 01126 promotes periodontitis pathogenesis of human periodontal ligament cells via miR‐518a‐5p/HIF‐1α/MAPK pathway. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1):e12957.
[83] WANG C, YANG Q, HAN Y, et al. A reduced level of the long non-coding RNA SNHG8 activates the NF-kappaB pathway by releasing functional HIF-1alpha in a hypoxic inflammatory microenvironment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):229.
[84] SHI B, SHAO B, YANG C, et al. Upregulation of JHDM1D-AS1 protects PDLSCs from H2O2-induced apoptosis by decreasing DNAJC10 via phosphorylation of eIF2α. Biochimie. 2019;165:48-56.
[85] CHENG L, FAN Y, CHENG J, et al. Long non-coding RNA ZFY-AS1 represses periodontitis tissue inflammation and oxidative damage via modulating microRNA-129-5p/DEAD-Box helicase 3 X-linked axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5): 12691-12705.
[86] SAYAD A, GHAFOURI-FARD S, SHAMS B, et al. Sex-specific up-regulation of p50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) lncRNA in periodontitis.Heliyon. 2020; 6(5):e03897.
[87] LIU X, ZHOU Y. Downregulation of lncRNA ANRIL Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Cells via Sponging miR-7 through NF-κB Pathway. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021;2021:7890674. |
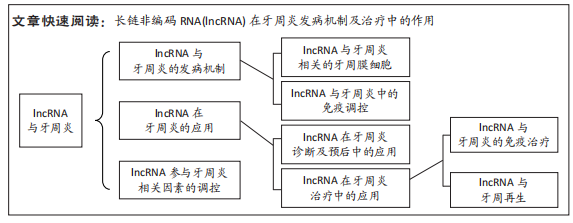

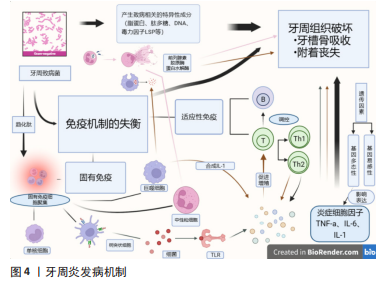
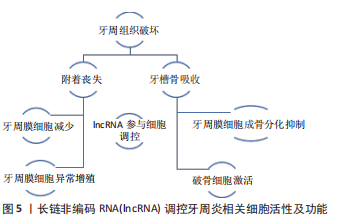
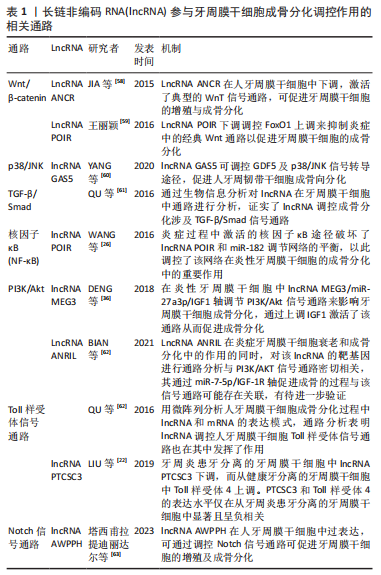


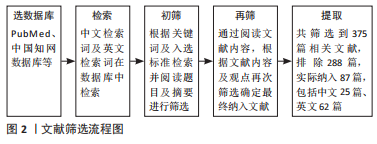
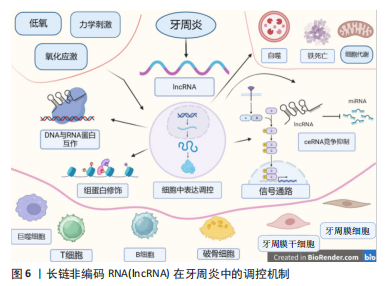 单纯是在诊断与预测上来看,lncRNA实现临床作用还需进一步探究。lncRNA在慢性牙周炎及侵袭性牙周炎B细胞中表达量不同[44],在牙周炎患者血液水平中不同性别的表达量不同[86],据此lncRNA在血液中表达水平的不同是否有望能辅助诊断不同类型的牙周疾病,对于lncRNA评估牙周疾病的危险因素是否有一定临床意义有待商榷。目前的研究主要在集中于慢性牙周炎及侵袭性牙周炎上,对lncRNA在不同牙周疾病中与已有研究机制对比是否起着同样调控作用有待进一步验证。
单纯是在诊断与预测上来看,lncRNA实现临床作用还需进一步探究。lncRNA在慢性牙周炎及侵袭性牙周炎B细胞中表达量不同[44],在牙周炎患者血液水平中不同性别的表达量不同[86],据此lncRNA在血液中表达水平的不同是否有望能辅助诊断不同类型的牙周疾病,对于lncRNA评估牙周疾病的危险因素是否有一定临床意义有待商榷。目前的研究主要在集中于慢性牙周炎及侵袭性牙周炎上,对lncRNA在不同牙周疾病中与已有研究机制对比是否起着同样调控作用有待进一步验证。