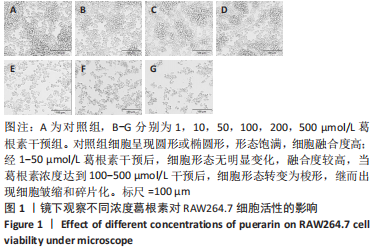
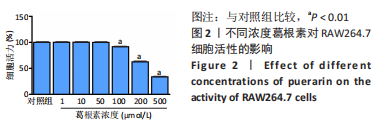
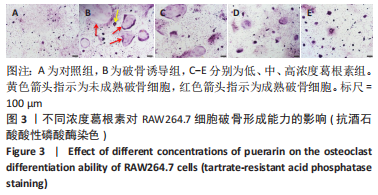
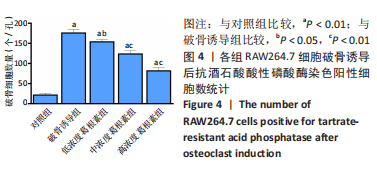
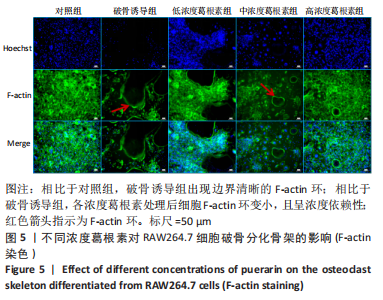
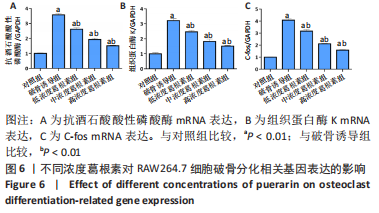
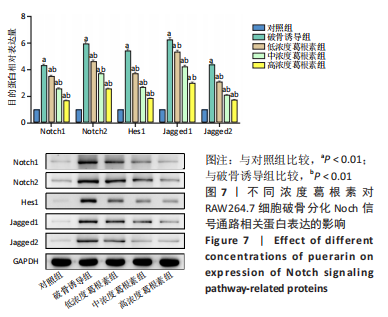
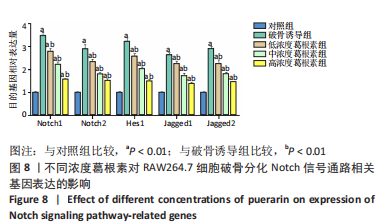
[1] NAKASHIMA T, HAYASHI M, TAKAYANAGI H. New insights into osteoclastogenic signaling mechanisms. Trends Endocrin Met. 2012;23(11):582-590.
[2] KIM H, LEE K, KIM JM, et al. Selenoprotein W ensures physiological bone remodeling by preventing hyperactivity of osteoclasts. Nat Commun. 2021;12:2258.
[3] 任明诗,丁羽,李子涵,等.成骨细胞与破骨细胞相互调节作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):822-827
[4] DA W, TAO L, ZHU Y. The Role of Osteoclast Energy Metabolism in the Occurrence and Development of Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol. 2021; 12:675385.
[5] LEWIECKI, MICHAEL E. New targets for intervention in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(11):631-638.
[6] KAZUHIRO Y, KOJIRO S, TAKASHI M, et al. Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(7):1145-1154.
[7] CHEN X, WANG ZQ, DUAN NA, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[8] RACZ GZ, KADAR K, FOLDES A, et al. Immunomodulatory and potential therapeutic role of mesenchymal stem cells in periodontitis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;65(3):327-339.
[9] SIEBEL C, LENDAHL U. Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol. 2017;97(4):1235-1294.
[10] RAPHAEL K, MA XL. The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Unfolding the Activation Mechanism. Cell. 2009;137:216-233.
[11] YU J, CANALIS E. Notch and the Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation and Function. Bone. 2020;138:115474.
[12] ZHAO B, GRIMES SN, LI S, et al. TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone resorption are inhibited by transcription factor RBP-J. J Exp Med. 2012;209(2):319-34.
[13] FUJIWARA T, ZHOU J, YE S, et al. RNA-binding protein Musashi2 induced by RANKL is critical for osteoclast surviva. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2300.
[14] 张峻玮,李琰,薛海鹏,等.骨碎补经骨髓间充质干细胞调节OPG/RANKL/RANK通路抑制破骨细胞的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(5):617-624.
[15] 王东红,王春爱,薛建军.葛根素的研究进展[J].西部中医药,2017, 30(1):139-142.
[16] 杨一秋,李兰,解继胜,等.葛根素介导PTEN-PI3K-AKT信号通路抑制绝经后骨质疏松症的机制研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(3): 347-351.
[17] WONG R, RABIE B. Effect of puerarin on bone formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(8):894-899.
[18] 周帅,芦山,郭森.基于Notch信号通路探究葛根素对肺动脉高压小鼠治疗作用机制研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2022,49(7):197-200.
[19] PARK J, ZHANG X, LEE S K, et al. CCL28-induced RARβ expression inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma bone invasion. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5381-5399.
[20] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent Advances in Osteoclast Biology.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149:325-341.
[21] LARROUTURE QC, CRIBBS AP, RAO S R, et al. Loss of mutual protection between human osteoclasts and chondrocytes in damaged joints initiates osteoclast-mediated cartilage degradation by MMPs. Sci Rep. 2021;11:22708.
[22] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL /RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371.
[23] 詹乐,马瑞堉,万妮,等.葛根素对牙周炎大鼠Th17/Treg细胞免疫平衡及相关转录因子表达的影响[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2022, 43(11):36-43.
[24] 高陆,刘欧胜,徐丽.司马西特通过Notch/RANKL诱导破骨细胞形成的初步研究[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(3):160-165.
[25] 季开心,陈思言,张敏杰,等.坏死性凋亡在大鼠牙移动过程中对牙周组织改建的影响[J].口腔医学,2021,41(12):1068-1087.
[26] MIZUKAMI J, TAKAESU G, AKATSUKA H, et al. Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activates TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase through a signaling complex containing RANK, TAB2, and TRAF6. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(4):992-1000.
[27] YAMAMOTO A, MIYAZAKI T, KADONO Y, et al. Possible Involvement of IκB Kinase 2 and MKK7 in Osteoclastogenesis Induced by Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor κB Ligand. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(4): 612-621.
[28] 闫波.葛根素抑制PMMA颗粒诱导破骨细胞形成及骨溶解的机制研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020.
[29] 于冬冬,赵丹阳,姚啸生,等.葛根素通过NF-κB信号通路调节破骨细胞的分化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(9):837-841.
[30] 袁斯远,何芳,孔蓓蓓,等.葛根素对破骨细胞形成以及成骨细胞OPG/RANKL mRNA表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(11): 3889-3892.
[31] FILIPOVIC M, FLEGAR D, SUCUR A, et al. Inhibition of Notch Signaling Stimulates Osteoclastogenesis From the Common Trilineage Progenitor Under Inflammatory Conditions. Front Immunol. 2022;13:902947.
[32] 刘官娟,宋娜,霍花,等.唑来膦酸调控NLRP3信号通路抑制脂多糖诱导的破骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29):4677-4683.
[33] 冯燕陵.FoxO1介导白藜芦醇、葛根素抑制破骨细胞生成和活性的机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018.
[34] 康鑫.葛根素促进成骨细胞增殖及信号调控机制的实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2015.
[35] ARMSTRONG AP, TOMETSKO ME, GLACCUM M, et al. A RANK/TRAF6-dependent signal transduction pathway is essential for osteoclast cytoskeletal organization and resorptive function. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(46):44347-44356.
[36] ZHOU B, LIN W, LONG Y, et al. Notch signaling pathway:architecture, disease,and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):95.
[37] ZENG XZ, HE LG, WANG S, et al. Aconine inhibits RANKL-in-duced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1 activation and DC-STAMP expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016; 37(2):255-263.
[38] WANG ZW, LI YW, SARKAR FH. Notch Signaling Proteins: Legitimate Targets for Cancer Therapy. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010;11(6):398-408.
[39] 平依林,娄锋,杨肖,等. Notch1蛋白高表达抑制破骨细胞增殖和分化[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2016,34(2):121-124.
[40] 王汝杰,刘复州,沈伟伟,等. Jagged1活化Notch通路促进RAW 264.7向破骨细胞分化但抑制增殖[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2014,30(7): 865-869. |