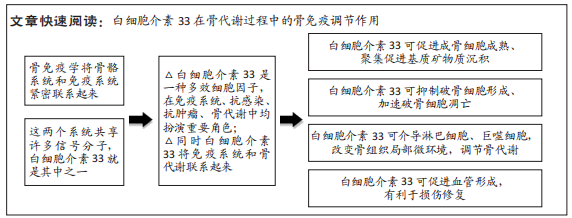
[1] RAI V, DILISIO MF, SAMADI F, et al. Counteractive Effects of IL-33 and IL-37 on Inflammation in Osteoarthritis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(9):5690.
[2] 冯瑶,吴素琴,吴英良.IL-33对RANKL诱导破骨细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2021,38(9):935-941.
[3] KELSEN SG, AGACHE IO, SOONG W, et al. Astegolimab (anti-ST2) efficacy and safety in adults with severe asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148(3):790-798.
[4] GINALDI L, DE MARTINIS M. Osteoimmunology and Beyond. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(33):3754-3774.
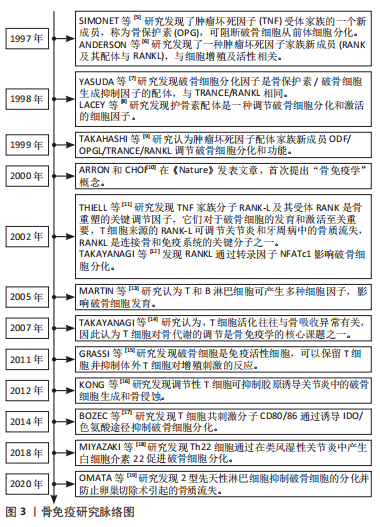
[5] SIMONET WS, LACEY DL, DUNSTAN CR, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997;89(2):309-319.
[6] ANDERSON DM, MARASKOVSKY E, BILLINGSLEY WL, et al. A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature. 1997;390(6656):175-179.
[7] YASUDA H, SHIMA N, NAKAGAWA N, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3597-3602.
[8] LACEY DL, TIMMS E, TAN HL, et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998;93(2):165-176.
[9] TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N, SUDA T. A new member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family, ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;256(3): 449-455.
[10] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812):535-536.
[11] THEILL LE, BOYLE WJ, PENNINGER JM. RANK-L and RANK: T cells, bone loss, and mammalian evolution. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:795-823.
[12] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901.
[13] MARTIN TJ, SIMS NA. Osteoclast-derived activity in the coupling of bone formation to resorption. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11(2):76-81.
[14] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(4):292-304.
[15] GRASSI F, MANFERDINI C, CATTINI L, et al. T cell suppression by osteoclasts in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(4):982-990.
[16] KONG N, LAN Q, SU W, et al. Induced T regulatory cells suppress osteoclastogenesis and bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis better than natural T regulatory cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(9):1567-1572.
[17] BOZEC A, ZAISS M, KAGWIRIA R, et al. T cell costimulation molecules CD80/86 inhibit osteoclast differentiation by inducing the IDO/tryptophan pathway. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(235):235r-260r.
[18] MIYAZAKI Y, NAKAYAMADA S, KUBO S, et al. Th22 Cells Promote Osteoclast Differentiation via Production of IL-22 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2901.
[19] OMATA Y, FRECH M, LUCAS S, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells inhibit the differentiation of osteoclasts and protect from ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Bone. 2020;136:115335.
[20] MARTYNOVA E, RIZVANOV A, URBANOWICZ RA, et al. Inflammasome Contribution to the Activation of Th1, Th2, and Th17 Immune Responses. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:851835.
[21] PINTO SM, SUBBANNAYYA Y, REX D, et al. A network map of IL-33 signaling pathway. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018;12(3):615-624.
[22] BARICHELLO T. The role of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in mental health. Discov Ment Health. 2022;2(1):2.
[23] LI Z, JIANG W, CHU H, et al. Exploration of potential mechanism of interleukin-33 up-regulation caused by 1,4-naphthoquinone black carbon in RAW264.7 cells. Sci Total Environ. 2022;835:155357.
[24] SCHIERING C, KRAUSGRUBER T, CHOMKA A, et al. The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature. 2014;513(7519):564-568.
[25] PI L, FANG B, MENG X, et al. LncRNA XIST accelerates burn wound healing by promoting M2 macrophage polarization through targeting IL-33 via miR-19b. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):220.
[26] MIYATA J, YOKOKURA Y, MORO K, et al. 12/15-Lipoxygenase Regulates IL-33-Induced Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Mice. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 687192.
[27] ROZARIO C, MARTINEZ-SOBRIDO L, MCSORLEY HJ, et al. Could Interleukin-33 (IL-33) Govern the Outcome of an Equine Influenza Virus Infection? Learning from Other Species. Viruses. 2021;13(12):2519.
[28] MURDACA G, PALADIN F, TONACCI A, et al. Involvement of Il-33 in the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Major Respiratory Viral Infections: Future Perspectives for Personalized Therapy. Biomedicines. 2022;10(3):715.
[29] SARANCHOVA I, HAN J, ZAMAN R, et al. Type 2 Innate Lymphocytes Actuate Immunity Against Tumours and Limit Cancer Metastasis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2924.
[30] EBERL G, COLONNA M, DI SANTO JP, et al. Innate lymphoid cells. Innate lymphoid cells: a new paradigm in immunology. Science. 2015;348(6237):a6566.
[31] YANG K, TIAN C, ZHANG C, et al. The Controversial Role of IL-33 in Lung Cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13:897356.
[32] KENSWIL K, JARAMILLO AC, PING Z, et al. Characterization of Endothelial Cells Associated with Hematopoietic Niche Formation in Humans Identifies IL-33 As an Anabolic Factor. Cell Rep. 2018;22(3):666-678.
[33] TUCKERMANN J, ADAMS RH. The endothelium-bone axis in development, homeostasis and bone and joint disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(10):608-620.
[34] LOUISY A, GEOFFROY V, HALGAND B, et al. Interleukin-33 Deficiency Exacerbates Bone Loss Associated with Porphyromonas Gingivalis-Induced Experimental Periodontitis in Female Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2022;56(3):270-281.
[35] SALEH H, EELES D, HODGE JM, et al. Interleukin-33, a target of parathyroid hormone and oncostatin m, increases osteoblastic matrix mineral deposition and inhibits osteoclast formation in vitro. Endocrinology. 2011;152(5):1911-1922.
[36] WIERZBICKA JM, PIOTROWSKA A, PURZYCKA-BOHDAN D, et al. The Effects of Vitamin D on the Expression of IL-33 and Its Receptor ST2 in Skin Cells; Potential Implication for Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):12907.
[37] LOJK J, MARC J. Roles of Non-Canonical Wnt Signalling Pathways in Bone Biology. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10840.
[38] LIMA IL, MACARI S, MADEIRA MF, et al. Osteoprotective Effects of IL-33/ST2 Link to Osteoclast Apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(12):3338-3348.
[39] SCHULZE J, BICKERT T, BEIL FT, et al. Interleukin-33 is expressed in differentiated osteoblasts and blocks osteoclast formation from bone marrow precursor cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(4):704-717.
[40] MCDONALD MM, KIM AS, MULHOLLAND BS, et al. New Insights Into Osteoclast Biology. JBMR Plus. 2021;5(9):e10539.
[41] Ono T, Nakashima T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341.
[42] DE MARTINIS M, GINALDI L, SIRUFO MM, et al. Alarmins in Osteoporosis, RAGE, IL-1, and IL-33 Pathways: A Literature Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(3):138.
[43] KIYOMIYA H, ARIYOSHI W, OKINAGA T, et al. IL-33 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation through the regulation of Blimp-1 and IRF-8 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460(2):320-326.
[44] ZAISS M, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, BOHM C, et al. IL-33 shifts the balance from osteoclast to alternatively activated macrophage differentiation and protects from TNF-alpha-mediated bone loss. J Immunol. 2011;186(11):6097-6105.
[45] MUN SH, KO NY, KIM HS, et al. Interleukin-33 stimulates formation of functional osteoclasts from human CD14(+) monocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67(22): 3883-3892.
[46] MINE Y, MAKIHIRA S, YAMAGUCHI Y, et al. Involvement of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways on Interleukin-33-induced RANKL expression in osteoblastic cells. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(5):655-662.
[47] SAIDI S, BOURI F, LENCEL P, et al. IL-33 is expressed in human osteoblasts, but has no direct effect on bone remodeling. Cytokine. 2011;53(3):347-354.
[48] 左建峰. IL-33修饰的BMSCs对心肌梗死炎症和心功能的影响分析[D].苏州:苏州大学胸心血管外科学,2017.
[49] TERRAZA C, FUENTES R, PINO-LAGOS K. IFN-gamma and IL-33 modulate mesenchymal stem cells function targeting Th1/Th17 axis in a murine skin transplantation model. Cytokine. 2018;111:317-324.
[50] LI C, CHEN K, KANG H, et al. Double-stranded RNA released from damaged articular chondrocytes promotes cartilage degeneration via Toll-like receptor 3-interleukin-33 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(11):e3165.
[51] MOMIUCHI Y, MOTOMURA Y, SUGA E, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells in bone marrow regulate osteoclastogenesis in a reciprocal manner via RANKL, GM-CSF and IL-13. Int Immunol. 2021;33(11):573-585.
[52] DOHNKE S, MOEHSER S, SURNOV A, et al. Role of Dynamic Actin Cytoskeleton Remodeling in Foxp3(+) Regulatory T Cell Development and Function: Implications for Osteoclastogenesis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:836646.
[53] FISCHER L, HERKNER C, KITTE R, et al. Foxp3(+) Regulatory T Cells in Bone and Hematopoietic Homeostasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:578.
[54] XU H, ZHAO H, LU C, et al. Triptolide Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption In Vitro via Enhancing the Production of IL-10 and TGF-beta1 by Regulatory T Cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8048170.
[55] XIA Y, FAN D, LI X, et al. Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill Regulates the Bone Immune Microenvironment via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Vitro. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:746786.
[56] ZAISS M, FREY B, HESS A, et al. Regulatory T cells protect from local and systemic bone destruction in arthritis. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):7238-7246.
[57] GAJARDO T, MORALES RA, CAMPOS-MORA M, et al. Exogenous interleukin-33 targets myeloid-derived suppressor cells and generates periphery-induced Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in skin-transplanted mice. Immunology. 2015;146(1): 81-88.
[58] KAWAI K, UCHIYAMA M, HESTER J, et al. IL-33 drives the production of mouse regulatory T cells with enhanced in vivo suppressive activity in skin transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2021;21(3):978-992.
[59] SIEDE J, FROHLICH A, DATSI A, et al. IL-33 Receptor-Expressing Regulatory T Cells Are Highly Activated, Th2 Biased and Suppress CD4 T Cell Proliferation through IL-10 and TGFbeta Release. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e161507.
[60] VOCCA L, DI SANO C, UASUF CG, et al. IL-33/ST2 axis controls Th2/IL-31 and Th17 immune response in allergic airway diseases. Immunobiology. 2015;220(8):954-963.
[61] MURDACA G, GRECO M, TONACCI A, et al. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Immune-Mediated and Allergic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5856.
[62] DE MARTINIS M, SIRUFO MM, SUPPA M, et al. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1239.
[63] LI C, CHEN K, KANG H, et al. Double-stranded RNA released from damaged articular chondrocytes promotes cartilage degeneration via Toll-like receptor 3-interleukin-33 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(11):e3165.
[64] ALVAREZ MM, LIU JC, TRUJILLO-DE SG, et al. Delivery strategies to control inflammatory response: Modulating M1-M2 polarization in tissue engineering applications. J Control Release. 2016;240:349-363.
[65] LIN YC, LIN YC, TSAI ML, et al. IL-33 regulates M1/M2 chemokine expression via mitochondrial redox-related mitophagy in human monocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;359:109915.
[66] CHOI YS, CHOI HJ, MIN JK, et al. Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood. 2009;114(14):3117-3126.
[67] DONG Q, TIAN J, ZHENG W, et al. Interleukin-33 protects mice against hindlimb ischemic injury by enhancing endothelial angiogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;109:108850. |