[1] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, MüLLER WEG. Amorphous polyphosphate, a smart bioinspired nano-/bio-material for bone and cartilage regeneration: towards a new paradigm in tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(16):2385-2412.
[2] MüLLER WEG, SCHRöDER HC, WANG X. Inorganic Polyphosphates As Storage for and Generator of Metabolic Energy in the Extracellular Matrix. Chem Rev. 2019;119(24):12337-12374.
[3] BROWN MR, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate in the origin and survival of species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(46):16085-16087.
[4] EZAWA T, CAVAGNARO TR, SMITH SE, et al. Rapid accumulation of polyphosphate in extraradical hyphae of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as revealed by histochemistry and a polyphosphate kinase/luciferase system. New Phytol. 2004;161(2):387-392.
[5] FLEISH H, NEUMAN WF. Mechanisms of calcification: role of collagen, polyphosphates, and phosphatase. Am J Physiol. 1961;200:1296-1300.
[6] XIE L, JAKOB U. Inorganic polyphosphate, a multifunctional polyanionic protein scaffold. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(6):2180-2190.
[7] RAO NN, LIU S, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response. J Bacteriol. 1998;180(8):2186-2193.
[8] AHN K, KORNBERG A. Polyphosphate kinase from Escherichia coli. Purification and demonstration of a phosphoenzyme intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(20):11734-11739.
[9] RAO NN, GóMEZ-GARCíA MR, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate: essential for growth and survival. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:605-647.
[10] ITOH H, KAWAZOE Y, SHIBA T. Enhancement of protein synthesis by an inorganic polyphosphate in an E. coli cell-free system. J Microbiol Methods. 2006;64(2):241-249.
[11] RASHID MH, RAO NN, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate is required for motility of bacterial pathogens. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(1): 225-227.
[12] VARAS MA, RIQUELME-BARRIOS S, VALENZUELA C, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate is essential for salmonella typhimurium virulence and survival in dictyostelium discoideum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018;8:8.
[13] ARIGANELLO MB, OMELON S, VARIOLA F, et al. Osteogenic cell cultures cannot utilize exogenous sources of synthetic polyphosphate for mineralization. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(12):2089-2102.
[14] MüLLER WE, TOLBA E, SCHRöDER HC, et al. Polyphosphate: a morphogenetically active implant material serving as metabolic fuel for bone regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2015;15(9):1182-1197.
[15] GRAY MJ, WHOLEY WY, WAGNER NO, et al. Polyphosphate is a primordial chaperone. Mol Cell. 2014;53(5):689-699.
[16] STOTZ SC, SCOTT LO, DRUMMOND-MAIN C, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate regulates neuronal excitability through modulation of voltage-gated channels. Mol Brain. 2014;7:42.
[17] DHIVYA S, KESHAV NARAYAN A, LOGITH KUMAR R, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds containing chitosan, calcium polyphosphate and pigeonite for bone tissue engineering. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(1):e12408.
[18] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, MüLLER WE. Enzymatically synthesized inorganic polymers as morphogenetically active bone scaffolds: application in regenerative medicine. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;313:27-77.
[19] WANG Y, LI M, LI P, et al. Progress and applications of polyphosphate in bone and cartilage regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5141204.
[20] YUAN Q, KUBO T, DOI K, et al. Effect of combined application of bFGF and inorganic polyphosphate on bioactivities of osteoblasts and initial bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(5):1716-1724.
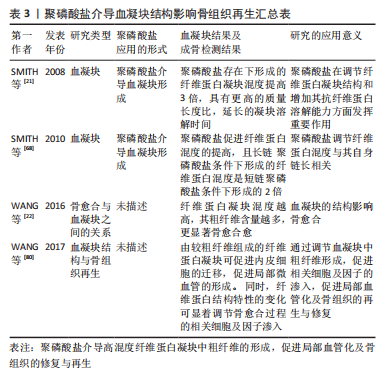
[21] SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate enhances fibrin clot structure. Blood. 2008;112(7):2810-2816.
[22] WANG X, FRIIS TE, MASCI PP, et al. Alteration of blood clot structures by interleukin-1 beta in association with bone defects healing. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35645.
[23] PHELIPE HATT L, THOMPSON K, MüLLER WEG, et al. Calcium polyphosphate nanoparticles act as an effective inorganic phosphate source during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5801.
[24] XI Y, MIAO X, LI Y, et al. BMP2-mimicking peptide modified with E7 coupling to calcined bovine bone enhanced bone regeneration associating with activation of the Runx2/SP7 signaling axis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1):80-93.
[25] LIU XW, MA B, ZI Y, et al. Effects of rutin on osteoblast MC3T3-E1 differentiation, ALP activity and Runx2 protein expression. Eur J Histochem. 2021;65(1):3195.
[26] ZHAO J, LIU R, ZHU J, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation through their immunosuppressive function. J Oral Biosci. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2021.07.003.
[27] MüLLER WEG, NEUFURTH M, WANG S, et al. Amorphous, smart, and bioinspired polyphosphate nano/microparticles: a biomaterial for regeneration and repair of osteo-articular impairments in-situ. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):427.
[28] MOSSAHEBI-MOHAMMADI M, QUAN M, ZHANG JS, et al. FGF signaling pathway: a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:79.
[29] KAWAZOE Y, KATOH S, ONODERA Y, et al. Activation of the FGF signaling pathway and subsequent induction of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by inorganic polyphosphate. Int J Biol Sci. 2008;4(1):37-47.
[30] OZEKI N, MOGI M, HASE N, et al. Polyphosphate-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 is required for osteoblast-like cell differentiation in human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biosci Trends. 2016;10(5):365-371.
[31] GARG P, MAZUR MM, BUCK AC, et al. Prospective review of mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into osteoblasts. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):13-19.
[32] KAWAZOE Y, SHIBA T, NAKAMURA R, et al. Induction of calcification in MC3T3-E1 cells by inorganic polyphosphate. J Dent Res. 2004;83(8): 613-618.
[33] ZHANG M, QIAN T, DENG Z, et al. 3D printed double-network alginate hydrogels containing polyphosphate for bioenergetics and bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;188;639-648.
[34] MüLLER WE, WANG X, DIEHL-SEIFERT B, et al. Inorganic polymeric phosphate/polyphosphate as an inducer of alkaline phosphatase and a modulator of intracellular Ca2+ level in osteoblasts (SaOS-2 cells) in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2661-2671.
[35] USKOKOVIĆ V, HOOVER C, VUKOMANOVIĆ M, et al. Osteogenic and antimicrobial nanoparticulate calcium phosphate and poly-(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) powders for the treatment of osteomyelitis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(6):3362-3373.
[36] USUI Y, UEMATSU T, UCHIHASHI T, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate induces osteoblastic differentiation. J Dent Res. 2010;89(5):504-509.
[37] WANG X, YU Y, JI L, et al. Calcium phosphate-based materials regulate osteoclast-mediated osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12): 4517-4530.
[38] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, SCHLOßMACHER U, et al. Inorganic polyphosphates: biologically active biopolymers for biomedical applications. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2013;54:261-294.
[39] OMELON S, GEORGIOU J, HENNEMAN ZJ, et al. Control of vertebrate skeletal mineralization by polyphosphates. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5634.
[40] VASIKARAN SD, MIURA M, PIKNER R, et al. Practical considerations for the clinical application of bone turnover markers in osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00930-4.
[41] LJUSBERG J, WANG Y, LåNG P, et al. Proteolytic excision of a repressive loop domain in tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase by cathepsin K in osteoclasts. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(31):28370-28381.
[42] HARADA K, ITOH H, KAWAZOE Y, et al. Polyphosphate-mediated inhibition of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and suppression of bone resorption of osteoclasts. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78612.
[43] LEE ZH, KIM HH. Signal transduction by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 305(2):211-214.
[44] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, DIEHL-SEIFERT B, et al. Dual effect of inorganic polymeric phosphate/polyphosphate on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(10):767-776.
[45] MARSELL R, EINHORN TA. The biology of fracture healing. Injury. 2011; 42(6):551-555.
[46] FROST HM. The biology of fracture healing. An overview for clinicians. Part I. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248):283-293.
[47] XIAO L, MA YP, CRAWFORD R, et al. The interplay between hemostasis and immune response in biomaterial development for osteogenesis. Materials Today. 2022;54: 202-224.
[48] ALMEIDA CR, CAIRES HR, VASCONCELOS DP, et al. NAP-2 secreted by human nk cells can stimulate mesenchymal stem/stromal cell recruitment. Stem Cell Rep. 2016;6(4):466-473.
[49] OMAR OM, GRANéLI C, EKSTRöM K, et al. The stimulation of an osteogenic response by classical monocyte activation. Biomaterials. 2011;32(32):8190-8204.
[50] NIU Y, LI Q, XIE R, et al. Modulating the phenotype of host macrophages to enhance osteogenesis in MSC-laden hydrogels: design of a glucomannan coating material. Biomaterials. 2017;139;39-55.
[51] CHAMPAGNE CM, TAKEBE J, OFFENBACHER S, et al. Macrophage cell lines produce osteoinductive signals that include bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone. 2002;30(1):26-31.
[52] FROMIGUé O, MARIE PJ, LOMRI A. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-beta2 interact to modulate human bone marrow stromal cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1998;68(4):411-426.
[53] CHO SW. Role of osteal macrophages in bone metabolism. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(2):102-104.
[54] WHEATLEY BM, NAPPO KE, CHRISTENSEN DL, et al. Effect of NSAIDs on bone healing rates: a meta-analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019; 27(7):e330-e336.
[55] BAHNEY CS, ZONDERVAN RL, ALLISON P, et al. Cellular biology of fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(1):35-50.
[56] BAE JS, LEE W, REZAIE AR. Polyphosphate elicits pro-inflammatory responses that are counteracted by activated protein C in both cellular and animal models. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(6):1145-1151.
[57] WANG H, BLOOM O, ZHANG M, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285(5425):248-251.
[58] XU J, ZHANG X, PELAYO R, et al. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat Med. 2009;15(11):1318-1321.
[59] DINARVAND P, HASSANIAN SM, QURESHI SH, et al. Polyphosphate amplifies proinflammatory responses of nuclear proteins through interaction with receptor for advanced glycation end products and P2Y1 purinergic receptor. Blood. 2014;123(6):935-945.
[60] HASSANIAN SM, DINARVAND P, SMITH SA, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate elicits pro-inflammatory responses through activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2 in vascular endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(5):860-871.
[61] OSCHATZ C, MAAS C, LECHER B, et al. Mast cells increase vascular permeability by heparin-initiated bradykinin formation in vivo. Immunity. 2011;34(2):258-268.
[62] MüLLER F, MUTCH NJ, SCHENK WA, et al. Platelet polyphosphates are proinflammatory and procoagulant mediators in vivo. Cell. 2009; 139(6):1143-1156.
[63] MORENO-SANCHEZ D, HERNANDEZ-RUIZ L, RUIZ FA, et al. Polyphosphate is a novel pro-inflammatory regulator of mast cells and is located in acidocalcisomes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(34):28435-28444.
[64] WAT JM, FOLEY JH, KRISINGER MJ, et al. Polyphosphate suppresses complement via the terminal pathway. Blood. 2014;123(5):768-776.
[65] GU JT, JIAO K, LI J, et al. Polyphosphate-crosslinked collagen scaffolds for hemostasis and alveolar bone regeneration after tooth extraction. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:68-81.
[66] EINHORN TA, GERSTENFELD LC. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45-54.
[67] LAZZARO MA, ZAIDAT OO. Multimodal endovascular reperfusion therapies: adjunctive antithrombotic agents in acute stroke. Neurology. 2012;78(7):501-506.
[68] SMITH SA, CHOI SH, DAVIS-HARRISON R, et al. Polyphosphate exerts differential effects on blood clotting, depending on polymer size. Blood. 2010;116(20):4353-4359.
[69] BAHAMMAM MA, ATTIA MS. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor using platelet rich fibrin (PRF) and nanohydroxyapatite(nano-HA) in treatment of periodontal intra-bony defects - a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(1):870-878.
[70] MUTCH NJ, ENGEL R, UITTE DE WILLIGE S, et al. Polyphosphate modifies the fibrin network and down-regulates fibrinolysis by attenuating binding of tPA and plasminogen to fibrin. Blood. 2010;115(19):3980-3988.
[71] GRUNDNES O, REIKERåS O. The importance of the hematoma for fracture healing in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64(3):340-342.
[72] VAN DER ENDE J, VAN BAARDEWIJK LJ, SIER CF, et al. Bone healing and mannose-binding lectin. Int J Surg. 2013;11(4):296-300.
[73] CHOI SH, SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate accelerates factor V activation by factor XIa. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(3):599-604.
[74] CHOI SH, SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate is a cofactor for the activation of factor XI by thrombin. Blood. 2011;118(26):6963-6970.
[75] PUY C, TUCKER EI, IVANOV IS, et al. Platelet-derived short-chain polyphosphates enhance the inactivation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor by activated coagulation factor XI. PLoS One. 2016;11(10): e0165172.
[76] SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate as a general procoagulant agent. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6(10):1750-1756.
[77] WHYTE CS, CHERNYSH IN, DOMINGUES MM, et al. Polyphosphate delays fibrin polymerisation and alters the mechanical properties of the fibrin network. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116(5):897-903.
[78] CARR ME JR, HERMANS J. Size and density of fibrin fibers from turbidity. Macromolecules. 1978;11(1):46-50.
[79] COLLEN A, KOOLWIJK P, KROON M, et al. Influence of fibrin structure on the formation and maintenance of capillary-like tubules by human microvascular endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. 1998;2(2):153-165.
[80] WANG X, FRIIS T, GLATT V, et al. Structural properties of fracture haematoma: current status and future clinical implications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(10):2864-2875. |
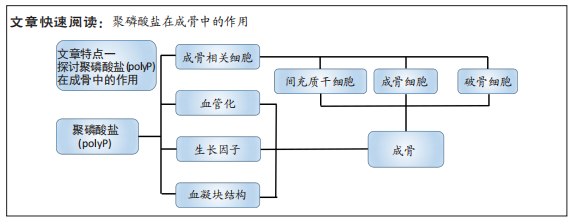
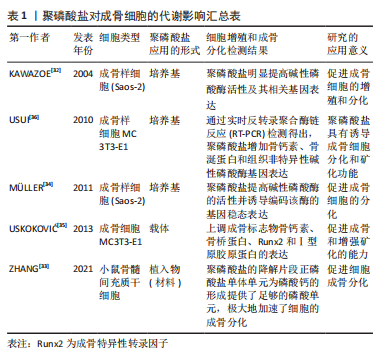
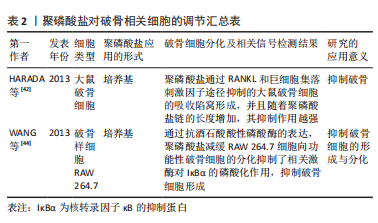
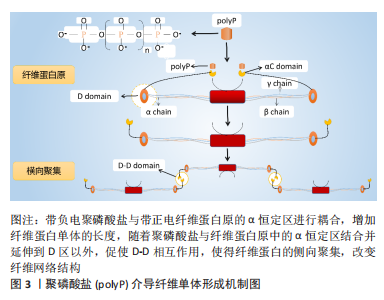
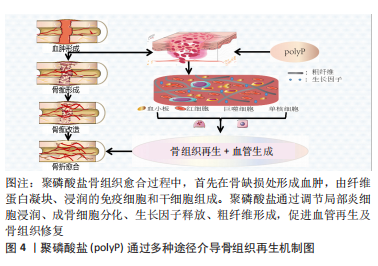
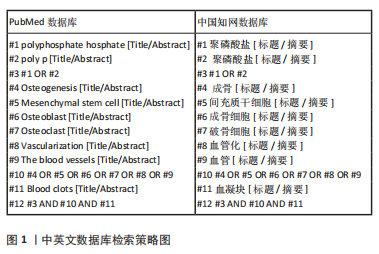
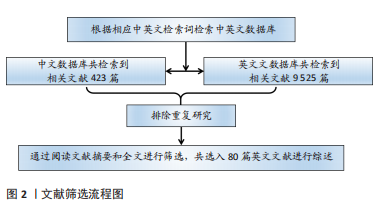
 #br#
#br#