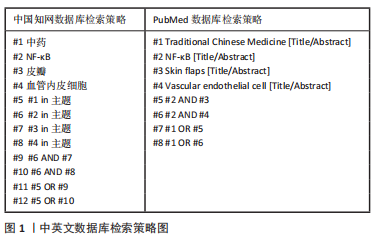
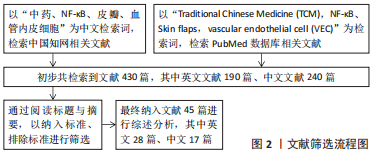
[1] WU XR, WEI PJ, ZHAO YH, et al. Effects of ilioinguinal composite tissue flaps in repairing skin and soft tissue defects on hand or foot. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020;36(8):722-725.
[2] YUAN K, ZHANG F, LINEAWEAVER WC, et al. The coverage of soft-tissue defects around the foot and ankle using free or local flaps: a comparative cohort study. Ann Plast Surg. 2021;86(6):668-673.
[3] WANG L, SONG D, SONG A, et al. Application of modified designed bilobed latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap in chest wall reconstruction of locally advanced breast cancer patients. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(9):1172-1176.
[4] CERVENKA B, BEWLEY AF. Free flap monitoring: a review of the recent literature. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;23(5):393-398.
[5] BALLESTÍN A, CASADO JG, ABELLÁN E, et al. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat microvascular skin free flap model: a histological, genetic, and blood flow study. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0209624.
[6] 章盖,耿乐乐,方勇.缺血再灌注对小鼠胸部皮瓣的影响及机制研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2019,14(6):416-425.
[7] 王海刚,何志军.皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的相关机制研究进展[J].甘肃科技,2022,38(20):129-134.
[8] EISENHARDT SU, SCHMIDT Y, KARAXHA G, et al. Monitoring molecular changes induced by ischemia/reperfusion in human free muscle flap tissue samples. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;68(2):202-208.
[9] LEE JH, YOU HJ, LEE TY, et al. Current status of experimental animal skin flap models: ischemic preconditioning and molecular factors. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):5234.
[10] DACHO A, HANUSCH C, LYUTENSKI S, et al. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate as an effector and trigger in ischemia-reperfusion injury in adipocutaneous flaps in rats. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;41(3):176-182.
[11] WENG H, HE L, LIU X, et al. Natural lactucopicrin alleviates importin-α3-mediated NF-κB activation in inflammated endothelial cells and improves sepsis in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;186:114501.
[12] KAILEH M, SEN R. NF-κB function in B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 2012; 246(1):254-271.
[13] PATEL H, ZAGHLOUL N, LIN K, et al. Hypoxia-induced activation of specific members of the NF-kB family and its relevance to pulmonary vascular remodeling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;92:141-147.
[14] WILLIAMS LM, GILMORE TD. Looking down on NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 2020; 40(15):e00104-20.
[15] THOMS HC, STARK LA. The NF-κB nucleolar stress response pathway. Biomedicines. 2021;9(9):1082.
[16] DURAND JK, BALDWIN AS. Targeting IKK and NF-κB for therapy. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;107:77-115.
[17] MULERO MC, HUXFORD T, GHOSH G. NF-κB, IκB, and IKK: integral components of immune system signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1172:207-226.
[18] MCCORKELL KA, MAY MJ. Noncanonical NF-κB activation and SDF-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1280:155-180.
[19] RAH DK, MIN HJ, KIM YW, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on ischemia-reperfusion injury in a skin flap mouse model. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(9):829-839.
[20] MAO X, LIU L, CHENG L, et al. Adhesive nanoparticles with inflammation regulation for promoting skin flap regeneration. J Control Release. 2019;297: 91-101.
[21] LIU X, SHAO Y, TU J, et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide-stimulated hepatocyte-derived exosomes promote inflammation and endothelial dysfunction through nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(22):1670.
[22] BISWAS R, BAGCHI A. Inhibition of TRAF6-Ubc13 interaction in NFkB inflammatory pathway by analyzing the hotspot amino acid residues and protein-protein interactions using molecular docking simulations. Comput Biol Chem. 2017;70:116-124.
[23] LI F, LIANG H, YOU H, et al. Targeting HECTD3-IKKα axis inhibits inflammation-related metastasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):264.
[24] CHEN Y, ZHENG Y, LIU L, et al. Adiponectin inhibits TNF-α-activated PAI-1 expression via the cAMP-PKA-AMPK-NF-κB axis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(6):2342-2352.
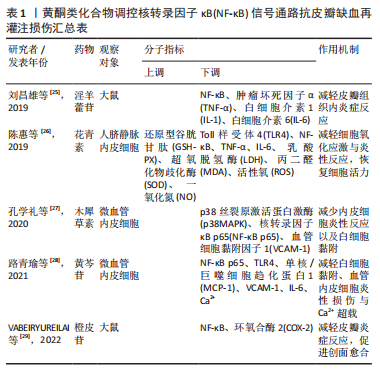
[25] 刘昌雄,黄雄杰,肖湘君,等.淫羊藿苷对大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤后炎症反应的抑制作用[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2019,35(6):532-535.
[26] 陈惠,胡勇.花青素通过TLR4/NF-κB通路对脂多糖诱导的血管内皮损伤的保护作用[J].实用医药杂志,2019,36(1):59-62.
[27] 孔学礼,霍桂桃,李佳,等.木犀草素通过抑制p65 NF-κB、促进p85 PI3K调节微血管内皮细胞VCAM-1表达[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2020,47(8):675-684.
[28] 路青瑜,郭丽,张启云,等.黄芩苷对脂多糖致内皮细胞炎症反应的保护作用及机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(2):251-257.
[29] VABEIRYUREILAI M, LALRINZUALI K, JAGETIA GC. NF-κB and COX-2 repression with topical application of hesperidin and naringin hydrogels augments repair and regeneration of deep dermal wounds. Burns. 2022;48(1):132-145.
[30] SONG C, WANG Y, CUI L, et al. Triptolide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells: involvement of NF-κB pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):198.
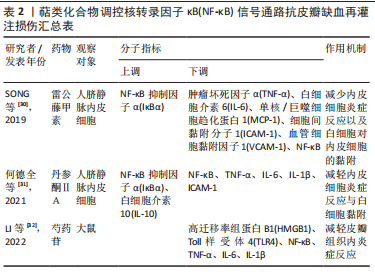
[31] 何德全,陈友权,王世祥.丹参酮ⅡA通过NF-κB通路抑制脂多糖诱导人脐静脉血管内皮细胞炎性反应的作用机制[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021,19(3):428-432.
[32] LI WJ, LIU YY, HE JB, et al. Effect of paeoniflorin on distal survival of random flaps. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;105:108562.
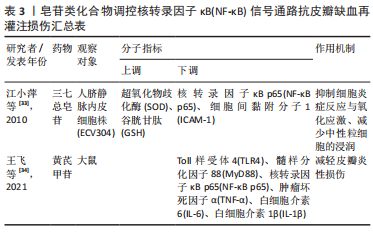
[33] 江小萍,李海全,潘少霞,等.三七总皂苷对缺氧再给氧血管内皮细胞NF-κB及ICAM-1表达的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2010,8(9): 1086-1088.
[34] 王飞,田阳,徐骁然,等.黄芪甲苷通过调控TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路对大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2021,35(5):497-503.
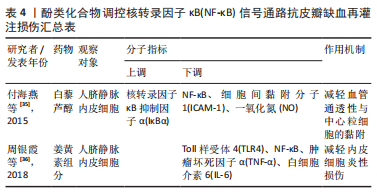
[35] 付海燕,胡占升,杜红阳,等.白藜芦醇衍生物TMS对脂多糖诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞中一氧化氮、血管细胞间黏附分子1及核转录因子κB表达的影响[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2015,28(8):808-813.
[36] 周银霞,张崇,傅海珍,等.姜黄素类组分通过下调TLR4/NF-κB通路抑制LPS诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤[J].中南药学,2018,16(11):1521-1525.
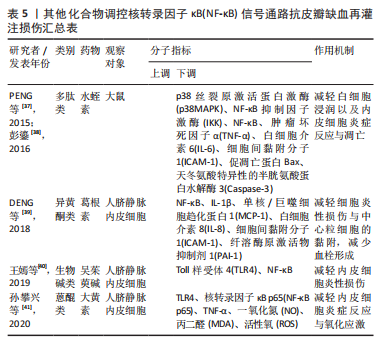
[37] PENG L, PAN X, YIN G. Natural hirudin increases rat flap viability by anti-inflammation via PARs/p38/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 597264.
[38] 彭鎏. 水蛭素通过p38 MAPK/IKK/NF-κB通路调节大鼠血运障碍皮瓣炎症反应及细胞凋亡相关因子表达的研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2016.
[39] DENG HF, WANG S, LI L, et al. Puerarin prevents vascular endothelial injury through suppression of NF-κB activation in LPS-challenged human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:261-267.
[40] 王嫣,杨卫平,彭芳,等.吴茱萸碱通过TLR4/NF-κB通路抑制脂多糖诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2019,35(12): 1088-1093.
[41] 孙攀兴,邱春光.大黄素通过调控TLR4/NF-κB通路对脂多糖诱导血管内皮细胞氧化损伤的保护作用研究[J].药物评价研究,2020,43(6):1040-1045.
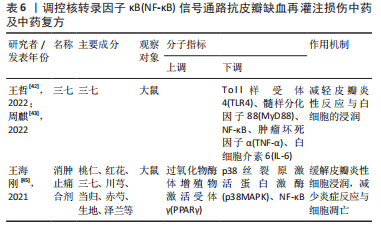
[42] 王哲.基于网络药理学探讨三七对大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的影响及作用机制[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2022.
[43] 周麒.三七调控大鼠腹壁穿支皮瓣缺血再灌注TLR4-MyD88-NF-kB信号通路的实验研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2022.
[44] XIANG S, CHEN K, XU L, et al. Bergenin exerts hepatoprotective effects by inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors, apoptosis and autophagy via the PPAR-γ pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:129-143.
[45] 王海刚.基于p38MAPK-PPARγ/NF-κB信号通路探讨消肿止痛合剂对皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的干预机制研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2021.
|