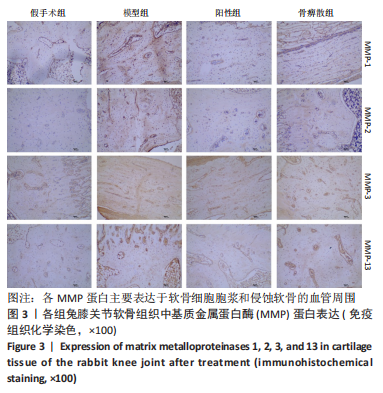
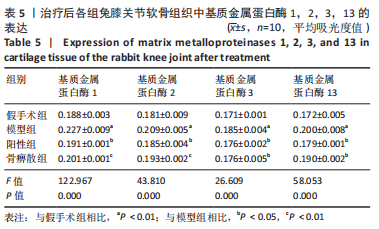
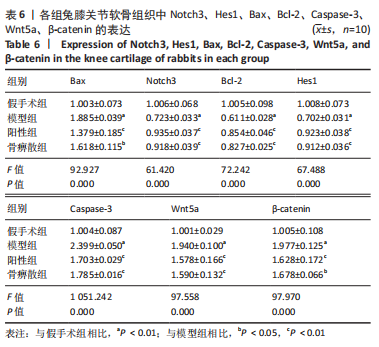
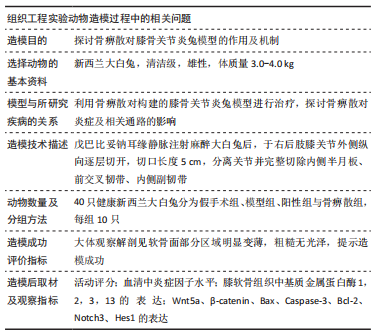
[1] BEARD DJ, DAVIES LJ, COOK JA, et al. The clinical and cost-effectiveness of total versus partial knee replacement in patients with medial compartment osteoarthritis (TOPKAT): 5-year outcomes of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10200):746-756.
[2] YIN Z, QIAN P, WU X, et al. Unicondylar knee arthroplasty versus total knee arthroplasty in adults with isolated medial osteoarthritis: A matched study protocol. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(35):e21868.
[3] 霍少川,王海彬,唐宏宇,等.补肾健脾活血中药干预膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞IL-1β/ERRα/SOX9/Col2α1信号通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5577-5581.
[4] 夏璇,王焕锐,吕媛,等.痹祺胶囊治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效及影像学评价[J].中草药,2020,51(13):3518-3522.
[5] JUNG JH, IKEDA G, TADA Y, et al. miR-106a-363 cluster in extracellular vesicles promotes endogenous myocardial repair via Notch3 pathway in ischemic heart injury. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021;116(1):19.
[6] LUO X, ZHANG L, HAN GD, et al. MDM2 inhibition improves cisplatin-induced renal injury in mice via inactivation of Notch/hes1 signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40(2):369-379.
[7] 朱星昊,陈亚楠,魏丹丹,等.七味红花殊胜丸对肝纤维化小鼠Notch/Hes1信号通路的影响[J].中国医院药学杂志,2021,41(1):8-12.
[8] 岳宗进,刘汝银,于露,等.牛膝多糖通过Notch1通路影响骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的机制[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2022,43(4):600-606.
[9] 曾凡,陈柏屹,王康,等.加味独活寄生合剂对膝骨关节炎模型兔膝关节软骨组织细胞自噬及凋亡相关蛋白的影响[J].中医杂志,2022,63(8): 773-780.
[10] GUERMAZI A, NEOGI T, KATZ JN, et al. Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injections for the Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis-related Pain: Considerations and Controversies with a Focus on Imaging-Radiology Scientific Expert Panel. Radiology. 2020;297(3):503-512.
[11] 冀海军,张永红.阳和汤含药血清对膝骨性关节炎兔膝软骨MMP-1,MMP-3和TIMP-1表达的影响[J].四川中医,2020,38(3):72-76.
[12] 陶金刚,黄媛霞.右归丸联合美洛昔康治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2020,35(10):2057-2062.
[13] ARDEN NK, PERRY TA, BANNURU RR, et al. Non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis: comparison of ESCEO and OARSI 2019 guidelines. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):59-66.
[14] CHEN Y, WU YY, SI HB, et al. Mechanistic insights into AMPK-SIRT3 positive feedback loop-mediated chondrocyte mitochondrial quality control in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;166:105497.
[15] WU X, CAI Y, LU S, et al. Intra-articular Injection of Chloramphenicol Reduces Articular Cartilage Degeneration in a Rabbit Model of Osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(12):2785-2797.
[16] 孙立平,周霞,刘炬,等.从调控血管内皮生长因子及其受体激活Notch信号通路角度探讨生地梓醇促血管新生及神经功能重塑作用[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2021,29(11):63-68.
[17] 韩莎莎,张贺鹏,李跃峰.玻璃体腔注射TA对光化学诱导大鼠BRVO模型血管生成及Notch通路的影响[J].国际眼科杂志,2020,20(6):951-955.
[18] TURHAN Y, ARICAN M, KARADUMAN ZO, et al. Chondroprotective effect of Nigella sativa oil in the early stages of osteoarthritis: an experimental study in rabbits. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019;19(3):362-369.
[19] ZIPPORAH E B, PATRA B, GOVARTHANAN K, et al.Defective cell proliferation is an attribute of overexpressed Notch1 receptor and impaired autophagy in Fanconi Anemia. Genomics. 2020;112(6):4628-4639.
[20] LEE YC, CHUNG CP, CHANG MH, et al. NOTCH3 cysteine-altering variant is an important risk factor for stroke in the Taiwanese population. Neurology. 2020;94(1):e87-e96.
[21] 陈谱,阮安民,周俊,等.通络止痛凝胶对不同程度膝关节骨性关节炎家兔滑膜炎性程度的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2020,43(12):1011-1017.
[22] 杨少辉,许红霞,孙卫强,等.杯苋甾酮通过上调miR-204表达抑制IL-1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡的实验研究[J].河北医学,2021,27(3):368-374.
[23] AN Y, WAN G, TAO J, et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-203a suppresses IL-1β-induced inflammation and cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes through Smad3 signaling. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(3):BSR20192723.
[24] TIMUR UT, CARON MMJ, JEUKEN RM, et al. Chondroprotective Actions of Selective COX-2 Inhibitors In Vivo: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(18):6962.
[25] KAJINO-SAKAMOTO R, FUJISHITA T, TAKETO MM, et al. Synthetic lethality between MyD88 loss and mutations in Wnt/β-catenin pathway in intestinal tumor epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2021;40(2):408-420.
[26] BARTOLETTI G, DONG C, UMAR M, et al. Pdgfra regulates multipotent cell differentiation towards chondrocytes via inhibiting Wnt9a/beta-catenin pathway during chondrocranial cartilage development. Dev Biol. 2020; 466(1-2):36-46.
[27] 李慧,马玉环,许丽梅,等.独活寄生汤拆方通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制软骨细胞炎症反应[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5589-5594.
[28] XIA C, WANG P, FANG L, et al. Activation of β-catenin in Col2-expressing chondrocytes leads to osteoarthritis-like defects in hip joint. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18535-18543.
[29] MA L, LIU Y, ZHAO X, et al. Rapamycin attenuates articular cartilage degeneration by inhibiting β-catenin in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;60(5):452-462.
[30] 冯玮,谢正松,罗岑,等.过表达Notch配体Delta-like基因的MLO-Y4骨细胞株的建立及其对骨髓基质细胞成骨分化的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(9):899-907.
[31] SZEMES M, MELEGH Z, BELLAMY J, et al. A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Cells. 2020;9(3):783.
[32] ESMAIL MM, SAEED NM, MICHEL HE, et al. The ameliorative effect of niclosamide on bile duct ligation induced liver fibrosis via suppression of NOTCH and Wnt pathways. Toxicol Lett. 2021;347:23-35.
|