2.1 牙周膜干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路研究历程 从2012年到目前为止,对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路的研究越来越多,大多数研究采用的主要方法为细胞培养和矿化实验等,通过利用各种细胞因子证实了与牙周膜干细胞成骨分化相关的各类信号通路,研究历程经过多次演变。
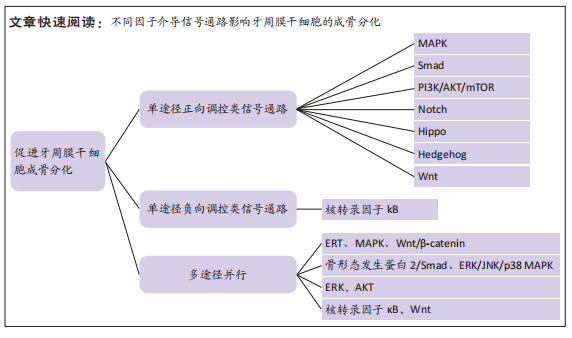
2.2 牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的正向调控类信号通路 正向调控即为牙周膜干细胞接受外界刺激后,激活相应信号通路,进而对牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化起到正向调控作用。正向调控类信号通路包括MAPK信号通路、Wnt/β-catenin通路、Smad信号通路、PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路、Notch信号通路、Hippo信号通路和Hedgehog通路,见图3。
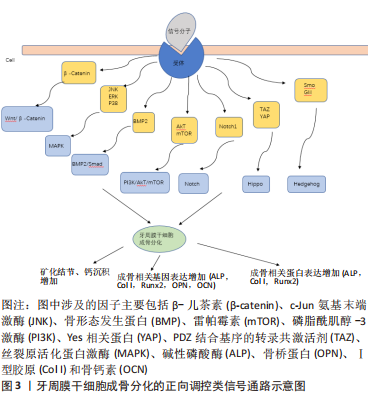
牙周膜干细胞表面的受体接受来自外界信号分子的刺激后,影响了信号通路中某些关键物质的表达或使其发生磷酸化,从而激活相应的信号通路。接受刺激的牙周膜干细胞内β-儿茶素增加进而激活Wnt/β-catenin通路;增加磷酸化p38、EPK、JNK水平进而激活MAPK信号通路;增加骨形态发生蛋白的蛋白水平进而激活Smad信号通路;增加磷酸化Akt、mTOR水平进而激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路;表达Notch受体进而激活Notch信号通路;上调YAP和TAZ的表达水平调节下游基因进而激活Hippo信号通路;增加Hh受体Smo和转录因子Gli1蛋白水平以激活Hedgehog通路,各类因子可分别调控某一信号通路,促进牙周膜干细胞中矿化结节形成以及成骨相关基因和相关蛋白的表达增加。
2.2.1 MAPK信号通路 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶 (mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPK) 是调节细胞增殖、分化、应激和凋亡的关键信号通路[8],包括3种主要的激酶(MAPK kinase kinase,MAPK kinase,MAPK,即MAPKKK,MAPKK和MAPK),它们可激活和磷酸化下游蛋白[9-10]。目前已有研究表明MAPK通路与牙周组织再生修复有关联[11]。
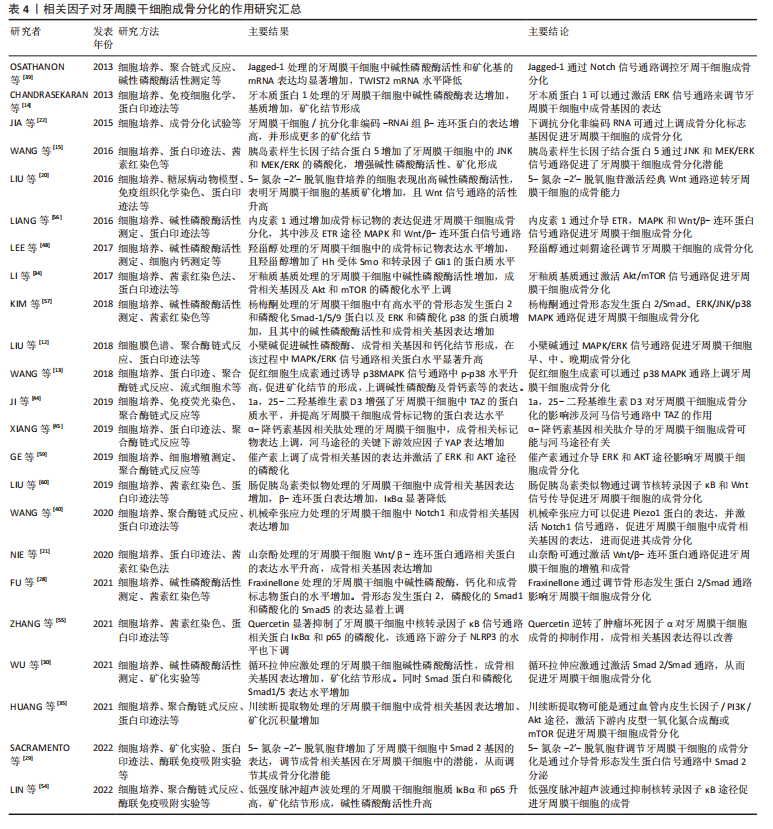
小檗碱(Berberine,BER)是从黄连根瘤中提取出来的活性成分,在调节牙周膜干细胞骨平衡中发挥着重要作用,尤其是在促进牙槽骨再生方面。LIU等[12]研究者证明小檗碱可以与牙周膜干细胞膜上的上皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)结合,激活磷酸化级联(EGF/EGFR?→?Ras?→?Raf?→?MAPK/ERK),进而使核相关基因FOS上调,促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。小檗碱这种促进牙周膜干细胞增殖和成骨分化的作用,使其有希望应用于修复牙槽骨缺损的治疗中,成为一种治疗牙周炎的新药。近年来,基于间充质干细胞的促进牙周组织再生的组织工程方法备受人们关注,促红细胞生成素(erythropoietin,Epo)作为一种重要的生长因子,可以通过多种方式调节间充质干细胞的成骨分化。WANG等[13]研究者证明促红细胞生成素通过增加p38的磷酸化激活P38MAPK信号通路,进而促进矮小相关转录因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline 1phosphatase,ALP)和骨钙素(osteocalcin,OCN)的表达,从而促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。
牙本质蛋白1(dentin matrix protein 1,DMP1)中存在特异性调节骨骼的转录因子,表明其在调节矿化组织形成中发挥着重要作用。有研究者证明牙本质蛋白1可以使细胞质的EPK磷酸化,并使其从细胞质易位到细胞核,激活EPK信号通路,上调基质金属蛋白酶2、碱性磷酸酶和转化生长因子β1,调节牙周膜干细胞基因和表型的表达,进而促进其成骨分化[14]。胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5 (insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein 5,IGFBP5)在成骨细胞中的表达率高,且具有刺激细胞生长和增殖的作用。Wang等[15]研究证明胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5过度表达增加了牙周膜干细胞中磷酸化的 c-Jun N-末端激酶 (phosphorylation of c-jun N-terminal kinase,p-JNK)、磷酸化丝裂原活化蛋白激酶 1 和 2 (phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases 1 and 2,p-MEK1/2) 和磷酸化细胞外调节蛋白激酶 (phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase1/2,p-Erk1/2),进而激活相应信号通路,并发现胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5抑制剂可以抑制其成骨分化,反向证明胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5通过JNK和MEK/Erk信号通路促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。
由此可知,MAPK信号通路的4个亚族均参与牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,各类因子可分别通过增加细胞内p38,ERK,EPK及p-JNK的磷酸化,从而激活MAPK信号通路进而促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。大量研究证实MAPK信号通路在牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化中起着至关重要的作用,但对于各类因子激活MAPK信号通路的潜在机制仍还有待研究,明确激活牙周膜干细胞中MAPK信号通路的靶点,将为基于细胞的促进牙周再生的组织工程方法提供有价值的研究依据。
2.2.2 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt信号通路在牙周组织破坏、再生和重建中有重要作用[16],主要包括经典的Wnt/β-catenin通路和非经典的Wnt/PCP通路和Win/Ca2+通路[17]。目前已有研究表明Wnt通路的激活是干细胞成骨分化的关键[18-19]。
在高糖环境下,DNA甲基化会导致牙周膜干细胞的成骨能力减弱,LIU等[20]研究者发现体外应用DNA甲基转移酶抑制剂5-氮杂-2′-脱氧胞苷(5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine,5-aza-dC)可降低牙周膜干细胞中的DNA甲基化水平,逆转高糖环境下牙周膜干细胞成骨分化能力的减弱,而应用经典Wnt信号通路的有效拮抗剂Dickkopf-1能阻断5-aza-dC逆转成骨分化减弱的能力,提示激活经典Wnt信号通路对于临床治疗糖尿病患者牙槽骨流失具有指导意义。有研究发现山奈酚可通过上调磷酸化-Ser9的表达,抑制糖原合成酶激酶3β(glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)的磷酸化,从而增加β-连环蛋白进入细胞核,并与LEF作用最终诱导碱性磷酸酶、Runx2和骨γ-羧基谷氨酸蛋白等成骨相关基因的表达,促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[21]。JIA等[22]研究者证实下调抗分化非编码RNA(Anti-differentiation noncoding RNA,ANCR),细胞中GSK3β的mRNA表达被下调,β-连环蛋白的mRNA表达被上调,从而使GSK3β的表达水平受到抑制,导致胞质中β-连环蛋白积累并促进其核移位,进而激活Runx2的表达,最终促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。
以上研究表明经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在牙周膜干细胞成骨分化中起着重要作用, Wnt/β-catenin途径可以通过增强成骨细胞分化和抑制破骨细胞分化来维持牙周组织的稳态并抑制牙周炎的发展,该作用发挥的关键是β-连环蛋白在细胞核中的积累,而β-连环蛋白的表达可以进一步激活典型Wnt信号通路的靶基因Runx2,促进Runx2的表达,进而促进牙周膜干细胞成骨能力。虽然有大量研究证明许多因子可通过介导Wnt信号通路参与牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,但目前对于各类因子调控Wnt信号通路潜在机制的研究仍然匮乏。
2.2.3 Smad信号通路 Smad蛋白家族是一种细胞内信号传导蛋白,包括受体调控Smad蛋白(R-Smad)、共用Smad蛋白(co-Smad)、抑制性Smad蛋白(I-Smad)[23-24]。其在转化生长因子β超家族成员的信号转导中具有重要作用,与骨形态发生蛋白(骨形态发生蛋白是转化生长因子β超家族中最大一族,具有30余种亚型)关系最为密切[25]。骨形态发生蛋白与Ⅰ型受体和Ⅱ型受体形成的异源四聚体结合,从而激活Ⅱ型受体, 激活的Ⅱ型受体使Ⅰ型受体去磷酸化,可激活依赖Smad蛋白的经典骨形态发生蛋白信号通路,从而将骨形态发生蛋白与受体结合的信号由细胞表面转导至细胞核,调节目标基因的表达[26-27]。
脂多糖刺激可下调骨形态发生蛋白2(骨形态发生蛋白2是成骨分化中的关键诱导因子)、磷酸化Smad1和磷酸化Smad5的水平。FU等[28]研究者观察到fraxinellone治疗后骨形态发生蛋白2表达显著上调,骨形态发生蛋白2与异聚受体复合物结合,可促进Smad1和Smad5的磷酸化,形成Smad复合物,并转运至细胞核内调控转录,显著提高了碱性磷酸酶、成骨标记蛋白水平,从而促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。然而当细胞转染 shRNA-骨形态发生蛋白2-1,使骨形态发生蛋白2水平显著下降时,牙周膜干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化能力显著降低,同时碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Runx2、骨唾液蛋白、骨桥蛋白和胶原蛋白Ⅰ的表达均下调[28]。SACRAMENTO等[29]研究者证实5-aza-dC可显著提高骨形态发生蛋白2 羟甲基化水平,增加牙周膜干细胞中骨形态发生蛋白2基因的表达,骨形态发生蛋白2 信号分子可激活 Smad 蛋白的磷酸化和核转位,Smad蛋白与 Runx2 相互作用,导致碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素转录物的上调,从而促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。WU等[30]研究者证实循环拉伸应激(cyclic tensile stress,CTS)可促进碱性磷酸酶活性增加和成骨相关基因的表达;同时循环拉伸应激抑制miR-129-5p表达,促进牙周膜干细胞中骨形态发生蛋白2表达和p-Smad1/5水平,激活骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad途径,从而促进其成骨分化。
大量的研究表明,通过调控Smad信号通路可以抑制炎症并促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,而这样的作用主要是通过介导Smad蛋白的磷酸化和核转位完成,但大部分的研究缺乏动物实验,因此缺乏一定的安全性和适用性,提示牙周炎的治疗可以以激活Smad信号通路作为导向进行研究。
2.2.4 PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路 PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号传导主要由磷脂酰肌苷3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase,PI3Ks)、蛋白激酶B和哺乳动物的雷帕霉素靶点(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)3个核心成分构成[31-32]。目前已有研究证实该信号通路参与了牙周膜干细胞的增殖与成骨分化[33]。
搪瓷基质衍生物(enamel matrix derivative,EMD)是从猪牙中提取的细胞外基质衍生物,是可帮助牙周再生的生物材料。Li等[34]发现其显著上调了牙周膜干细胞中Akt和mTOR的磷酸化水平,同时提高了碱性磷酸酶的活性和Runx2和骨钙素的表达,表明EMD通过Akt/mTOR信号通路促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。川续断(dipsacus asper wall,DA)作为一种中国传统药材,其提取物DAE可以促进软骨增殖、骨折愈合。有研究发现DAE在最佳浓度下可以诱导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化,其主要是通过刺激内源性血管内皮生长因子的产生,由此激活PI3K/Akt通路,调节下游的内皮型一氧化氮合成酶或mTOR,并促进成骨分化标志物骨钙素的升高,从而增强牙周膜干细胞成骨能力[35]。
PI3K/AKT/mTOR 通路参与调节细胞增殖的过程,其中AKT是调节骨骼发育的关键因素,mTOR在调节细胞增殖和成骨分化具有重要作用。以上研究表明牙周膜干细胞中Akt、mTOR的磷酸化水平可影响其成骨能力,EMD和川续断等因子可激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路调节成骨相关基因的表达,促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化,表明PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路在牙周膜干细胞成骨分化中发挥着一定作用,但各类因子影响该通路介导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的具体机制还有待进一步研究。
2.2.5 Notch信号通路 是存在于相邻细胞间的配体-受体结合时的信号通路[36],经典Notch通路有一个与大多数通路不同的特征:缺乏信号级联放大[37]。该通路对牙齿的相关组织再生和成骨分化、牙齿硬组织钙化等方面起重要作用[38]。
OSATHANON等[39]发现Jagged-1作为Notch的配体可以调节细胞中TWIST1和TWIST2基因的表达,从而使成骨分化的负调节剂TWIST水平降低,而其水平降低可促进成骨基因的表达,最终促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,提示Jagged-1可作为指导牙周组织再生的再生膜。机械应力刺激可以促进牙槽骨组织再生,有研究进一步探讨了其机制表明机械牵张应力促进Piezo1蛋白的表达,同时使更多的Ca2+在通过Piezo1蛋白离子通道进入细胞内作为第二信使,促进Notch1受体的表达来激活Notch信号通路,从而促进碱性磷酸酶、Runx2及骨钙素和骨涎蛋白等成骨基因的表达,最终诱导牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[40]。表明激活Notch信号通路促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化可能与Piezo1蛋白的表达具有一定关系,因此作者设想牙周炎的治疗可以Piezo1蛋白作为靶点进而促进牙周膜干细胞在重建牙周组织方面的作用。
以上研究均表明Notch通路可以调节牙周膜干细胞的生物学行为,也就是说该通路可以通过调节牙周膜干细胞的增殖以及成骨分化的能力,进而促进成骨相关物质的表达用于治疗牙周炎疾病中牙槽骨缺失,另外可以Notch配体作为靶点调节相关成骨基因的表达,从而运用于牙槽骨丧失疾病的治疗,增加了某些物质用于牙周炎治疗的可能性,为牙周再生的基础研究和临床运用提供新思路。目前虽然很多研究也证明了此观点,但是其具体机制仍有待进一步研究。
2.2.6 Hippo信号通路 此通路不依赖配体-受体传导,其上游信号多样,机械应力、细胞极性等均可影响上游通路[41-42]。目前已有文献表明河马途径在牙周组织再生方面的作用显著[43]。
1α,25-二羟基维生素D3(1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3,1,25-D3)是一种活性维生素D,主要通过与其核维生素D受体结合来发挥作用,大量研究表明其对促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化具有重要作用。有研究就其成骨诱导机制进行实验,发现1,25-D3上调了TAZ(TAZ为河马途径的核心,是成骨分化的关键)的蛋白质水平和碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素这类成骨标记物[44]。有研究报告在α-降钙素基因相关肽(calcitonin gene related peptide,αCGRP)转染的牙周膜干细胞中,作为河马途径的下游效应器YAP的表达增加,相关成骨基因(碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、骨涎蛋白和Runx)表达也上调,由此得出αCGRP介导的成骨作用与河马途径有关[45]。
以上研究表明,YAP和TAZ作为河马途径的典型效应器,可以对各种信号作出反应。激活河马途径,上调YAP和TAZ的表达水平,可以调控下游基因的表达,促进牙周膜干细胞成骨表型的表达,从而阻止牙周炎的骨吸收。表明河马信号通路在调控牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化及增殖中发挥重要作用,提示河马通路在治疗牙周炎中骨缺失方面有潜在利用价值,但该通路上游信号易受多种因素的影响且难以控制,还需进一步研究用于牙周组织再生的潜在机制,并进行综合评估。因此,进一步深入河马信号通路对牙周膜干细胞生物学功能的研究,可在细胞层面为修复牙周支持组织缺失提供新思路。
2.2.7 Hedgehog信号通路 哺乳动物的Hedgehog信号通路较复杂,主要涉及以配体命名的Shh,Dhh和Ihh通路[46]。近年来有学者研究得出Hh信号通过参与胶质细胞的分化促进成骨,且能和骨形态发生蛋白相互作用促进牙周再生[47]。
有研究表明22(S)-羟基胆固醇和20(S)-羟基胆固醇(SS)的特异性氧化甾醇组合可增加Hh受体Smo和转录因子Gli1的蛋白质水平,以激活Hh通路,导致成骨相关标记物水平升高,从而促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[48],而使用Smo抑制剂22-NHC处理牙周膜干细胞,则抑制了碱性磷酸酶的活性以及骨钙素等的mRNA和蛋白质的表达。表明Hh信号分子的表达增加,将提高牙周膜干细胞成骨相关基因、基质矿化的水平,进而增强其成骨分化。
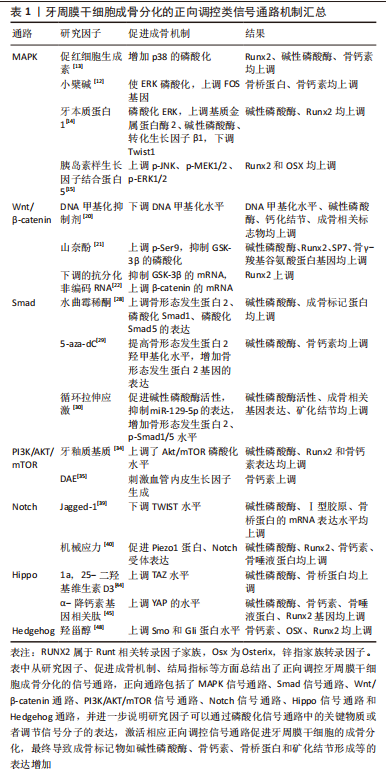
文章总结了牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的正向调控类信号通路机制研究进展,见表1。
以上研究表明Hedgehog信号通路介导了牙周膜干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,但该通路涉及3个通路,各信号分子之间的表达也具有特异性,比如Shh主要在釉质细胞表达,可以参与牙齿的形成和发育,而目前并没有相关研究说明是否3个通路都参与了诱导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的机制,还需要进一步研究阐明。
2.3 牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的负向调控类信号通路 负向调控即为牙周膜干细胞接受到外界刺激后,可激活相应的信号通路,进而可抑制牙周膜干细胞成骨相关基因和蛋白的表达,抑制牙周膜干细胞成骨分化,导致成骨丧失。负向调控类信号通路较为特殊,从该综述纳入的研究来看,已知的通路仅有核转录因子κB信号通路,见图4。
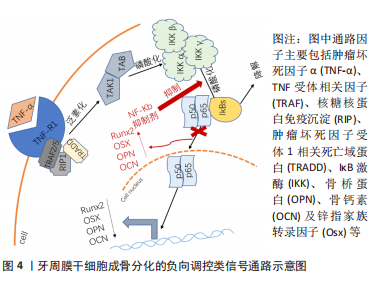
配体肿瘤坏死因子α与牙周膜干细胞表面相应的受体结合后形成TRFRs复合物,TRAF通过泛素化介导激酶TAK1和TAB的活化,这些激酶进一步磷酸化下游IκB激酶(IKK),IKK可以将IκB磷酸化,IκB被磷酸化后发生泛素化降解,并释放p50/p65复合物转移到细胞核内调控转录,而发生核转位的p50/p65复合物会使成骨标记物表达降低,导致骨丧失。因此使用核转录因子κB抑制剂阻断了IκB的磷酸化就可以阻止p50/p65复合物的核转位,从而可以促进成骨标记物骨钙素和骨桥蛋白等的表达,最终起到促进成骨的作用。
核转录因子κB 通路在细胞增殖分化、机体防御、损伤和应激反应中发挥重要作用[49]。核转录因子κB信号通路是由IKK激活,IKK是由两个催化亚基 (IKKα、IKKβ) 和一个调节亚基 (IKKγ) 构成;激活的IKK将IκB磷酸化, 磷酸化后的IκB被泛素连接酶选择性泛素化后降解,受IκB抑制的核转录因子κB被释放出来, 并快速转移到细胞核内,诱导目标基因的表达[50-51]。核转录因子κB通路的激活可能会影响成骨细胞的形成而有助于牙周炎的发展[52]。
已有研究发现在牙周炎的发生中,活化的T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞大量表达核转录因子κB配体的受体激活剂,并诱导破骨细胞的骨吸收;此外核转录因子κB还可调节炎症,抑制牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[53]。因此,通过介导核转录因子κB信号通路进而调节牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化不失为一种治疗牙周炎的方法。有研究发现低强度脉冲超声波可抑制核转录因子κB通路,并且随着低强度脉冲超声波强度的增强,牙周膜干细胞的细胞质中IκBα和p65增加,p-IκBα水平下降,同时在低强度脉冲超声波辐照的牙周膜干细胞中可以观察到成骨相关基因、矿化结节、碱性磷酸酶活性的增强,从而增强了牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力[54]。肿瘤坏死因子α水平升高可激活核转录因子κB信号通路从而对干细胞的成骨分化产生负性调控,有研究发现Quercetin显著减轻了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的对牙周膜干细胞中成骨相关基因和蛋白质、碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化基质的抑制,进一步研究其机制发现Quercetin显著抑制了牙周膜干细胞中核转录因子κB信号通路相关蛋白IκBα和p65的磷酸化,该通路下游分子NLRP3的水平也下调(其中NLRPL3激活可抑制牙周膜干细胞的成骨),表明Quercetin可通过抑制核转录因子κB通路逆转肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的牙周膜干细胞的成骨抑制[55]。
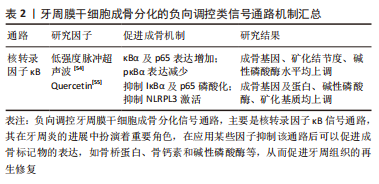
文章总结了牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的负向调控类信号通路机制进展,见表2。
以上研究表明核转录因子κB信号通路在牙周膜干细胞成骨分化中起着重要作用,但该通路与大多数信号通路存在显著差异,对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化起负向调控作用。可通过应用某些因子抑制IκBα的磷酸化,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进一步阻碍p65发生核转位,从而逆转成骨丧失。虽然目前该通路在许多研究中已经被证实可以参与炎症和牙周组织再生,但综合考虑有效性及安全性,仍需要进一步深入研究。
2.4 牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的多途径并行信号调节通路 牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化十分复杂,不仅仅只存在独立信号通路的调控,各信号通路之间也存在着一定的协同作用,牙周膜干细胞中可以有多条信号通路同时激活,共同促进其成骨分化,如Wnt信号通路、ETR信号通路和MAPK信号通路之间的协同作用,MAPK信号通路和骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad信号通路之间的协同作用,Wnt信号通路和核转录因子κB信号通路的共同作用等,见图5。
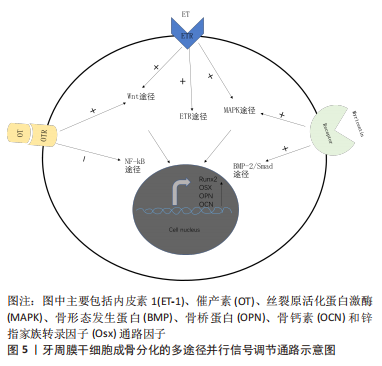
某些因子可以通过多种信号通路联合作用促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,催产素与细胞表面的受体结合后可以激活Wnt信号通路和抑制核转录因子κB信号通路,内皮素与细胞表面受体结合可激活Wnt信号通路、ETR信号通路和MAPK信号通路,Myricetin与牙周膜干细胞表面的受体结合后可以激活MAPK信号通路和骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad信号通路,促进了牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,使细胞内的成骨标记物表达有所增加,如骨桥蛋白和骨钙素等。
2.4.1 ETR,MAPK和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 内皮素1与牙周炎有关,并参与细胞因子的调节。有研究者对内皮素1治疗后的牙周膜干细胞进行碱性磷酸酶染色,发现碱性磷酸酶活性增加;通过评估与成骨相关的蛋白:骨钙素和Ⅰ型胶原表达的变化,观察到骨钙素和Ⅰ型胶原的mRNA水平随着内皮素1的暴露而逐渐增加,明确了内皮素1治疗可促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。通过进一步研究牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的机制,研究者在内皮素1治疗后,提取牙周膜干细胞中的mRNA和蛋白质,可观察到ETRA mRNA和蛋白表达水平随着治疗时间的增加而增加,表明内皮素1可通过ETR途径促进牙周膜干细胞的分化。与此同时,研究者还发现Wnt信号通路中关键物质Axin、APC、β-catenin和TCF/LEF的mRNA水平上调,p-GSK3β下调,表明Wnt/β-catenin途径的激活与其成骨分化相关。使用Western Blot分析还发现暴露于内皮素1的牙周膜干细胞中p-ERK1/2、p-JNK和p-p38的水平显著增加了,说明p38和ERK1/2 MAPK也参与了ET-1诱导的牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[56]。
2.4.2 骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad和ERK/JNK/p38 MAPK信号通路 杨梅酮是一种类黄酮,据报道它具有各种药理作用,如抗炎、抗氧化和抗癌活性,并且可以促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化。有研究者研究了杨梅酮增加牙周膜干细胞成骨分化潜能及其潜在的分子机制,发现杨梅酮通过上调骨形态发生蛋白2,从而诱导骨形态发生蛋白受体IB型Smad-1/5/9的表达。同时还增强了细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、c-Jun N端激酶(JNK)、p38有丝分裂原激活蛋白激酶(MAPK)和Smads的磷酸化,从而显著增加了牙周膜干细胞中的碱性磷酸酶活性和茜素红矿化活性。这些结果表明,杨梅酮可通过骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad和ERK/JNK/p38 MAPK途径上调碱性磷酸酶活性和促进成骨相关基因的表达来增强牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[57]。
2.4.3 ERK和AKT信号通路 激素水平在牙周组织丧失,尤其是在牙槽骨的丧失中发挥着重要作用[58]。催产素(Oxytocin,OT)与牙周膜干细胞上表达的催产素受体结合形成复合物并转移到细胞核,通过增加ERK和AKT的磷酸化,进而通过ERK通路和AKT通路增加成骨标志物的基因以及成骨标志物的蛋白质表达如碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素及骨桥蛋白等,参与骨骼的合成与代谢,从而在牙周膜干细胞成骨分化中发挥着重要作用。表明催产素可通过ERK和AKT信号通路诱导牙周膜干细胞分化为成骨表型,促进其成骨分化[59]。
2.4.4 核转录因子κB和Wnt信号通路 已有大量研究证明肠促胰岛素类似物(exendin-4,Ex-4)具有抗炎和促进骨骼再生能力。有研究发现Ex-4降低了牙周膜干细胞中IκBα和p-IκBα的表达,抑制了核转录因子κB/p65的核易位,并通过与脂多糖联合处理后,使β-连环蛋白在细胞核中的表达减少,从而提高了Runx、碱性磷酸酶等的水平,这些数据表明,Ex-4通过调节核转录因子κB和Wnt信号传导,促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[60]。
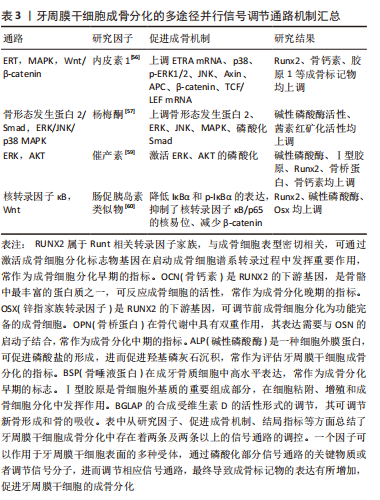
文章总结了牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的多途径并行信号调节通路机制研究进展,见表3。
综上所述,牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的机制十分复杂,涉及多种信号通路,目前大多数研究是针对单条信号通路对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响,但也有部分研究发现某些因子在调控牙周膜干细胞成骨分化过程中存在着2条及2条以上信号通路关键物质的mRNA和蛋白质的改变,说明牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的过程中可能涉及多条信号通路的协同作用,如MAPK信号通路和Smad信号通路、MAPK信号通路和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路等,由此说明在牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化中各条信号通路并非孤立存在,它们之间具有一定的交互作用,但目前并没有相关研究说明其中潜在的机制,由此也为进一步研究提供了新的思路。