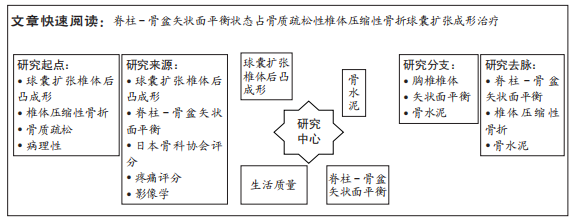
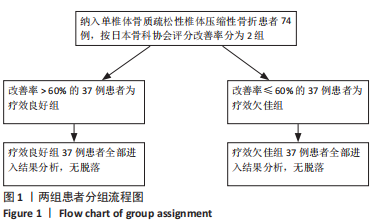
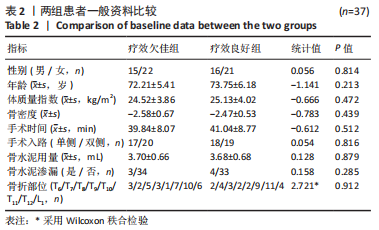
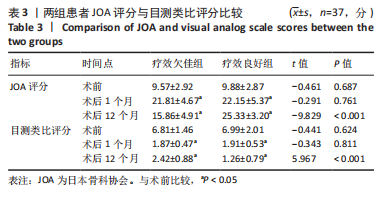
[1] LEI F, HE W, TIAN X, et al. Prophylactic Percutaneous Kyphoplasty Treatment for Nonfractured Vertebral Bodies in Thoracolumbar for Osteoporotic Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8593516.
[2] KYRIAKOU C, MOLLOY S, VRIONIS F, et al. The role of cement augmentation with percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures in multiple myeloma: a consensus statement from the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG). Blood Cancer J. 2019;9(3):27.
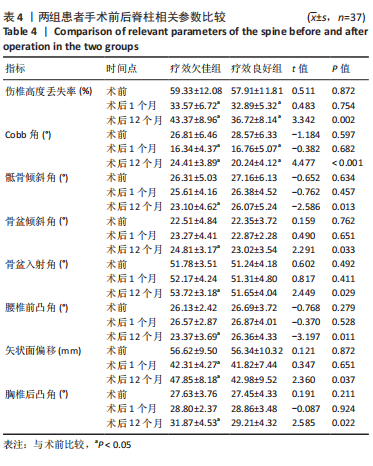
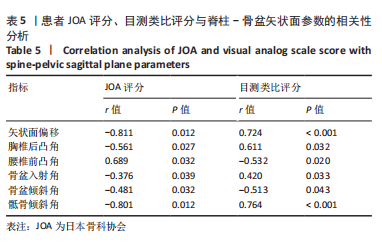
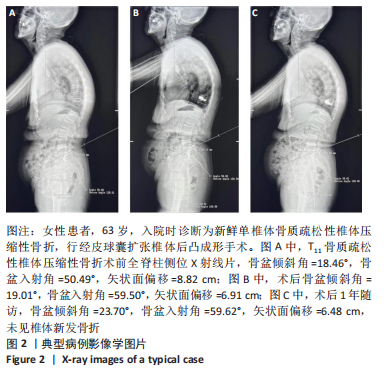
[3] 李伟, 赵立勇, 杨东. 脊柱骨盆矢状面平衡参数对老年单节段骨质疏松压缩性骨折行PKP术后继发椎体骨折的影响[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2019,21(6):48-50.
[4] 李耿, 欧阳智华, 于小华. 脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡状态对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折PVP术后继发骨折的影响[J]. 中国烧伤创疡杂志,2020,32(4):273-275.
[5] PARK EJ, LEE HJ, JANG MG, et al. A novel vertebroplasty technique using a larger-diameter needle for thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(22):e26174.
[6] LU W, WANG L, XIE C, et al. Analysis of percutaneous kyphoplasty or short-segmental fixation combined with vertebroplasty in the treatment of Kummell disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):311.
[7] 李伟, 赵立勇, 杨东. 脊柱骨盆矢状面平衡参数对老年单节段骨质疏松压缩性骨折行PKP术后继发椎体骨折的影响[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2019,21(6):442-444
[8] 王喜安, 杨六中, 何秉辉, 等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折PKP术后脊柱-骨盆矢状位失平衡对继发骨折、生存质量的影响[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2020,22(10):733-737.
[9] YILMAZ A, ÇAKIR M, YÜCETAŞ CŞ, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty: Is Bilateral Approach Necessary? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(14): 977-983.
[10] TAN G, LI F, ZHOU D, et al Unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(33):e11968.
[11] 陈新军, 朱旭, 赵刘军. PKP治疗骨质疏松椎体骨折矢状面形态变化的X线研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2018,39(13):21-23.
[12] KIM SK, CHUNG JY, PARK YJ, et al. Modified Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):388-395.
[13] BUCHBINDER R, JOHNSTON RV, RISCHIN KJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;4(4):CD006349.
[14] 陶文生,王建伟,郭安丰.骨水泥填充剂量对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折行PKP手术疗效的影响研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(2):73-75.
[15] COLLINET A, CHARLES YP, NTILIKINA Y, et al. Analysis of intervertebral discs adjacent to thoracolumbar A3 fractures treated by percutaneous instrumentation and kyphoplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020; 106(6):1221-1226.
[16] NIKOOBAKHT M, GERSZTEN PC, SHOJAEI SF, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a single-center analysis of pain and quality of life outcomes. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):166-169.
[17] COHEN L, PAPPAS E, REFSHAUGE K, et al. Associations between potentially modifiable clinical factors and sagittal balance of the spine in older adults from the general population. Spine Deformity. 2021; 10(2):433-441.
[18] CEJUDO A, CENTENERA-CENTENERA JM, SANTONJA-MEDINA F. The Potential Role of Hamstring Extensibility on Sagittal Pelvic Tilt, Sagittal Spinal Curves and Recurrent Low Back Pain in Team Sports Players: A Gender Perspective Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(16):8654.
[19] ARNOLD MJ, KEUNG JJ, MCCARRAGHER B. Interventional Radiology: Indications and Best Practices. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(9):547-556.
[20] ZHANG Y, MANDELLI F, MÜNDERMANN A, et al. Association between fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscle, sagittal spinopelvic alignment and stenosis grade in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. N Am Spine Soc J (NASSJ). 2021;5(1):100054.
[21] BURKE CJ, SAMIM M, ALIZAI H, et al. Clinical feasibility of 2D dynamic sagittal HASTE flexion-extension imaging of the cervical spine for the assessment of spondylolisthesis and cervical cord impingement. Eur J Radiol. 2021;134(6):109447.
[22] 万广, 杨慧, 吴大鹏, 等.脊柱-骨盆参数对椎体成形术效果的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(16):1472-1476.
[23] CAO Z, WANG G, HUI W, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures improves spino-pelvic alignment and global sagittal balance maximally in the thoracolumbar region. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0228341.
[24] PHAN K, NAZARETH A, HUSSAIN AK, et al. Relationship between sagittal balance and adjacentsegment disease insurgical treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease: meta-analysis and implications for choice offusion technique. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(12):3774-3774.
[25] AZIMI P, YAZDANIAN T, BENZEL EC, et al. Global sagittal balance of spine in asymptomatic controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;154:93-108.
[26] ALIJANPOUR E, ABBASI A, NEEDHAM RA, et al. Spine and pelvis coordination variability in rowers with and without chronic low back pain during rowing. J Biomech. 2021;120(14):1-10.
[27] GRIFFONI C, LUKASSEN JNM, BABBI L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective randomized comparison. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1614-1620.
[28] SMORGICK Y, GRANEK T, MIROVSKY Y, et al. Routine sagittal whole-spine magnetic resonance imaging in finding incidental spine lesions. MAGMA. 2020;34(3):421-426.
[29] HE X, YANG F, REN E, et al. Trapezoidal Vertebral Body and Spine-Pelvis Sagittal Alignment in Patients with Lumber Spondylolisthesis. Medical Science Monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2020;26:e927747-1-e927747-9.
[30] PUMBERGER M, SCHITZ F, BÜRGER J, et al. Kyphoplasty Restores the Global Sagittal Balance of the Spine Independently from Pain Reduction. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):8894-8900. |