[1] FELDMAN EL, NAVE KA, JENSEN TS, et al. New horizons in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms, bioenergetics, and pain. Neuron. 2017;93(6):1296-1313.
[2] GONCALVES NP, VAEGTER CB, ANDERSEN H, et al. Schwann cell interactions with axons and microvessels in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(3):135-147.
[3] FELDMAN EL, CALLAGHAN BC, POP-BUSUI R, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):42.
[4] SLOAN G, SELVARAJAH D, TESFAYE S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(7):400-420.
[5] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843.
[6] ALAVI A, SIBBALD RG, MAYER D, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers: Part I. Pathophysiology and prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(1):1.e1-e18; quiz 19-20.
[7] MONTEIRO-SOARES M, RUSSELL D, BOYKO EJ, et al. Guidelines on the classification of diabetic foot ulcers (IWGDF 2019). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36 Suppl 1:e3273.
[8] PECORARO RE, REIBER GE, BURGESS EM. Pathways to diabetic limb amputation - basis for prevention. Diabetes Care. 1990;13(5):513-521.
[9] JEFFCOATE WJ, VILEIKYTE L, BOYKO EJ, et al. Current challenges and opportunities in the prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(4):645-652.
[10] ARMSTRONG DG, SWERDLOW MA, ARMSTRONG AA, et al. Five year mortality and direct costs of care for people with diabetic foot complications are comparable to cancer. J Foot Ankle Res. 2020;13(1):16.
[11] WILLIAMS DT, PRICE P, HARDING KG. Amputation and mortality in new-onset diabetic foot ulcers stratified by etiology. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(11):3199-3200.
[12] LAVERY LA, ASHRY HR, VANHOUTUM W, et al. Variation in the incidence and proportion at diabetes-related amputations in minorities. Diabetes Care. 1996;19(1):48-52.
[13] SUN Y, GAO Y, CHEN J, et al. Evidence mapping of recommendations on diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for diabetes foot: an international review of 22 guidelines. Metabolism. 2019;100:153956.
[14] MOORE Z, CARVILLE K, WEIR D, et al. Consensus document strategies to reduce practice variation in wound assessment and management. 2020.
[15] SCHULTZ GS, SIBBALD RG, FALANGA V, et al. Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair Regen. 2003;11(2):S1-S28.
[16] GUARRO G, COZZANI F, ROSSINI M, et al. The modified TIME-H scoring system, a versatile tool in wound management practice:a preliminary report. Acta Biomed. 2021;92(4):e2021226.
[17] ORLANDO G, BALDUCCI S, BAZZUCCHI I, et al. Neuromuscular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes:underlying mechanisms and effect of resistance training. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(1):40-50.
[18] ORLANDO G, REEVES ND, BOULTON AJM, et al. Sedentary behaviour is an independent predictor of diabetic foot ulcer development: an 8-year prospective study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021;177:108877.
[19] ARMSTRONG DG, BOULTON AJM, BUS SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. New Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367-2375.
[20] JEYAM A, MCGURNAGHAN SJ, BLACKBOURN LAK, et al. Diabetic neuropathy is a substantial burden in people with type 1 diabetes and is strongly associated with socioeconomic disadvantage: a population-representative study from scotland. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(4):734-742.
[21] ESTHER CL, BELEN O AA, ARANZAZU RM, et al. Foot deformities in patients with diabetic mellitus (with and without peripheral neuropathy). J Tissue Viability. 2021;30(3):346-351.
[22] MOLINES-BARROSO RJ, LAZARO-MARTINEZ JL, ARAGON-SANCHEZ FJ, et al. Forefoot ulcer risk is associated with foot type in patients with diabetes and neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;114:93-98.
[23] BUS SA. The role of pressure offloading on diabetic foot ulcer healing and prevention of recurrence. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138: 179S-187S.
[24] BUS SA, ARMSTRONG DG, GOODAY C, et al. Guidelines on offloading foot ulcers in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36 Suppl 1:e3274.
[25] WUKICH DK, ARMSTRONG DG, ATTINGER CE, et al. Inpatient management of diabetic foot disorders: a clinical guide. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(9):2862-2871.
[26] LEPANTALO M, APELQVIST J, SETACCI C, et al. Diabetic foot. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42:S60-S74.
[27] MASSON EA, HAY EM, STOCKLEY I, et al. Abnormal foot pressures alone may not cause ulceration. Diabetic Medicine. 1989;6(5):426-428.
[28] VEVES A, MURRAY HJ, YOUNG MJ, et al. The risk of foot ulceration in diabetic-patients with high foot pressure -a prospective-study. Diabetologia. 1992;35(7):660-663.
[29] KOUTAKIS P, WEISS DJ, MISERLIS D, et al. Oxidative damage in the gastrocnemius of patients with peripheral artery disease is myofiber type selective. Redox Biol. 2014;2:921-928.
[30] ROBBINS JL, JONES WS, DUSCHA BD, et al. Relationship between leg muscle capillary density and peak hyperemic blood flow with endurance capacity in peripheral artery disease. J Appl Physiol. 2011; 111(1):81-86.
[31] BUS SA, ARMSTRONG DG, VAN DEURSEN RW, et al. IWGDF guidance on footwear and offloading interventions to prevent and heal foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32:25-36.
[32] VAN NETTEN JJ, LAZZARINI PA, ARMSTRONG DG, et al. Diabetic Foot Australia guideline on footwear for people with diabetes. J Foot Ankle Res. 2018;11:2.
[33] LAVERY LA, LAFONTAINE J, HIGGINS KR, et al. Shear-reducing insoles to prevent foot ulceration in high-risk diabetic patients. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2012;25(11):519-524.
[34] RIZZO L, TEDESCHI A, FALLANI E, et al. Custom-made orthesis and shoes in a structured follow-up program reduces the incidence of neuropathic ulcers in high-risk diabetic foot patients. Int J Lower Extrem Wounds. 2012;11(1):59-64.
[35] SCIRE V, LEPORATI E, TEOBALDI L, et al. Effectiveness and safety of using podikon digital silicone padding in the primary prevention of neuropathic lesions in the forefoot of diabetic patients. J Am Podiat Med Assn. 2009;99(1):28-34.
[36] KILICOGLU OI, DEMIREL M, AKTAS S. New trends in the orthopaedic management of diabetic foot. Efort Open Rev. 2018;3(5):269-277.
[37] FAGLIA E, CLERICI G, CAMINITI M, et al. Feasibility and effectiveness of internal pedal amputation of phalanx or metatarsal head in diabetic patients with forefoot osteomyelitis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;51(5):593-598.
[38] YAMMINE K, ASSI C. Surgical offloading techniques should be used more often and earlier in treating forefoot diabetic ulcers: an evidence-based review. Int J Lower Extrem Wounds. 2020;19(2):112-119.
[39] MESHKIN DH, FAGOTHAMAN K, ARNESON J, et al. Plantar foot ulcer recurrence in neuropathic patients undergoing percutaneous tendo-achilles lengthening. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;59(6):1177-1180.
[40] TAMIR E, VIGLER M, AVISAR E, et al. Percutaneous tenotomy for the treatment of diabetic toe ulcers. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(1):38-43.
[41] TAMIR E, MCLAREN AM, GADGIL A, et al. Outpatient percutaneous flexor tenotomies for management of diabetic claw toe deformities with ulcers:a preliminary report. Canadian J Surg. 2008;51(1):41-44.
[42] CHAUDHRY V, RUSSELL J, BELZBERG A. Decompressive surgery of lower limbs for symmetrical diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008(3):CD006152.
[43] DELLON AL. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic neuropathy by surgical decompression of multiple peripheral nerves. Plastic Reconstr Surg. 1992;89(4):689-697; discussion 98-99.
[44] HINCHLIFFE RJ, BROWNRIGG JRW, APELQVIST J, et al. IWGDF guidance on the diagnosis, prognosis and management of peripheral artery disease in patients with foot ulcers in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32:37-44.
[45] WECK M, SLESACZECK T, PAETZOLD H, et al. Structured health care for subjects with diabetic foot ulcers results in a reduction of major amputation rates. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:45.
[46] CHAN P, STUART W, HINCHLIFFE R. New reporting standards are required to assess the impact of vascular intervention on patients with diabetic foot ulceration. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015;50(2):139-140.
[47] MILLS JL. Lower limb ischaemia in patients with diabetic foot ulcers and gangrene:recognition, anatomic patterns and revascularization strategies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32:239-245.
[48] 王江宁,高磊.糖尿病足慢性创面治疗的新进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(7):832-837.
[49] CHEN Y, KUANG X, ZHOU J, et al. Proximal tibial cortex transverse distraction facilitating healing and limb salvage in severe and recalcitrant diabetic foot ulcers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;478(4):1.
[50] 赵劲民,李刚.胫骨横向骨搬移技术治疗糖尿病足的专家共识(2020)[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(8):945-950.
[51] 刘杰,花奇凯,李山郎,等.骨膜牵张技术用于糖尿病足治疗的理论基础及临床结果验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5236-5241.
[52] CAVANAGH PR, LIPSKY BA, BRADBURY AW, et al. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1725-1735.
[53] 王斌,刘伟,霍永新,等.股-股动脉旁路移植联合胫骨横向骨搬移术治疗下肢动脉硬化闭塞症或合并糖尿病足[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(12):1576-1580.
[54] CHANG CH, HUANG CC, HSU H, et al. Editor’s choice - diabetic limb salvage with endovascular revascularisation and free tissue transfer:long-term follow up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57(4):527-536.
[55] DAYYA D, O’NEILL OJ, HUEDO-MEDINA TB, et al. Debridement of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0016.
[56] LIU JQ, GE YN, WANG Q, et al. Waterjet in bacterial clearance of diabetic lower extremity contaminated wounds: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2021. doi: 10.1177/15347346211024204.
[57] 陈小丽,郑焱玲,曹茂华,等.超声水刀清创系统辅助治疗糖尿病足部皮肤溃疡的观察[J].局解手术学杂志,2013,22(1):78-79.
[58] PAJARILLO C, SHERMAN RA, SHERIDAN R, et al. Health professionals’ perceptions of maggot debridement therapy. J Wound Care. 2021; 30(Sup9a):VIIi-VIIxi.
[59] CEROVSKY V, BEM R. Lucifensins, the insect defensins of biomedical importance:the story behind maggot therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2014; 7(3):251-264.
[60] EHYA REM, ZHANG H, QI BW, et al. Application and clinical effectiveness of antibiotic-loaded bone cement to promote soft tissue granulation in the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers complicated by osteomyelitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes Res. 2021; 2021:9911072.
[61] JI SZ, LIU XB, HUANG J, et al. Consensus on the application of negative pressure wound therapy of diabetic foot wounds. Burns Trauma. 2021; 9:tkab018.
[62] BORYS S, HOHENDORFF J, FRANKFURTER C, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy use in diabetic foot syndrome-from mechanisms of action to clinical practice. Eur J Clin Invest. 2019;49(4):e13067.
[63] ANDREWS KL, HOUDEK MT, KIEMELE LJ. Wound management of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: from the basics to regenerative medicine. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2015;39(1):29-39.
[64] SANTEMA TB, POYCK PPC, UBBINK DT. Skin grafting and tissue replacement for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2(2):CD011255.
[65] TZENG YS, DENG SC, WANG CH, et al. Treatment of nonhealing diabetic lower extremity ulcers with skin graft and autologous platelet gel: a case series. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:837620.
[66] GKOTSOULIAS E. Split thickness skin graft of the foot and ankle bolstered with negative pressure wound therapy in a diabetic population: the results of a retrospective review and review of the literature. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020;13(5):383-391.
[67] JEON H, KIM J, YEO H, et al. Treatment of diabetic foot ulcer using matriderm in comparison with a skin graft. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40(4): 403-408.
[68] BATTISTON B, CICLAMINI D, TANG JB. Compound or specially designed flaps in the lower extremities. Clin Plast Surg. 2020;47(4):535-546.
[69] KWON JG, CHO MJ, PAK CJ, et al. A retrospective case series on free flap reconstruction for ischemic diabetic foot: the nutrient flap further explained. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(6):1452-1461.
[70] O’CONNOR EJF, VESELY M, HOLT PJ, et al. A systematic review of free tissue transfer in the management of non-traumatic lower extremity wounds in patients with diabetes. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; 41(3):391-399.
[71] KOTHA VS, FAN KL, SCHWITZER JA, et al. Amputation versus free flap:long-term outcomes of microsurgical limb salvage and risk factors for amputation in the diabetic population. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021; 147(3):742-750.
[72] IBRAHIM A. IDF Clinical practice recommendation on the diabetic foot: a guide for healthcare professionals. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017; 127:285-287.
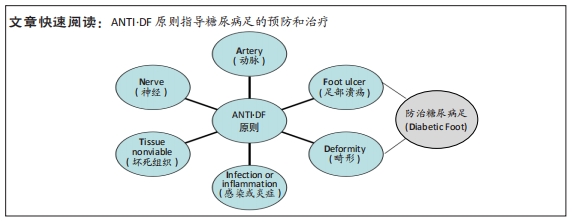
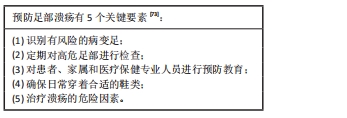
[73] SCHAPER NC, VAN NETTEN JJ, APELQVIST J, et al. Practical Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36 Suppl 1:e3266.
|