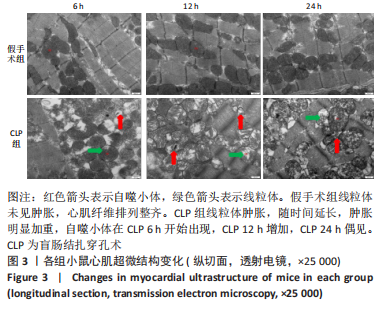
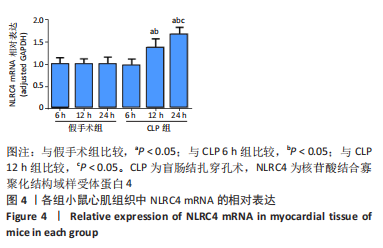
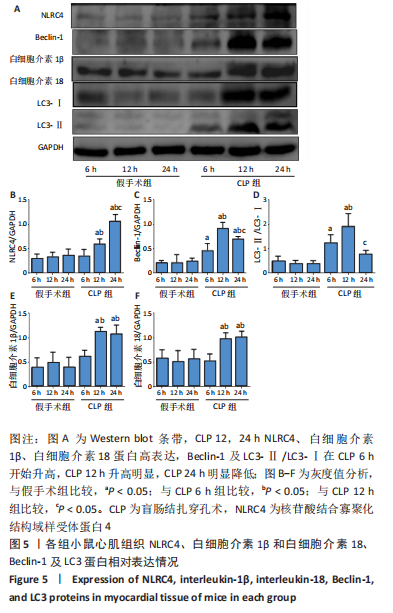
[1] SINGER M, DEUTSCHMAN CS, SEYMOUR CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801.
[2] 严静, 沈延飞. 脓毒症的诊断及治疗进展[J]. 浙江医学,2021,43(14): 1479-1482,1488.
[3] MORGAN RW, FITZGERALD JC, WEISS SL, et al. Sepsis-associated in-hospital cardiac arrest: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and potential therapies. J Crit Care. 2017;40:128-135.
[4] LIN H, WANG W, LEE M, et al. Current Status of Septic Cardiomyopathy: Basic Science and Clinical Progress. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:210.
[5] MARTIN L, DERWALL M, AL ZS, et al. The Septic Heart: Current Understanding of Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Chest. 2019;155(2):427-437.
[6] HOLLENBERG SM, SINGER M. Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18(6):424-434.
[7] YAO RQ, REN C, ZHENG LY, et al. Advances in Immune Monitoring Approaches for Sepsis-Induced Immunosuppression. Front Immunol. 2022;13:891024.
[8] BERGMANN CB, BECKMANN N, SALYER CE, et al. Lymphocyte Immunosuppression and Dysfunction Contributing to Persistent Inflammation, Immunosuppression, and Catabolism Syndrome (PICS). Shock. 2021;55(6):723-741.
[9] MIRA JC, GENTILE LF, MATHIAS BJ, et al. Sepsis Pathophysiology, Chronic Critical Illness, and Persistent Inflammation-Immunosuppression and Catabolism Syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(2):253-262.
[10] 杨贵芳,彭文,赵琴,等.心力衰竭免疫学机制及治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国循环杂志,2015,30(2):193-195.
[11] PIQUEREAU J, GODIN R, DESCHENES S, et al. Protective role of PARK2/Parkin in sepsis-induced cardiac contractile and mitochondrial dysfunction. Autophagy. 2013;9(11):1837-1851.
[12] WASYLUK W, NOWICKA-STAZKA P, ZWOLAK A. Heart Metabolism in Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy-Unusual Metabolic Dysfunction of the Heart. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(14):7598.
[13] WEN X, XIE B, YUAN S, et al. The “Self-Sacrifice” of ImmuneCells in Sepsis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:833479.
[14] BARDET J, LAVERDURE N, FUSARO M, et al. NLRC4 GOF Mutations, a Challenging Diagnosis from Neonatal Age to Adulthood. J Clin Med. 2021;10(19):4369.
[15] ZHANG X, CUI Y, DING X, et al. Analysis of mRNAlncRNA and mRNAlncRNA-pathway coexpression networks based on WGCNA in developing pediatric sepsis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):1457-1470.
[16] RITTIRSCH D, HUBER-LANG MS, FLIERL MA, et al. Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):31-36.
[17] ANTONUCCI E, FIACCADORI E, DONADELLO K, et al. Myocardial depression in sepsis: from pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment. J Crit Care. 2014;29(4):500-511.
[18] L’HEUREUX M, STERNBERG M, BRATH L, et al. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020; 22(5):35.
[19] BELTRAN-GARCIA J, OSCA-VERDEGAL R, ROMA-MATEO C, et al. Epigenetic biomarkers for human sepsis and septic shock: insights from immunosuppression. Epigenomics. 2020;12(7):617-646.
[20] HALADE GV, LEE DH. Inflammation and resolution signaling in cardiac repair and heart failure. EBio Medicine. 2022;79:103992.
[21] LEE H, LIM JM, LEE J, et al. Positive Role of Delta Neutrophil Index (DNI) as a Prodiagnostic Marker in Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Sepsis Murine Model. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(3):369.
[22] SUNDARAM B, KANNEGANTI TD. Advances in Understanding Activation and Function of the NLRC4 Inflammasome. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1048.
[23] KANNEGANTI TD. Intracellular innate immune receptors: Life inside the cell. Immunol Rev. 2020;297(1):5-12.
[24] DINARELLO CA, SIMON A, VAN DER MEER JW. Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(8):633-652.
[25] AINSCOUGH JS, GERBERICK GF, KIMBER I, et al. Interleukin-1beta Processing Is Dependent on a Calcium-mediated Interaction with Calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(52):31151-31161.
[26] VECCHIE A, BONAVENTURA A, TOLDO S, et al. IL-18 and infections: Is there a role for targeted therapies? J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(3):1638-1657.
[27] OKUHARA Y, YOKOE S, IWASAKU T, et al. Interleukin-18 gene deletion protects against sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting PP2A activity. Int J Cardiol. 2017;243:396-403.
[28] LIU G, LIU Y, TAO J, et al. [Differential gene expression and bioinformatics analysis in sepsis secondary to pneumonia]. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022;34(2):138-144.
[29] WANG SS, YAN CS, LUO JM. NLRC4 gene silencing-dependent blockade of NOD-like receptor pathway inhibits inflammation, reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis of dendritic cells in mice with septic shock. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(1):1440-1457.
[30] VANDEN BT, DEMON D, BOGAERT P, et al. Simultaneous targeting of IL-1 and IL-18 is required for protection against inflammatory and septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189(3):282-291.
[31] SMEDING L, PLOTZ FB, GROENEVELD AB, et al. Structural changes of the heart during severe sepsis or septic shock. Shock. 2012;37(5):449-456.
[32] CHEN P, AN Q, HUANG Y, et al. Prevention of endotoxin-induced cardiomyopathy using sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate: Involvement of augmented autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome suppression. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;909:174438.
[33] HUANG Z, ZHANG H, FU X, et al. Autophagy-driven neutrophil extracellular traps: The dawn of sepsis. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;234:153896.
[34] HSIAO HW, TSAI KL, WANG LF, et al. The decline of autophagy contributes to proximal tubular dysfunction during sepsis. Shock. 2012; 37(3):289-296.
[35] HOTCHKISS RS, TINSLEY KW, SWANSON PE, et al. Depletion of dendritic cells, but not macrophages, in patients with sepsis. J Immunol. 2002; 168(5):2493-2550.
[36] SCHMID D, PYPAERT M, MUNZ C. Antigen-loading compartments for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules continuously receive input from autophagosomes. Immunity. 2007;26(1):79-92.
[37] HOHLSTEIN P, GUSSEN H, BARTNECK M, et al. Prognostic Relevance of Altered Lymphocyte Subpopulations in Critical Illness and Sepsis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(3):353.
[38] WATANABE E, MUENZER JT, HAWKINS WG, et al. Sepsis induces extensive autophagic vacuolization in hepatocytes: a clinical and laboratory-based study. Lab Invest. 2009;89(5):549-561.
[39] JABIR MS, RITCHIE ND, LI D, et al. Caspase-1 cleavage of the TLR adaptor TRIF inhibits autophagy and beta-interferon production during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15(2): 214-227.
[40] PU Q, GAN C, LI R, et al. Atg7 Deficiency Intensifies Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis in Pseudomonas Sepsis. J Immunol. 2017; 198(8):3205-3213.
|