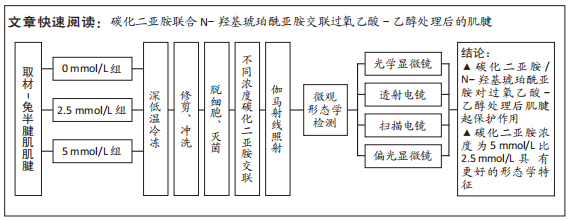
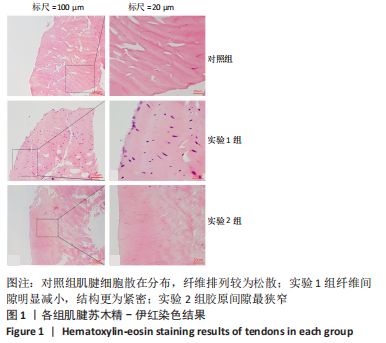
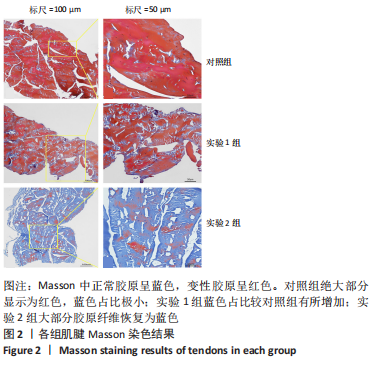
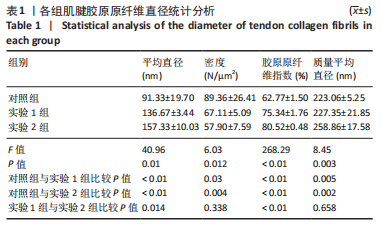
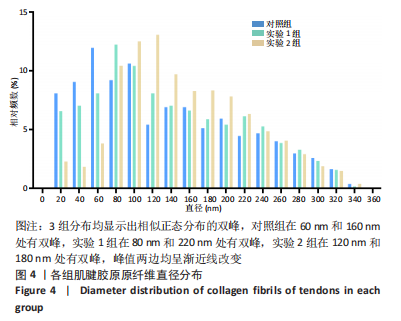
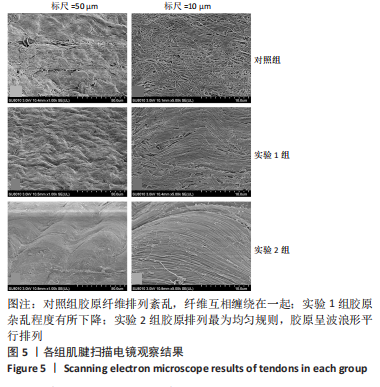
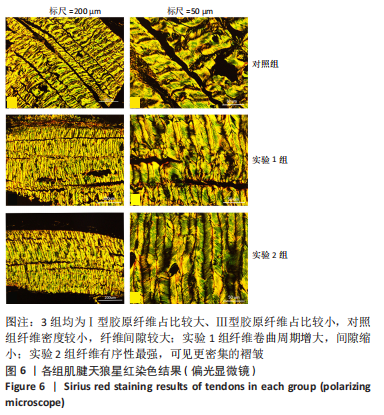
[1] SUAREZ LS, RICHMOND JC. Overview of procurement, processing, and sterilization of soft tissue allografts for sports medicine. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2007;15(3):106-113.
[2] EASTLUND T. Bacterial infection transmitted by human tissue allograft transplantation. Cell Tissue Bank. 2006;7(3):147-166.
[3] ZHOU M, ZHANG N, LIU X, et al. Tendon allograft sterilized by peracetic acid/ethanol combined with gamma irradiation. J Orthop Sci. 2014; 19(4):627-636.
[4] FARAGO D, KOZMA B, KISS RM. Different sterilization and disinfection methods used for human tendons - a systematic review using mechanical properties to evaluate tendon allografts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):404.
[5] YANG X, FENG J, WANG F, et al. Irradiation sterilization used for allogenetic tendon: a literature review of current concept. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):129-139.
[6] XU MY, ZHANG HR, ZHANG L, et al. Peracetic Acid-Ethanol Processed Human Tendon Allograft: A Morphological, Biochemical, and Biomechanical Study In Vitro. Orthop Surg. 2021; doi:10.111/os.13030.
[7] HU W, WANG Z, XIAO Y, et al. Advances in crosslinking strategies of biomedical hydrogels. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):843-855.
[8] KEW SJ, GWYNNE JH, ENEA D, et al. Synthetic collagen fascicles for the regeneration of tendon tissue. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(10):3723-3731.
[9] ENEA D, GWYNNE J, KEW S, et al. Collagen fibre implant for tendon and ligament biological augmentation. In vivo study in an ovine model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1783-1793.
[10] SHEPHERD JH, GHOSE S, KEW SJ, et al. Effect of fiber crosslinking on collagen-fiber reinforced collagen-chondroitin-6-sulfate materials for regenerating load-bearing soft tissues. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013; 101(1):176-184.
[11] ULUBAYRAM K, AKSU E, GURHAN SI, et al. Cytotoxicity evaluation of gelatin sponges prepared with different cross-linking agents. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2002;13(11):1203-1219.
[12] OLDE DAMINK LH, DIJKSTRA PJ, VAN LUYN MJ, et al. Cross-linking of dermal sheep collagen using a water-soluble carbodiimide. Biomaterials. 1996;17(8):765-773.
[13] OLDE DAMINK LH, DIJKSTRA PJ, VAN LUYN MJ, et al. In vitro degradation of dermal sheep collagen cross-linked using a water-soluble carbodiimide. Biomaterials. 1996;17(7):679-684.
[14] ZEEMAN R, DIJKSTRA PJ, VAN WACHEM PB, et al. Successive epoxy and carbodiimide cross-linking of dermal sheep collagen. Biomaterials. 1999;20(10):921-931.
[15] AHN JI, KUFFOVA L, MERRETT K, et al. Crosslinked collagen hydrogels as corneal implants: effects of sterically bulky vs. non-bulky carbodiimides as crosslinkers. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(8):7796-7805.
[16] CAI J, ZHANG L, CHEN J, et al. Silk fibroin coating through EDC/NHS crosslink is an effective method to promote graft remodeling of a polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligament. J Biomater Appl. 2019; 33(10):1407-1414.
[17] WANG Y, WANG X, SHANG J, et al. Repairing the ruptured annular fibrosus by using type I collagen combined with citric acid, EDC and NHS: an in vivo study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3):884-893.
[18] GOODARZI H, JADIDI K, POURMOTABED S, et al. Preparation and in vitro characterization of cross-linked collagen-gelatin hydrogel using EDC/NHS for corneal tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:620-632.
[19] SCHEFFEL DL, BIANCHI L, SOARES DG, et al. Transdentinal cytotoxicity of carbodiimide (EDC) and glutaraldehyde on odontoblast-like cells. Oper Dent. 2015;40(1):44-54.
[20] AHMAD Z, SHEPHERD JH, SHEPHERD DV, et al. Effect of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide concentrations on the mechanical and biological characteristics of cross-linked collagen fibres for tendon repair. Regen Biomater. 2015; 2(2):77-85.
[21] YEH WL, LIN SS, YUAN LJ, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on tendon graft and tendon-bone integration in bone tunnel: biochemical and histological analysis in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2007; 25(5):636-645.
[22] SCHINDELIN J, ARGANDA-CARRERAS I, FRISE E, et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9(7): 676-682.
[23] SUZUKI D, OTSUBO H, WATANABE T, et al. Ultrastructure of the three anterior cruciate ligament bundles. Clin Anat. 2015; 28(7): 910-916.
[24] JONES PN. On collagen fibril diameter distributions. Connect Tissue Res. 1991;26(1-2):11-21.
[25] SETO A, GATT CJ, JR., DUNN MG. Improved tendon radioprotection by combined cross-linking and free radical scavenging. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(11):2994-3001.
[26] CARUSO AB, DUNN MG. Functional evaluation of collagen fiber scaffolds for ACL reconstruction: cyclic loading in proteolytic enzyme solutions. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;69(1):164-171.
[27] HU Y, LIU L, DAN W, et al. Synergistic effect of carbodiimide and dehydrothermal crosslinking on acellular dermal matrix. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;55:221-230.
[28] POWELL HM, BOYCE ST. EDC cross-linking improves skin substitute strength and stability. Biomaterials. 2006;27(34):5821-5827.
[29] LOMAS RJ, JENNINGS LM, FISHER J, et al. Effects of a peracetic acid disinfection protocol on the biocompatibility and biomechanical properties of human patellar tendon allografts. Cell Tissue Bank. 2004; 5(3):149-160.
[30] HUANG YZ, WANG JJ, HUANG YC, et al. Organic composite-mediated surface coating of human acellular bone matrix with strontium. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;84:12-20.
[31] XIAO D, ZHANG Y, WANG R, et al. Emodin alleviates cardiac fibrosis by suppressing activation of cardiac fibroblasts via upregulating metastasis associated protein 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019;9(4):724-733.
[32] LI N, ZHOU L, XIE W, et al. Alkaline phosphatase enzyme-induced biomineralization of chitosan scaffolds with enhanced osteogenesis for bone tissue engineering. Chemi Eng. 2019;371:618-630.
[33] EDWARDS JH, HERBERT A, JONES GL, et al. The effects of irradiation on the biological and biomechanical properties of an acellular porcine superflexor tendon graft for cruciate ligament repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(8):2477-2486.
[34] BIRCH HL, THORPE CT, RUMIAN AP. Specialisation of extracellular matrix for function in tendons and ligaments. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013;3(1):12-22.
[35] LEE AH, ELLIOTT DM. Comparative multi-scale hierarchical structure of the tail, plantaris, and Achilles tendons in the rat. J Anat. 2019;234(2): 252-262.
[36] NICHOLLS SP, GATHERCOLE LJ, SHAH JS. Morphology of human palmaris longus tendon. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984;43(3):477-482.
[37] CUI J, NING LJ, YAO X, et al. Influence of the integrity of tendinous membrane and fascicle on biomechanical characteristics of tendon-derived scaffolds. Biomed Mater. 2020;16(1):015029.
[38] LI Y, WU B, QIU Z, et al. [A correlation study between the Mohawk expression level and the collagen fiber diameter of hamstring tendon graft after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(9):1095-1101.
[39] TAKAHASHI N, KAMETANI K, OTA R, et al. Three-dimensional ultrastructure reconstruction of tendinous components at the bifurcation of the bovine superficial digital flexor tendon using array and STEM tomographies. J Anat. 2021;238(1):63-72.
[40] SCHMIDT EC, CHIN M, AOYAMA JT, et al. Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Pediatric Anterior Cruciate Ligaments and Autograft Tendons Used for Reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(1):2325967118821667.
|