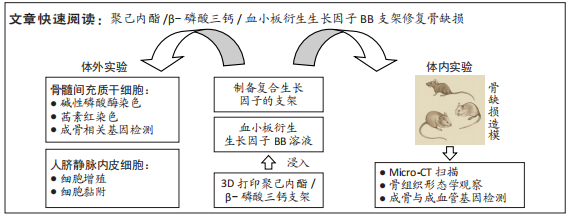
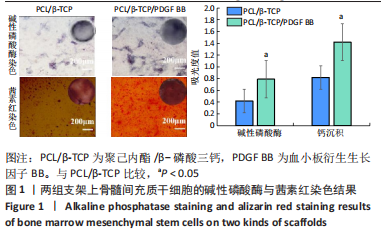
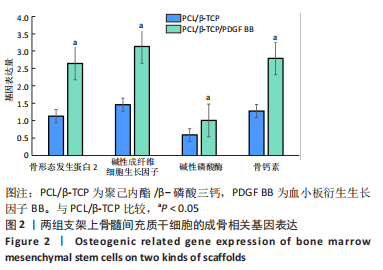
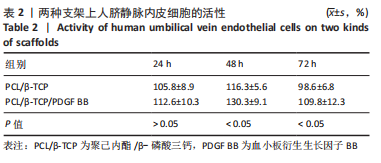
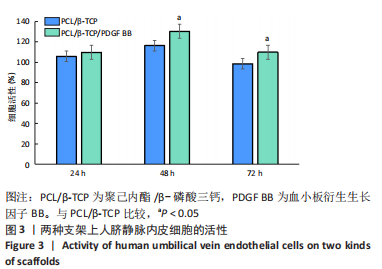
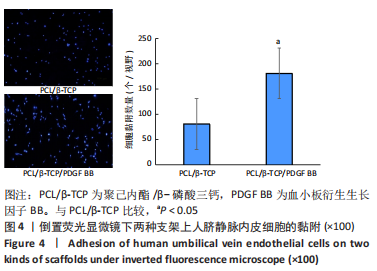
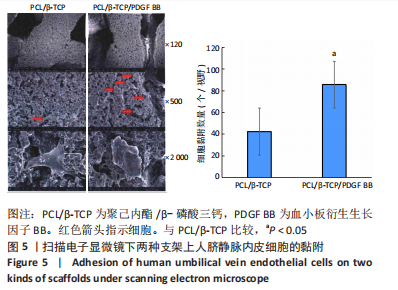
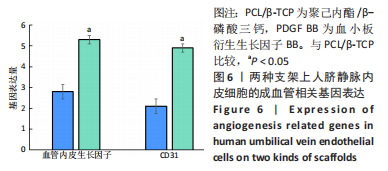
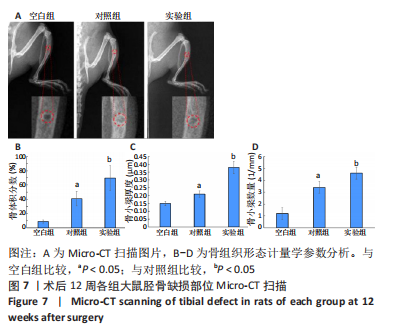
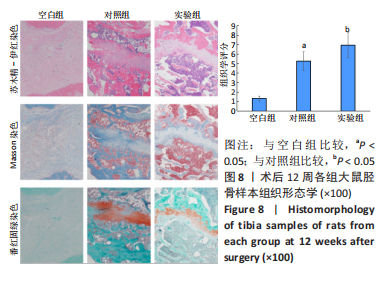
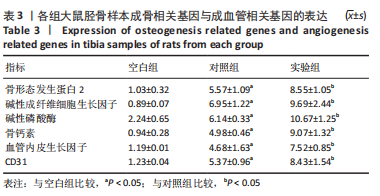
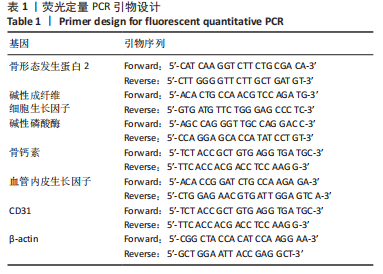
[1] KHARE D, BASU B, DUBEY AK. Electrical stimulation and piezoelectric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120280.
[2] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LIU Y, et al. Four-dimensional bioprinting: Current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:26-42.
[3] SHEN C, WITEK L, FLORES RL, et al.Three-Dimensional Printing for Craniofacial Bone Tissue Engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(23-24): 1303-1311.
[4] RAJ PREETH D, SARAVANAN S, SHAIRAM M, et al. Bioactive Zinc(II) complex incorporated PCL/gelatin electrospun nanofiber enhanced bone tissue regeneration. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;160:105768.
[5] MAHALINGAM S, BAYRAM C, GULTEKINOGLU M, et al. Co-Axial Gyro-Spinning of PCL/PVA/HA Core-Sheath Fibrous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering.Macromol Biosci. 2021;21(10):e2100177.
[6] MURUGAN S, PARCHA SR. Fabrication techniques involved in developing the composite scaffolds PCL/HA nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(8):93.
[7] BIGHAM A, SALEHI AOM, RAFIENIA M, et al. Zn-substituted Mg2SiO4 nanoparticles-incorporated PCL-silk fibroin composite scaffold: A multifunctional platform towards bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;127:112242.
[8] PAZARÇEVIREN AE, TEZCANER A, KESKIN D, et al. Boron-doped Biphasic Hydroxyapatite/β-Tricalcium Phosphate for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199(3):968-980.
[9] DING X, LI A, YANG F, et al. β-tricalcium phosphate and octacalcium phosphate composite bioceramic material for bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl. 2020;34(9):1294-1299.
[10] LEE DH, TRIPATHY N, SHIN JH, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of β-tricalcium phosphate reinforced silk fibroin scaffold for bone tissue biofabrication. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;95:14-23.
[11] NAKHAEE FM, RAJABI M, BAKHSHESHI-RAD HR. In-vitroassessment of β-tricalcium phosphate/bredigite-ciprofloxacin (CPFX) scaffolds for bone treatment applications. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(4). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac0590.
[12] LEE S, CHOI D, SHIM JH, et al. Efficacy of three-dimensionally printed polycaprolactone/beta tricalcium phosphate scaffold on mandibular reconstruction. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4979.
[13] LU L, ZHANG Q, WOOTTON D, et al. Biocompatibility and biodegradation studies of PCL/β-TCP bone tissue scaffold fabricated by structural porogen method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(9):2217-2226.
[14] BRUYAS A, LOU F, STAHL AM, et al. Systematic characterization of 3D-printed PCL/β-TCP scaffolds for biomedical devices and bone tissue engineering: influence of composition and porosity. J Mater Res. 2018; 33(14):1948-1959.
[15] WANG Q, YE W, MA Z, et al. 3D printed PCL/β-TCP cross-scale scaffold with high-precision fiber for providing cell growth and forming bones in the pores. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;127:112197.
[16] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.
[17] HUDDLESTON PM, STECKELBERG JM, HANSSEN AD, et al. Ciprofloxacin inhibition of experimental fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(2):161-173.
[18] YUAN J, MATURAVONGSADIT P, METAVARAYUTH K, et al. Enhanced Bone Defect Repair by Polymeric Substitute Fillers of MultiArm Polyethylene Glycol-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(6):e1900021.
[19] WANG D, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al. A dual functional bone-defect-filling material with sequential antibacterial and osteoinductive properties for infected bone defect repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(10):2360-2370.
[20] HAN D, LI J. Repair of bone defect by using vascular bundle implantation combined with Runx II gene-transfected adipose-derived stem cells and a biodegradable matrix. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;352(3):561-571.
[21] YIN Y, TANG Q, XIE M, et al. Insights into the mechanism of vascular endothelial cells on bone biology.Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1):BSR20203258.
[22] ROMEO SG, ALAWI KM, RODRIGUES J, et al. Endothelial proteolytic activity and interaction with non-resorbing osteoclasts mediate bone elongation. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(4):430-441.
[23] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[24] 刘慧,陈慧鸿,廖红兵.破骨细胞衍生的偶联因子鞘氨醇-1-磷酸及血小板衍生生长因子BB对成骨细胞的调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(23):3739-3745.
[25] BRUN J, ANDREASEN CM, EJERSTED C, et al. PDGF Receptor Signaling in Osteoblast Lineage Cells Controls Bone Resorption Through Upregulation of Csf1 Expression. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(12):2458-2469.
[26] 魏琴,张雪,马磊,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19): 2953-2957.
[27] 吴硕,魏琴,买买艾力·玉山.rrPDGF-BB基因修饰的自体BMSCs促进大鼠股骨牵张成骨[J].中华显微外科杂志,2021,44(5):526-534.
[28] CHENG J, YANG HL, GU CJ, et al. Melatonin restricts the viability and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells by suppressing HIF-1α/ROS/VEGF. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):945-955.
[29] CHAN CM, HSIAO CY, LI HJ, et al. The Inhibitory Effects of Gold Nanoparticles on VEGF-A-Induced Cell Migration in Choroid-Retina Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):109.
[30] POH CK, SHI Z, LIM TY, et al. The effect of VEGF functionalization of titanium on endothelial cells in vitro. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1578-1585.
[31] HUANG J, ZHANG S. Overexpressed Neuropilin-1 in Endothelial Cells Promotes Endothelial Permeability through Interaction with ANGPTL4 and VEGF in Kawasaki Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2021; 2021:9914071. |