[1] SUI B, CHEN C, KOU X, et al. Pulp stem cell-mediated functional pulp regeneration. J Dent Res. 2019;98(1):27-35.
[2] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97(25):13625-13630.
[3] CHEUNG VC, PENG CY, MARINIĆ M, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived endometrial stromal fibroblasts in a cyclic, hormone-responsive, coculture model of human decidua. Cell Rep. 2021;35(7):109138.
[4] ANITUA E, TROYA M, ZALDUENDO M. Progress in the use of dental pulp stem cells in regenerative medicine. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(4):479-498.
[5] BATTISTON KG, CHEUNG JW, JAIN D, et al. Biomaterials in co-culture systems: towards optimizing tissue integration and cell signaling within scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(15):4465-4476.
[6] TRAN-HUNG L, LAURENT P, CAMPS J, et al. Quantification of angiogenic growth factors released by human dental cells after injury. Arch Oral Biol. 2008;53(1):9-13.
[7] DISSANAYAKA WL, ZHU L, HARGREAVES KM, et al. In vitro analysis of scaffold-free prevascularized microtissue spheroids containing human dental pulp cells and endothelial cells. J Endod. 2015;41(5):663-670.
[8] 黄雨亭,沈帅,蒋鹏飞,等.EphrinB2对TNF-α作用下的脐静脉内皮细胞与牙髓干细胞血管生成的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021,37(6): 773-777.
[9] 吴一梦,张爽,潘爽,等.脐静脉内皮细胞与牙本质浸提液诱导的牙髓干细胞共培养成血管的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(5):504-508.
[10] DISSANAYAKA WL, ZHAN X, ZHANG C, et al. Coculture of dental pulp stem cells with endothelial cells enhances osteo-/odontogenic and angiogenic potential in vitro. J Endod. 2012;38(4):454-463.
[11] LI M, WANG Q, HAN Q, et al. Novel molecule nell-1 promotes the angiogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Front Physiol. 2021;12:703593.
[12] MERCKX G, HOSSEINKHANI B, KUYPERS S, et al. Angiogenic effects of human dental pulp and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles. Cells. 2020;9(2):312.
[13] 安莉,沈帅,王璐瑶,等.TNF-α增强牙髓干细胞与脐静脉内皮细胞共培养血管生成能力[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(10):966-969.
[14] HONDA MJ, TSUCHIYA S, SUMITA Y, et al. The sequential seeding of epithelial and mesenchymal cells for tissue-engineered tooth regeneration. Biomaterials. 2007;28(4):680-689.
[15] LIU M, ZHAO L, HU J, et al. Endothelial cells and endothelin 1 promote the odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 18(1):893-901.
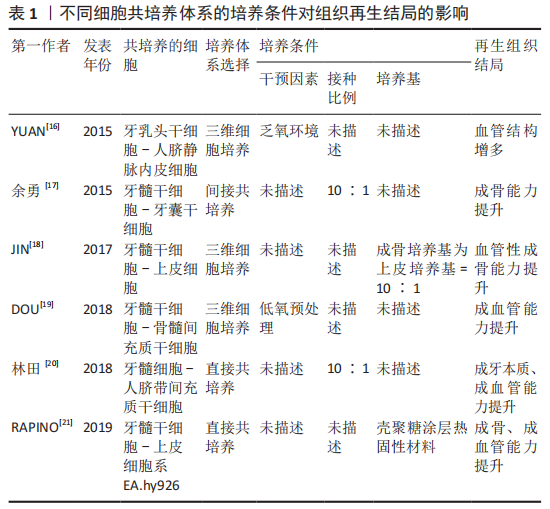
[16] YUAN C, WANG P, ZHU L, et al. Coculture of stem cells from apical papilla and human umbilical vein endothelial cell under hypoxia increases the formation of three-dimensional vessel-like structures in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6):1163-1172.
[17] 余勇,陶昱,邓锋,王睿,等.体外共培养人牙髓干细胞对人牙囊干细胞增殖、成骨分化的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(22):2267-2272.
[18] JIN GZ, KIM HW. Co-culture of human dental pulp stem cells and endothelial cells using porous biopolymer microcarriers: a feasibility study for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;14(4):393-401.
[19] DOU L, YAN Q, LIANG P, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis exploring the influence of hypoxia on the proteome of dental pulp stem cells under 3D culture. Proteomics. 2018. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201700215.
[20] 林田,赵文青,陆彦玲,等.人脐带间充质干细胞与牙髓细胞体外共培养对细胞生物学的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(4):365-369.
[21] RAPINO M, DI VALERIO V, ZARA S, et al. Chitlac-coated thermosets enhance osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a co-culture of dental pulp stem cells and endothelial cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019;9(7):928.
[22] RADDALL G, MELLO I, LEUNG BM. Biomaterials and scaffold design strategies for regenerative endodontic therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:317.
[23] 刘阳,莫春香,贺艳,等.组织工程支架材料研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2019,47(12):37-40.
[24] BADYLAK SF, FREYTES DO, GILBERT TW. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(1):1-13.
[25] YOUNG CS, TERADA S, VACANTI JP, et al. Tissue engineering of complex tooth structures on biodegradable polymer scaffolds. J Dent Res. 2002; 81(10):695-700.
[26] MOUSSA DG, APARICIO C. Present and future of tissue engineering scaffolds for dentin-pulp complex regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(1): 58-75.
[27] DISSANAYAKA WL, ZHU L, HARGREAVES KM, et al. Scaffold-free prevascularized microtissue spheroids for pulp regeneration. J Dent Res. 2014;93(12):1296-1303.
[28] DISSANAYAKA WL, ZHU L, HARGREAVES KM, et al. In vitro analysis of scaffold-free prevascularized microtissue spheroids containing human dental pulp cells and endothelial cells. J Endod. 2015;41(5):663-670.
[29] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2017;3(3):278-314.
[30] MA Y, XIE L, YANG B, et al. Three-dimensional printing biotechnology for the regeneration of the tooth and tooth-supporting tissues. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019;116(2):452-468.
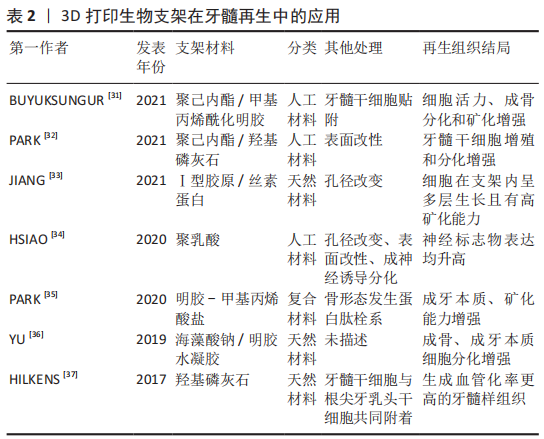
[31] BUYUKSUNGUR S, HASIRCI V, HASIRCI N. 3D printed hybrid bone constructs of PCL and dental pulp stem cells loaded GelMA. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(12):2425-2437.
[32] PARK S, KIM JE, HAN J, et al. 3D-printed poly (ε-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite scaffolds modified with alkaline hydrolysis enhance osteogenesis in vitro. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(2):257.
[33] JIANG S, YU Z, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of different aperture-sized type I collagen/silk fibroin scaffolds on the proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(4):rbab028.
[34] HSIAO D, HSU SH, CHEN RS, et al. Characterization of designed directional polylactic acid 3D scaffolds for neural differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020;119(1 Pt 2):268-275.
[35] PARK JH, GILLISPIE GJ, COPUS JS, et al. The effect of BMP-mimetic peptide tethering bioinks on the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in 3D bioprinted dental constructs. Biofabrication. 2020;12(3):035029.
[36] YU H, ZHANG X, SONG W, et al. Effects of 3-dimensional bioprinting alginate/gelatin hydrogel scaffold extract on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2019;45(6):706-715.
[37] HILKENS P, BRONCKAERS A, RATAJCZAK J, et al. The angiogenic potential of dpscs and scaps in an in vivo model of dental pulp regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2582080.
[38] THURLEY K, WU LF, ALTSCHULER SJ. Modeling cell-to-cell communication networks using response-time distributions. Cell Syst. 2018;6(3):355-367.e5.
[39] CORDERO CERVANTES D, ZURZOLO C. Peering into tunneling nanotubes-The path forward. EMBO J. 2021;40(8):e105789.
[40] BEYER EC, BERTHOUD VM. Gap junction gene and protein families: connexins, innexins, and pannexins. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018; 1860(1):5-8.
[41] VINKEN M, VANHAECKE T, PAPELEU P, et al. Connexins and their channels in cell growth and cell death. Cell Signal. 2006;18(5):592-600.
[42] YIN J, XU J, CHENG R, et al. Role of connexin 43 in odontoblastic differentiation and structural maintenance in pulp damage repair. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):1.
[43] LIU W, CUI Y, WEI J, et al. Gap junction-mediated cell-to-cell communication in oral development and oral diseases: a concise review of research progress. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):17.
[44] QIN L, LIU W, CAO H, et al. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020;8:23.
[45] SIMON AM, MCWHORTER AR. Decreased intercellular dye-transfer and downregulation of non-ablated connexins in aortic endothelium deficient in connexin 37 or connexin 40. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 11):2223-2236.
[46] LI M, ZHANG A, LI J, et al. Osteoblast/fibroblast coculture derived bioactive ECM with unique matrisome profile facilitates bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):938-948.
[47] CHAI Y, YU R, LIU Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates monocyte-endothelial adherence via inhibiting connexin43 on vascular endothelial cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7039854.
[48] JI H, QIU R, GAO X, et al. Propofol attenuates monocyte-endothelial adhesion via modulating connexin43 expression in monocytes. Life Sci. 2019;232:116624.
[49] MURAMATSU T, HASHIMOTO S, SHIBUKAWA Y, et al. Immunoelectron microscopic observation of connexin43 in rat odontoblasts. Microsc Res Tech. 2013;76(10):988-991.
[50] LI S, HU J, ZHANG G, et al. Extracellular Ca2+ promotes odontoblastic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via bmp2-mediated Smad1/5/8 and Erk1/2 pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(9):2164-2173.
[51] MATSUBARA T, IGA T, SUGIURA Y, et al. Coupling of angiogenesis and odontogenesis orchestrates tooth mineralization in mice. J Exp Med. 2022; 219(4):e20211789.
[52] IWAYA SI, IKAWA M, KUBOTA M. Revascularization of an immature permanent tooth with apical periodontitis and sinus tract. Dent Traumatol. 2001;17(4):185-187.
[53] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264.
[54] SIMONS M, GORDON E, CLAESSON-WELSH L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(10): 611-625.
[55] CHENG HW, JAMES AF, FOSTER RR, et al. VEGF activates receptor-operated cation channels in human microvascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(8):1768-1776.
[56] HEINOLAINEN K, KARAMAN S, D’AMICO G, et al. VEGFR3 modulates vascular permeability by controlling VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling. Circ Res. 2017; 120(9):1414-1425.
[57] SHIN MR, KANG SK, KIM YS, et al. TNF-α and LPS activate angiogenesis via VEGF and SIRT1 signalling in human dental pulp cells. Int Endod J. 2015; 48(7):705-716.
[58] WANG HJ, RAN HF, YIN Y, et al. Catalpol improves impaired neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke rats via enhancing VEGF-PI3K/AKT and VEGF-MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(7):1670-1685.
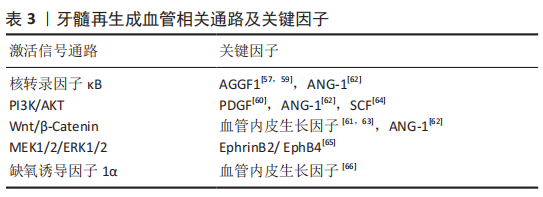
[59] SHEN S, SHANG L, LIU H, et al. AGGF1 inhibits the expression of inflammatory mediators and promotes angiogenesis in dental pulp cells. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(2):581-592.
[60] ZHANG M, JIANG F, ZHANG X, et al. The effects of platelet-derived growth factor-bb on human dental pulp stem cells mediated dentin-pulp complex regeneration. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2126-2134.
[61] ZHANG Z, NÖR F, OH M, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling determines the vasculogenic fate of postnatal mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(6):1576-1587.
[62] YUN HM, KANG SK, SINGH RK, et al. Magnetic nanofiber scaffold-induced stimulation of odontogenesis and pro-angiogenesis of human dental pulp cells through Wnt/MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Dent Mater. 2016;32(11): 1301-1311.
[63] LEE SI, KIM SY, PARK KR, et al. Baicalein promotes angiogenesis and odontoblastic differentiation via the BMP and Wnt pathways in human dental pulp cells. Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(7):1457-1472.
[64] PAN S, DANGARIA S, GOPINATHAN G, et al. SCF promotes dental pulp progenitor migration, neovascularization, and collagen remodeling - potential applications as a homing factor in dental pulp regeneration. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013;9(5):655-667.
[65] GONG T, XU J, HENG B, et al. EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling regulates DPSCs to induce sprouting angiogenesis of endothelial cells. J Dent Res. 2019; 98(7):803-812.
[66] YUAN C, WANG P, ZHU L, et al. Coculture of stem cells from apical papilla and human umbilical vein endothelial cell under hypoxia increases the formation of three-dimensional vessel-like structures in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6):1163-1172.
[67] HUANG GT. Dental pulp and dentin tissue engineering and regeneration: advancement and challenge. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2011;3(2):788-800. |