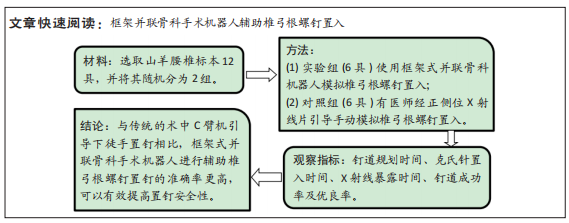
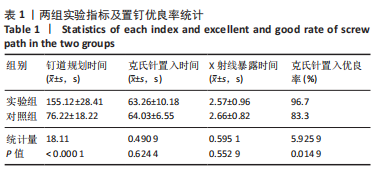
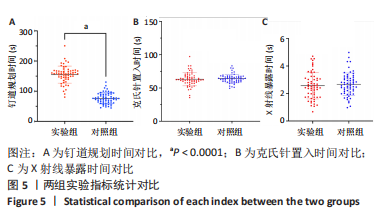
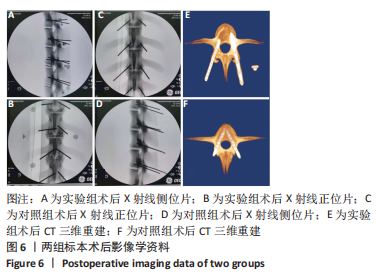
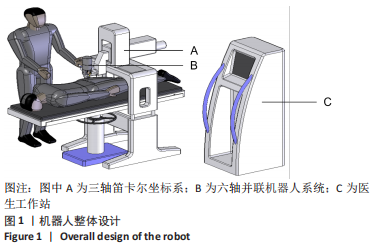
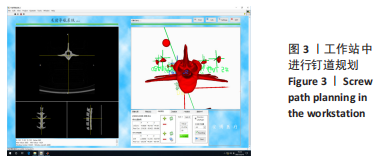
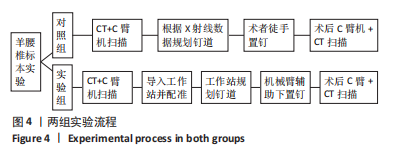
[1] YAO Y, LIU Y, LI Z, et al. Chinese surgical robot micro hand S: A consecutive case series in general surgery. Int J Surg (London, England). 2020;75:55-59.
[2] ZHANG W, LI H, CUI L, et al. Research progress and development trend of surgical robot and surgical instrument arm. Int J Med Robot. 2021;17(5):e2309.
[3] 李扬,周岷峰.我国医疗机器人产业发展特征分析[J].机器人产业, 2018(2):95-100.
[4] LIOW MHL, CHIN PL, PANG HN, et al. THINK surgical TSolution-One® (Robodoc) total knee arthroplasty. SICOT J. 2017;3:63.
[5] JEON SW, KIM KI, SONG SJ. Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Does Not Improve Long-Term Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1656-1661.
[6] DEVITO DP, KAPLAN L, DIETL R, et al. Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with SpineAssist surgical robot: retrospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(24):2109-2115.
[7] PENG YN, TSAI LC, HSU HC, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted versus conventional freehand pedicle screw placement in spine surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(13):824.
[8] 王成勇,谢国能,赵丹娜,等.医疗手术机器人发展概况[J].工具技术,2016,50(7): 3-12.
[9] 张伟,胡豇,唐六一,等.机器人辅助经皮穿刺活检诊断脊柱病变的优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):844-848.
[10] WANG B, CAO J, CHANG J, et al. Effectiveness of Tirobot-assisted vertebroplasty in treating thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):65.
[11] BARBASH GI, GLIED SA. New technology and health care costs--the case of robot-assisted surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):701-704.
[12] CHENG P, HE Y, XIN B. A Novel Registration Method for Robot-assisted Percutaneous Vertebroplasty[C]//2019 IEEE 7th International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology (ICCSNT), 2019:530-534.
[13] GERTZBEIN SD, ROBBINS SE. Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(1):11-14.
[14] FENG S, TIAN W, WEI Y. Clinical Effects of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion by Conventional Open versus Percutaneous Robot‐Assisted Minimally Invasive Pedicle Screw Placement in Elderly Patients. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):86-93.
[15] ZHANG W, LI H, CUI L, et al. Research progress and development trend of surgical robot and surgical instrument arm. Int J Med Robot. 2021; 17(5):e2309.
[16] STÜBIG T, WINDHAGEN H, KRETTEK C, et al. Computer-Assisted Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2020;117(47):793-800.
[17] D’SOUZA M, GENDREAU J, FENG A, et al. Robotic-Assisted Spine Surgery: History, Efficacy, Cost, And Future Trends. Robot Surg. 2019;6: 9-23.
[18] PERFETTI DC, KISINDE S, ROGERS-LAVANNE MP, et al. Robotic Spine Surgery: Past, Present and Future. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004357.
[19] HUANG M, TETREAULT TA, VAISHNAV A, et al. The current state of navigation in robotic spine surgery. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(1):86.
[20] ZHANG JN, FAN Y, HAO DJ. Risk factors for robot-assisted spinal pedicle screw malposition. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3025.
[21] ZHANG H, FAN Y, WANG R, et al. Research trends and hotspots of high tibial osteotomy in two decades (from 2001 to 2020): a bibliometric analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):512.
[22] MCDONNELL JM, AHERN DP, Ó DOINN T, et al. Surgeon proficiency in robot-assisted spine surgery: a narrative review. Bone Joint J. 2020; 102-B(5):568-572.
[23] SABRI SA, YORK PJ. Preoperative planning for intraoperative navigation guidance. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(1):87.
[24] FENG S, TIAN W, WEI Y. Clinical Effects of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion by Conventional Open versus Percutaneous Robot‐Assisted Minimally Invasive Pedicle Screw Placement in Elderly Patients. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1): 86-93.
[25] LI HM, ZHANG RJ, SHEN CL. Accuracy of Pedicle Screw Placement and Clinical Outcomes of Robot-assisted Technique Versus Conventional Freehand Technique in Spine Surgery From Nine Randomized Controlled Trials: A Meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(2): E111-E119.
[26] FU W, TONG J, LIU G, et al. Robot-assisted technique vs conventional freehand technique in spine surgery: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(5):e13964.
[27] YU L, CHEN X, MARGALIT A, et al. Robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery - a systematic review and a meta-analysis of comparative studies. Int J Med Robot. 2018;14(3):e1892.
[28] GAO S, WEI J, LI W, et al. Accuracy of Robot-Assisted Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement under Regional Anesthesia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pain Res Manag. 2021;2021:6894001.
[29] VILLARD J, RYANG YM, DEMETRIADES AK, et al. Radiation exposure to the surgeon and the patient during posterior lumbar spinal instrumentation: a prospective randomized comparison of navigated versus non-navigated freehand techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(13):1004-1009.
[30] HYUN S J, KIM K J, JAHNG T A, et al. Minimally Invasive Robotic Versus Open Fluoroscopic-guided Spinal Instrumented Fusions: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(6):353-358.
[31] LEE NJ, BUCHANAN IA, ZUCKERMANN SL, et al. What Is the Comparison in Robot Time per Screw, Radiation Exposure, Robot Abandonment, Screw Accuracy, and Clinical Outcomes Between Percutaneous and Open Robot-Assisted Short Lumbar Fusion?: A Multicenter, Propensity-Matched Analysis of 310 Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(1): 42-48.
[32] DU J, GAO L, HUANG D, et al. Radiological and Clinical Differences between Tinavi Orthopedic Robot and O-Arm Navigation System in Thoracolumbar Screw Implantation for Reconstruction of Spinal Stability. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e924770.
[33] BI B, ZHANG S, ZHAO Y. The effect of robot-navigation-assisted core decompression on early stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):375.
[34] RINGEL F, STÜER C, REINKE A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(8):E496-501.
[35] 林云志,方国芳,李修往,等.半自动脊柱手术机器人系统在脊柱外科治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3792-3796.
[36] BHANDARI M, ZEFFIRO T, REDDIBOINA M. Artificial intelligence and robotic surgery: current perspective and future directions. Curr Opin Urol. 2020;30(1):48-54.
[37] ZHANG TT, WANG ZP, WANG ZH, et al. [Clinical application of Orthopedic Tianji Robot in surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fracture]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021;34(11):1034-1039.
[38] FAVRE A, HUBERLANT S, CARBONNEL M, et al. Pedagogic Approach in the Surgical Learning: The First Period of “Assistant Surgeon” May Improve the Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy. Front Surg. 2016;3:58.
[39] ZHANG C, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A hybrid feature-based patient-to-image registration method for robot-assisted long bone osteotomy. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021;16(9):1507-1516.
[40] BAI S, LIAO S, HAN F, et al. Automatic Real-Time Space Registration Application for Simulating Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2022. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000008505.
[41] WU JY, YUAN Q, LIU YJ, et al. Robot-assisted Percutaneous Transfacet Screw Fixation Supplementing Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Procedure: Accuracy and Safety Evaluation of This Novel Minimally Invasive Technique. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):25-33.
[42] HAN X, TIAN W, LIU Y, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;1-8.
|