[1] ARABBI KC, SHARANAPPA M, PRIYA Y, et al. Socket Shield: A Case Report. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019;11(Suppl 1):S72-S75.
[2] VINA-ALMUNIA J, CANDEL-MARTI ME, CERVERA-BALLESTER J, et al. Buccal bone crest dynamics after immediate implant placement and ridge preservation techniques: review of morphometric studies in animals. Implant Dent. 2013;22(2):155-160.
[3] MOURYA A, MISHRA SK, GADDALE R, et al. Socket-shield technique for implant placement to stabilize the facial gingival and osseous architecture: A systematic review. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019;10(4):e12449.
[4] CHEN ST, BUSER D. Esthetic outcomes following immediate and early implant placement in the anterior maxilla--a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29 Suppl:186-215.
[5] TIWARI S, BEDI RS, WADHWANI P, et al. Comparison of Immediate Implant Placement Following Extraction with and Without Socket-Shield Technique in Esthetic Region. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2020;19(4): 552-560.
[6] DAYAKAR MM, WAHEED A, BHAT HS, et al. The socket-shield technique and immediate implant placement. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018;22(5):451-455.
[7] 马国武,薛藏辉.“盾构术”在前牙美学区种植中的应用[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(6):581-584.
[8] SCHWIMER C, PETTE GA, GLUCKMAN H, et al. Human Histologic Evidence of New Bone Formation and Osseointegration Between Root Dentin (Unplanned Socket-Shield) and Dental Implant: Case Report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):e19-e23.
[9] SALAMA M, ISHIKAWA T, SALAMA H, et al. Advantages of the root submergence technique for pontic site development in esthetic implant therapy. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2007;27(6):521-527.
[10] HURZELER MB, ZUHR O, SCHUPBACH P, et al. The socket-shield technique: a proof-of-principle report. J Clin Periodontol. 2010;37(9): 855-862.
[11] MITSIAS ME, SIORMPAS KD, KOTSAKIS GA, et al. The Root Membrane Technique: Human Histologic Evidence after Five Years of Function. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7269467.
[12] TAN Z, KANG J, LIU W, et al. The effect of the heights and thicknesses of the remaining root segments on buccal bone resorption in the socket-shield technique: An experimental study in dogs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(3): 352-359.
[13] GLUCKMAN H, SALAMA M, DU TOIT J. Partial Extraction Therapies (PET) Part 2: Procedures and Technical Aspects. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2017;37(3):377-385.
[14] Du TOIT J, GLUCKMAN H. The Modified Socket-Shield Technique. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(7):2005-2006.
[15] CALVO-GUIRADO JL, TROIANO M, LOPEZ-LOPEZ PJ, et al. Different configuration of socket shield technique in peri-implant bone preservation: An experimental study in dog mandible. Ann Anat. 2016;208:109-115.
[16] CALVO-GUIRADO JL, BENITEZ-GARCIA JA, MATE SDVJ, et al. Socket-shield technique: the influence of the length of the remaining buccal segment of healthy tooth structure on peri-implant bone and socket preservation. A study in dogs. Ann Anat. 2019;221:84-92.
[17] ROE P, KAN J, RUNGCHARASSAENG K. Residual root preparation for socket-shield procedures: a facial window approach. Int J Esthet Dent. 2017;12(3): 324-335.
[18] MITSIAS ME, SIORMPAS KD, KONTSIOTOU-SIORMPA E, et al. A Step-by-Step Description of PDL-Mediated Ridge Preservation for Immediate Implant Rehabilitation in the Esthetic Region. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2015;35(6):835-841.
[19] GUO T, NIE R, XIN X, et al. Tissue preservation through socket-shield technique and platelet-rich fibrin in immediate implant placement: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(50):e13175.
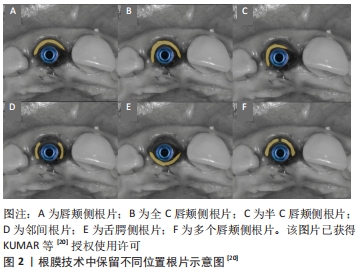
[20] KUMAR PR, KHER U. Shield the socket: Procedure, case report and classification. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018;22(3):266-272.
[21] GLUCKMAN H, Du TOIT J, SALAMA M, et al. A decade of the socket-shield technique: a step-by-step partial extraction therapy protocol. Int J Esthet Dent. 2020;15(2):212-225.
[22] COVANI U, MARCONCINI S, GALASSINI G, et al. Connective tissue graft used as a biologic barrier to cover an immediate implant. J Periodontol. 2007; 78(8):1644-1649.
[23] PAOLANTONIO M, DOLCI M, SCARANO A, et al. Immediate implantation in fresh extraction sockets. A controlled clinical and histological study in man. J Periodontol. 2001;72(11):1560-1571.
[24] CARDAROPOLI D, TAMAGNONE L, ROFFREDO A, et al. Preservation of Peri-implant Hard Tissues Following Immediate Postextraction Implant Placement. Part I: Radiologic Evaluation. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2019;39(5):633-641.
[25] CHU SJ, SALAMA MA, GARBER DA, et al. Flapless Postextraction Socket Implant Placement, Part 2: The Effects of Bone Grafting and Provisional Restoration on Peri-implant Soft Tissue Height and Thickness- A Retrospective Study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2015;35(6):803-809.
[26] ARAUJO MG, LINDER E, LINDHE J. Bio-Oss collagen in the buccal gap at immediate implants: a 6-month study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(1):1-8.
[27] CHU SJ, SAITO H, SALAMA MA, et al. Flapless Postextraction Socket Implant Placement, Part 3: The Effects of Bone Grafting and Provisional Restoration on Soft Tissue Color Change-A Retrospective Pilot Study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2018;38(4):509-516.
[28] TARNOW DP, CHU SJ, SALAMA MA, et al. Flapless postextraction socket implant placement in the esthetic zone: part 1. The effect of bone grafting and/or provisional restoration on facial-palatal ridge dimensional change-a retrospective cohort study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34(3):323-331.
[29] SCHNEIDER D, GRUNDER U, ENDER A, et al. Volume gain and stability of peri-implant tissue following bone and soft tissue augmentation: 1-year results from a prospective cohort study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(1):28-37.
[30] GLUCKMAN H, DU TOIT J, SALAMA M. The Pontic-Shield: Partial Extraction Therapy for Ridge Preservation and Pontic Site Development. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2016;36(3):417-423.
[31] BAUMER D, ZUHR O, REBELE S, et al. The socket-shield technique: first histological, clinical, and volumetrical observations after separation of the buccal tooth segment - a pilot study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; 17(1):71-82.
[32] BUSER D, JANNER SF, WITTNEBEN JG, et al. 10-year survival and success rates of 511 titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: a retrospective study in 303 partially edentulous patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012;14(6):839-851.
[33] FISCHER K, STENBERG T. Prospective 10-year cohort study based on a randomized controlled trial (RCT) on implant-supported full-arch maxillary prostheses. Part 1: sandblasted and acid-etched implants and mucosal tissue. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012;14(6):808-815.
[34] DASH S, MOHAPATRA A, SRIVASTAVA G, et al. Retaining and Regaining Esthetics in the Anterior Maxillary Region Using the Socket-Shield Technique. Contemp Clin Dent. 2020;11(2):158-161.
[35] BRAMANTI E, NORCIA A, CICCIU M, et al. Postextraction Dental Implant in the Aesthetic Zone, Socket Shield Technique Versus Conventional Protocol. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):1037-1041.
[36] ZHU YB, QIU LX, CHEN L, et al. [Clinical evaluation of socket shield technique in maxillary anterior region]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018; 53(10):665-668.
[37] BAUMER D, ZUHR O, REBELE S, et al. Socket Shield Technique for immediate implant placement - clinical, radiographic and volumetric data after 5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(11):1450-1458.
[38] SCHWIMER CW, GLUCKMAN H, SALAMA M, et al. The socket-shield technique at molar sites: A proof-of-principle technique report. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;121(2):229-233.
[39] HABASHNEH RA, WALID MA, ABUALTEEN T, et al. Socket-shield Technique and Immediate Implant Placement for Ridge Preservation: Case Report Series with 1-year Follow-up. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2019;20(9):1108-1117.
[40] GLUCKMAN H, SALAMA M, DU TOIT J. Partial Extraction Therapies (PET) Part 1: Maintaining Alveolar Ridge Contour at Pontic and Immediate Implant Sites. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2016;36(5):681-687.
[41] POLIS-YANES C, CADENAS-SEBASTIAN C, OLIVER-PUIGDOMENECH C, et al. A Double Case: Socket Shield and Pontic Shield Techniques on Aesthetic Zone. Case Rep Dent. 2020;2020:8891772.
[42] SIORMPAS KD, MITSIAS ME, KOTSAKIS GA, et al. The Root Membrane Technique: A Retrospective Clinical Study With Up to 10 Years of Follow-Up. Implant Dent. 2018;27(5):564-574.
[43] SUPRIYA SHAKYA,张鑫,王剑.种植盾构术的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(1):109-114.
[44] ABD-ELRAHMAN A, SHAHEEN M, ASKAR N, et al. Socket shield technique vs conventional immediate implant placement with immediate temporization. Randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2020;22(5):602-611.
[45] YAN SJ, ZHOU C, LIU J, et al. [Clinical evaluation of the socket-shield technique for immediate implantation in the maxillary anterior region]. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;37(6):615-620.
[46] BRAMANTI E, NORCIA A, CICCIU M, et al. Postextraction Dental Implant in the Aesthetic Zone, Socket Shield Technique Versus Conventional Protocol. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):1037-1041.
[47] HUANG H, SHU L, LIU Y, et al. Immediate Implant Combined With Modified Socket-Shield Technique: A Case Letter. J Oral Implantol. 2017;43(2):139-143.
[48] CHEREL F, ETIENNE D. Papilla preservation between two implants: a modified socket-shield technique to maintain the scalloped anatomy? A case report. Quintessence Int. 2014;45(1):23-30.
[49] KAN JY, RUNGCHARASSAENG K. Proximal socket shield for interimplant papilla preservation in the esthetic zone. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(1):e24-e31.
[50] ZUHR O, STAEHLER P, HUERZELER M. Complication Management of a Socket Shield Case After 6 Years of Function. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2020;40(3):409-415.
[51] GLUCKMAN H, NAGY K, DU TOIT J. Prosthetic management of implants placed with the socket-shield technique. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;121(4):581-585.
[52] GLUCKMAN H, SALAMA M, DU TOIT J. A retrospective evaluation of 128 socket-shield cases in the esthetic zone and posterior sites: Partial extraction therapy with up to 4 years follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(2):122-129.
[53] De KOK IJ, DUQUM IS, KATZ LH, et al. Management of Implant/Prosthodontic Complications. Dent Clin North Am. 2019;63(2):217-231.
[54] STAVROPOULOS A, BERTL K, EREN S, et al. Mechanical and biological complications after implantoplasty-A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(9):833-848.
[55] SAEIDI PR, ZUHR O, HURZELER M, et al. Clinical Benefits of the Immediate Implant Socket Shield Technique. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(2):93-101.
[56] 许亚梅,黄弘,王黎,等.改良盾构术与传统即刻种植术的临床效果对比研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2019,37(5):490-495.
[57] BLASCHKE C, SCHWASS DR. The socket-shield technique: a critical literature review. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):52.
[58] GHARPURE AS, BHATAVADEKAR NB. Current Evidence on the Socket-Shield Technique: A Systematic Review. J Oral Implantol. 2017;43(5):395-403.
|