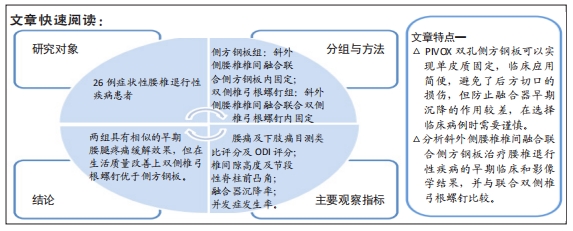
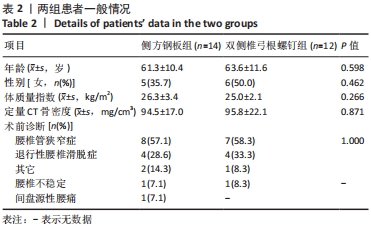
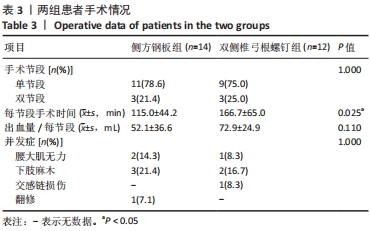
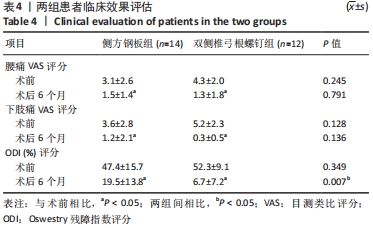
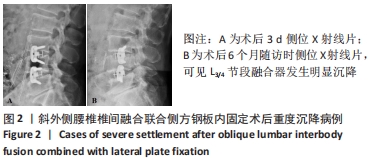
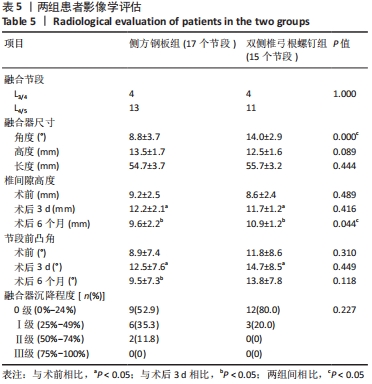
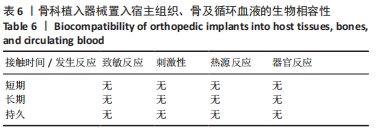
[1] HAH R, KANG HP. Lateral and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion-Current Concepts and a Review of Recent Literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019;12(3):305-310.
[2] LI R, LI X, ZHOU H, et al. Development and Application of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):355-365.
[3] LI JX, PHAN K, MOBBS R. Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Technical Aspects, Operative Outcomes, and Complications. World Neurosurg. 2017; 98:113-123.
[4] PHAN K, MAHARAJ M, ASSEM Y, et al. Review of early clinical results and complications associated with oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF). J Clin Neurosci. 2016;31:23-29.
[5] LI HM, ZHANG RJ, SHEN CL. Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Versus Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease. World Neurosurg. 2019; 122:e627-e638.
[6] SATO J, OHTORI S, ORITA S, et al. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3):671-678.
[7] ZHANG QY, TAN J, HUANG K, at al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):802.
[8] MALHAM GM, ELLIS NJ, PARKER RM, et al. Maintenance of Segmental Lordosis and Disk Height in Stand-alone and Instrumented Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion (XLIF) . Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(2):E90-E98.
[9] CARLSON BB, SAVILLE P, DOWDELL J, et al. Restoration of lumbar lordosis after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review. Spine J. 2019;19(5):951-958.
[10] MARCHI L, ABDALA N, OLIVEIRA L, et al. Radiographic and clinical evaluation of cage subsidence after stand-alone lateral interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(1):110-118.
[11] TEMPEL ZJ, GANDHOKE GS, BOLINGER BD, et al. Vertebral body fracture following stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF): report of two events out of 712 levels. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 Suppl 3:409-413.
[12] ABE K, ORITA S, MANNOJI C, et al. Perioperative Complications in 155 Patients Who Underwent Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Surgery: Perspectives and Indications From a Retrospective, Multicenter Survey. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(1):55-62.
[13] BOCAHUT N, AUDUREAU E, POIGNARD A, et al. Incidence and impact of implant subsidence after stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(3):405-410.
[14] LIU X, MA J, PARK P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of multilevel lateral interbody fusion with and without supplementary instrumentation: a three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1): 63.
[15] REIS MT, REYES PM BSE, ALTUN I, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of lateral lumbar interbody fusion with secondary augmentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(6):720-726.
[16] ZHANG Z, FOGEL GR, LIAO Z, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Constructs with Various Fixation Options: Based on a Validated Finite Element Model. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e1120-e1129.
[17] CHEN E, XU J, YANG S, et al. Cage Subsidence and Fusion Rate in Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion with and without Fixation. World Neurosurg. 2019; 122:e969-e977.
[18] PALEPU V, HELGESON M, MOLYNEAUX-FRANCIS M, et al. The effects of bone microstructure on subsidence risk for ALIF, LLIF, PLIF, and TLIF spine cages. J Biomech Eng. 2018. [Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.1115/1.4042181.
[19] MACKI M, ANAND SK, SURAPANENI A, et al. Subsidence Rates After Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:599-606.
[20] WALKER CT, FARBER SH, COLE TS, et al. Complications for minimally invasive lateral interbody arthrodesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing prepsoas and transpsoas approaches. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019; 1-15. [Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.3171/2018.9.SPINE18800.
[21] SPIESSBERGER A, ARVIND V, DIETZ N, et al. A Comparison of Complications and Clinical and Radiologic Outcome Between the Mini-open Prepsoas and Mini-open Transpsoas Approaches for Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Meta-Analysis. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(7):271-279.
[22] BEUTLER WJ, PEPPELMAN WC JR. Anterior lumbar fusion with paired BAK standard and paired BAK Proximity cages: subsidence incidence, subsidence factors, and clinical outcome. Spine J. 2003;3(4):289-293.
[23] SCHIFFMAN M, BRAU SA, HENDERSON R, et al. Bilateral implantation of low-profile interbody fusion cages: subsidence, lordosis, and fusion analysis. Spine J. 2003;3(5):377-387.
[24] TEMPEL ZJ, GANDHOKE GS, OKONKWO DO, et al. Impaired bone mineral density as a predictor of graft subsidence following minimally invasive transpsoas lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 Suppl 3: 414-419.
[25] TEMPEL ZJ, MCDOWELL MM, PANCZYKOWSKI DM, et al. Graft subsidence as a predictor of revision surgery following stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;28(1):50-56.
[26] FOGEL GR, PARIKH RD, RYU SI, et al. Biomechanics of lateral lumbar interbody fusion constructs with lateral and posterior plate fixation: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(3):291-297.
[27] TENDER GC. Caudal vertebral body fractures following lateral interbody fusion in nonosteoporotic patients. Ochsner J. 2014;14(1):123-130.
[28] LE TV, BAAJ AA, DAKWAR E, et al. Subsidence of polyetheretherketone intervertebral cages in minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(14):1268-1273.
[29] CHOI JY, SUNG KH. Subsidence after anterior lumbar interbody fusion using paired stand-alone rectangular cages. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(1):16-22.
[30] DUA K, KEPLER CK, HUANG RC, et al. Vertebral body fracture after anterolateral instrumentation and interbody fusion in two osteoporotic patients. Spine J. 2010;10(9):e11-e15.
[31] LE TV, SMITH DA, GREENBERG MS, et al. Complications of lateral plating in the minimally invasive lateral transpsoas approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(3):302-307.
|