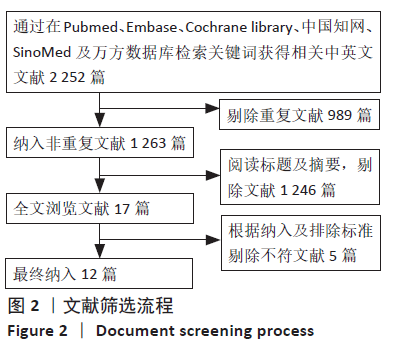
2.1 文献检索结果 共检索到相关文献2 252篇,剔除重复文献989篇,阅读文献标题及摘要后,排除与主题不符的研究、生物力学研究、尸体研究、动物研究等1 246篇,仔细阅读剩余17篇文献全文,根据纳入标准及排除标准排除5篇,最终纳入12篇文献[12-23]。共包括823例患者,其中应用骨水泥强化空心侧孔椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗者408例,应用常规椎弓根螺钉结合骨水泥强化治疗者415例。文献检索流程见图2。
2.2 纳入研究基本特征 见表1。

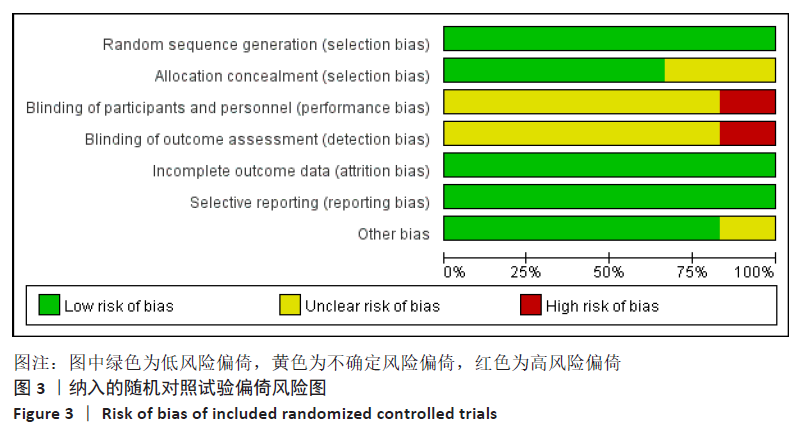
2.3 文献质量评价结果 有6项为随机对照试验[13-15,17-18,21],采用Cochrane风险偏倚评估工具进行质量评价,2项研究为高风险偏倚[15,21],4项研究为低风险偏倚[13-14,17-18],所有研究均未提及对受试者及研究者施盲,是否对结局评价者施盲对结局指标影响不大,见图3;
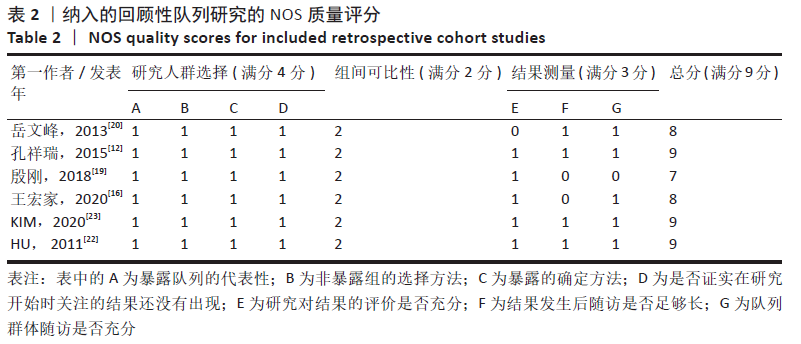
有6项为回顾性队列研
究[12,16,19-20,22-23],采用NOS量表进行质量评价,评分均在7分以上,为高质量文献,见表2。
2.4 Meta分析结果
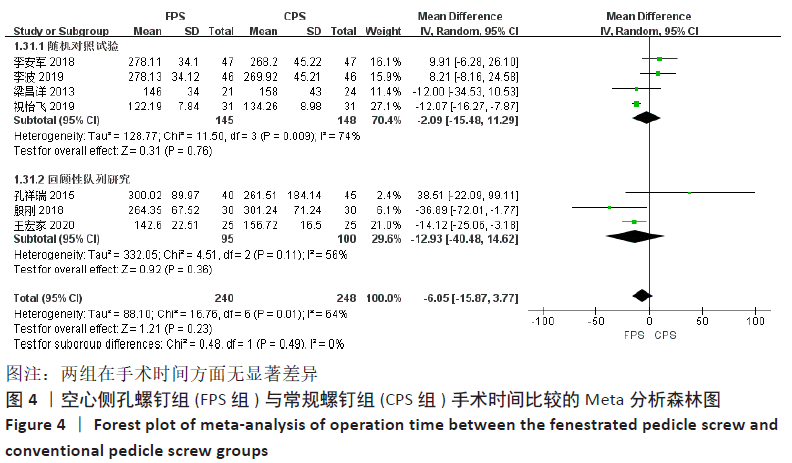
2.4.1 各组手术时间、术中出血量及住院时间差异 有7项研究报告了手术时间[12-16,19,21],各研究之间存在较大异质性(P=0.01,I2=64%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组之间的手术时间差异无显著性意义(MD=-6.05,95%CI:-15.87-3.77,P=0.23),按照不同研究类型进行亚组分析,4项随机对照试验合并结果显示两组手术时间差异无显著性意义(MD=-2.09,95%CI:-15.48-11.29,P=0.76) [13-15, 21],3项回顾性队列研究合并结果显示两组手术时间比较亦无显著性意义(MD=-12.93,95%CI:-40.48-14.62,P=0.36)[12, 16,19],见图4。
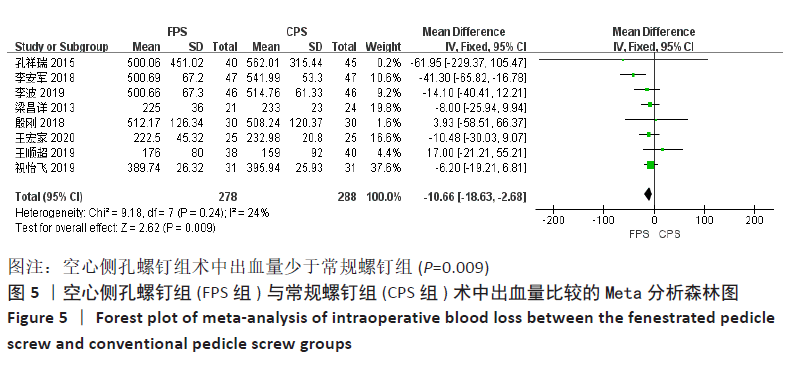
有8项研究报告了术中出血
量[12-17,19,21],各研究之间为轻度异质性(P=0.24,I2=24%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组之间的术中出血量差异有显著性意义(MD=-10.66,95%CI:-18.63至-2.68,P=0.009),空心侧孔椎弓根螺钉组术中出血量少于常规螺钉组,见图5。
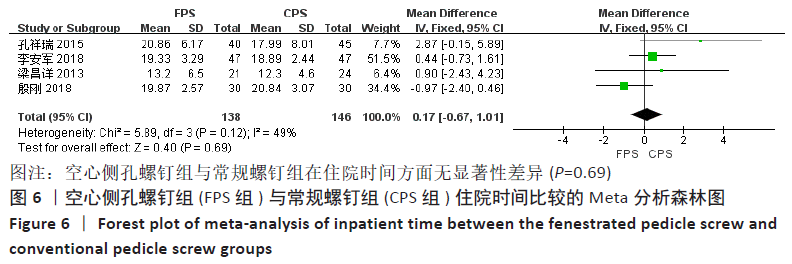
有4项研究报告了住院时间[12-13,15,19],各研究之间无明显异质性(P=0.12,I2=49%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组之间的住院时间不具有显著性差异(MD=0.17,95%CI:-0.67-1.01,P=0.69),见图6。
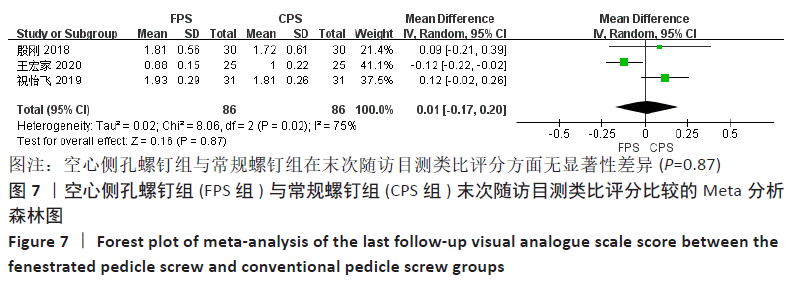
2.4.2 各组临床疗效差异 有3项研究比较了末次随访目测类比评分[16,19,21],两组术前目测类比评分无显著性差异(P=0.60),各研究间存在显著异质性(P=0.02,I2=75%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组的末次随访目测类比评分差异无显著性意义(MD=0.01,95%CI:-0.17-0.20,P=0.87),见图7。
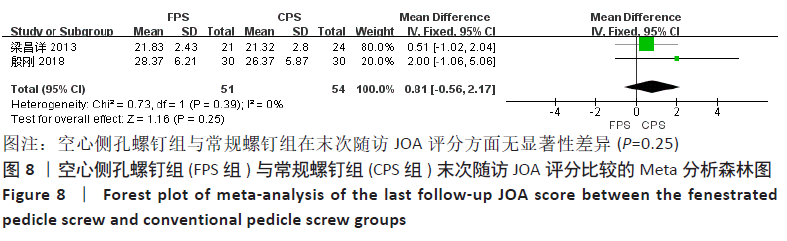
有2项研究比较了末次随访JOA评分[15,19],两组术前JOA评分无显著性差异(P=0.91),各研究之间不具有异质性(P=0.39,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组之间末次随访JOA评分差异无显著性意义(MD=0.81,95%CI:-0.56-2.17,P=0.25),见图8。
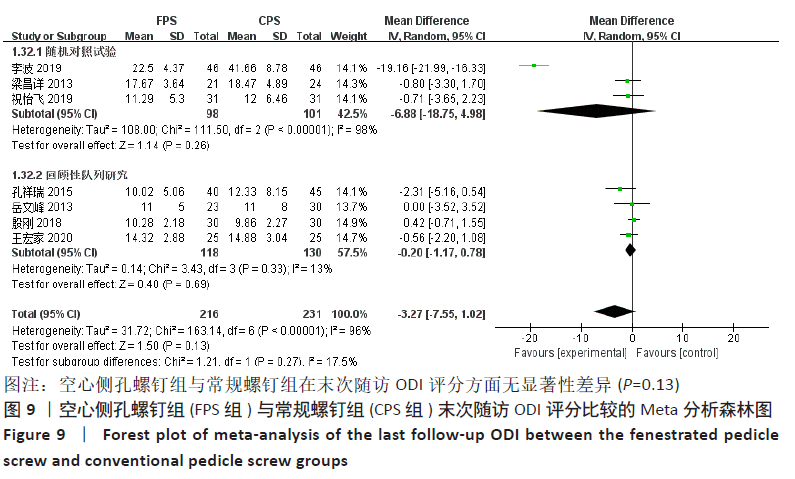
有7项研究比较了末次随访ODI评分[12,14-16,19-21],两组术前ODI评分无显著性差异(P=0.92),各研究之间有显著异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组末次随访ODI评分差异无显著性意义(MD= -3.27,95%CI:-7.55-1.02,P=0.13),按不同研究类型进行亚组分析,3项随机对照试验合并结果显示,两组末次随访ODI评分差异无显著性意义(MD=-6.88,95%CI:-18.75-4.98,P=0.26) [14-15,21],4项回顾性队列研究合并结果显示,两组末次随访ODI评分亦差异无显著性意义(MD=-0.20,95%CI:-1.17-0.78,P=0.33) [12,16,19-20],见图9。
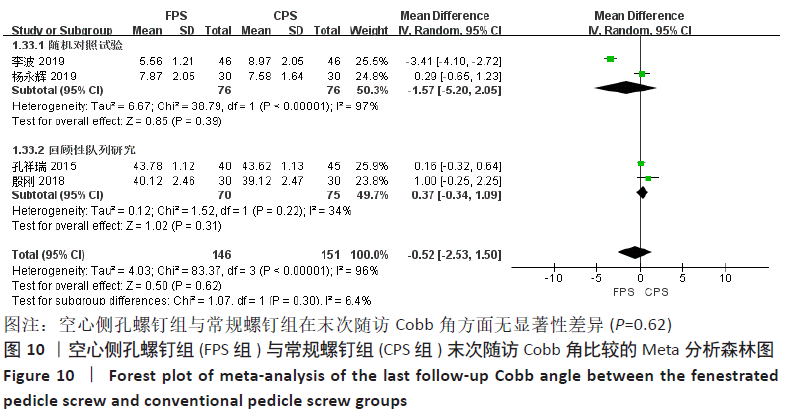
2.4.3 各组影像学结果参数差异 有4项研究比较了末次随访Cobb角[12,14,18-19],
两组间术前Cobb角无显著性差异(P=0.48),各研究之间存在显著异质性 (P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组的末次随访Cobb角差异无显著性意义(MD= -0.52,95%CI:-2.53-1.50,P=0.62),按不同研究类型进行亚组分析,有2项随机对照试验合并结果显示两组间末次随访Cobb角无显著性差异(MD=-1.57,95%CI:-5.20-2.05,P=0.39) [14, 18],有2项回顾性队列研究合并结果显示两组间末次随访Cobb角无显著性差异(MD= 0.37,95%CI:-0.34-1.09,P=0.31) [12, 19],见图10。
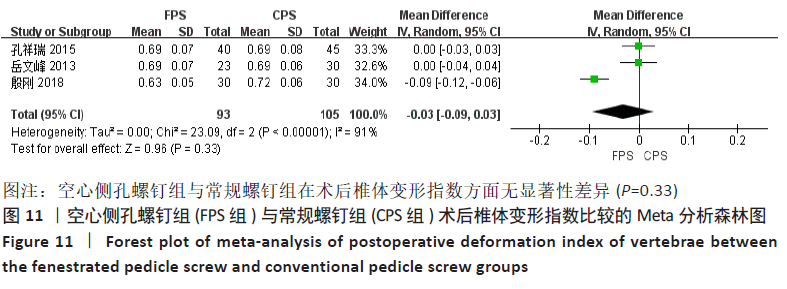
有3项研究比较了术后椎体变形指数[12,19,20],两组间术前椎体变形指数无显著性差异(P=0.79),各研究之间存在显著异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=91%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组术后椎体变形指数差异无显著性意义(MD=-0.03,95%CI:-0.09-0.03,P=0.33),见图11。
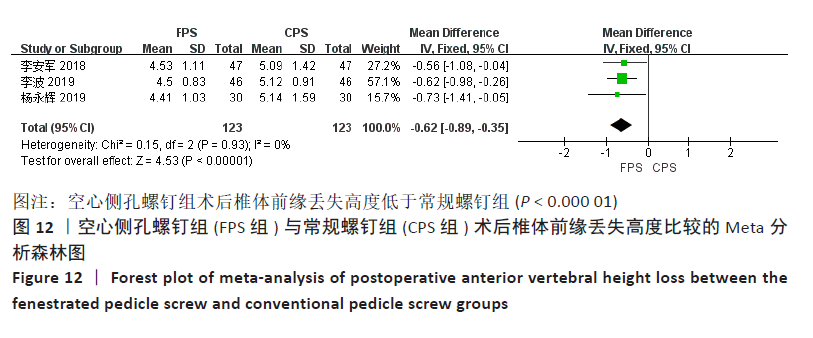
有3项研究比较了术后1个月椎体前缘丢失高度[13-14, 18],两组间术前椎体前缘丢失高度无显著性差异(P=0.91),各研究间不存在异质性(P=0.93,I2= 0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组间差异存在显著性意义(MD=-0.62,95%CI:-0.89至-0.35, P < 0.000 01),空心侧孔螺钉组术后1个月椎体前缘丢失高度低于常规螺钉组,见图12。
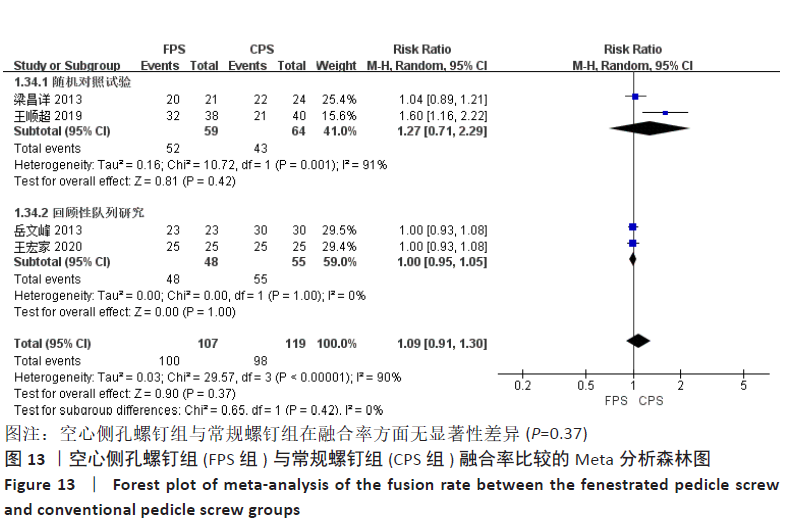
有4项研究比较了随访6个月以上的融合率[15-17,20],空心侧孔螺钉组融合率为93.46%,常规螺钉组融合率为82.35%。各研究间存在显著异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=90%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,两组间差异无显著性意义(MD=1.09,95%CI:0.91-1.30,P=0.37),按不同研究类型进行亚组分析,2项随机对照试验合并结果显示,两组间融合率无显著性差异(MD=1.27,95%CI:0.71-2.29,P=0.42) [15,17],2项回顾性队列研究合并结果显示,两组间融合率无显著性差异(MD=1.00,95%CI:0.95-1.05,P=1.00) [16,20],见图13。
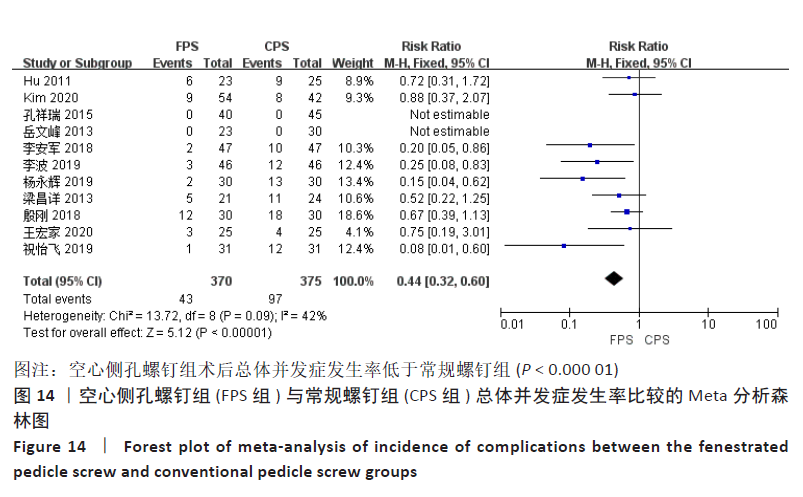
2.4.4 各组术后并发症发生率差异 有11项研究报告了术后总体并发症发生率[12-16,18-23],空心侧孔螺钉组总并发症发生率为11.62%,常规螺钉组总体并发症发生率为25.87%。各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.09,I2=42%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组间总体并发症发生率差异有显著性意义(RR=0.44,95%CI:0.32-0.60,P < 0.000 01),空心侧孔螺钉组总体并发症发生率显著低于常规螺钉组,见图14。
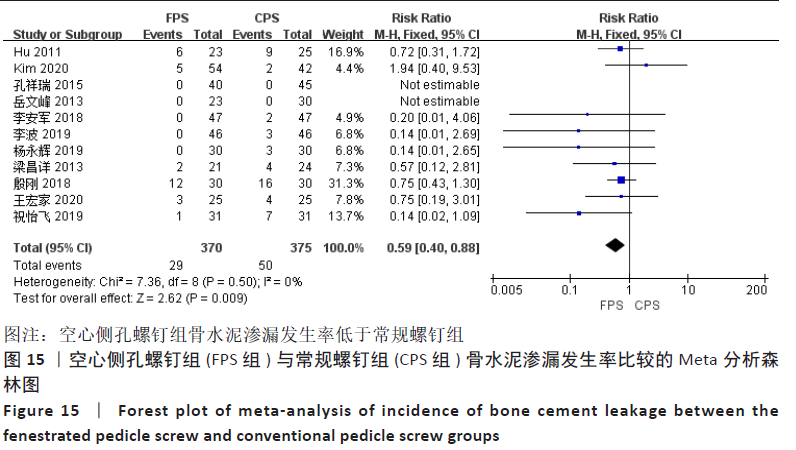
有11项研究报告了骨水泥渗漏发生率[12-16,18-23],空心侧孔螺钉组骨水泥渗漏发生率为7.84%,常规螺钉组为13.33%。各研究间无异质性(P=0.50,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组间差异有显著性意义(RR=0.59,95%CI:0.40-0.88,P=0.009),空心侧孔螺钉组骨水泥渗漏发生率显著低于常规螺钉组,见图15。
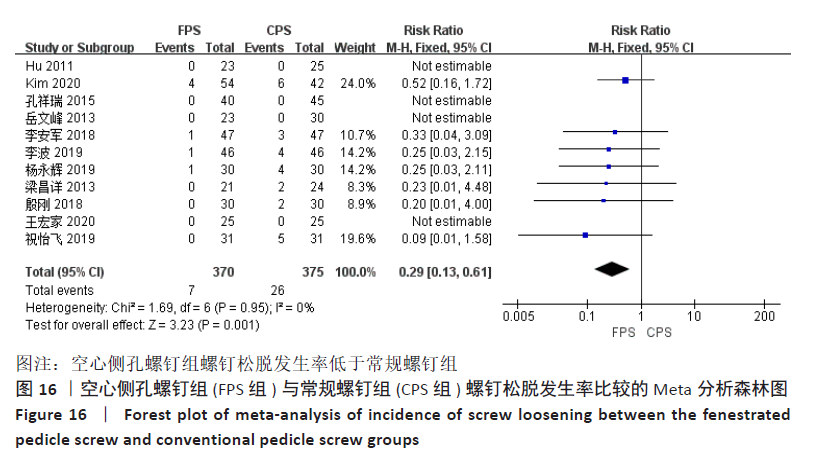
有11项研究报告了螺钉松脱率[12-16,18-23],空心侧孔螺钉组螺钉松脱发生率为1.89%,常规螺钉组为6.93%,各研究间不存在异质性(P=0.95,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:两组间差异有显著性意义(RR=0.29,95%CI:0.13-0.61,P=0.001),空心侧孔螺钉组螺钉松脱发生率显著低于常规螺钉组,见图16。
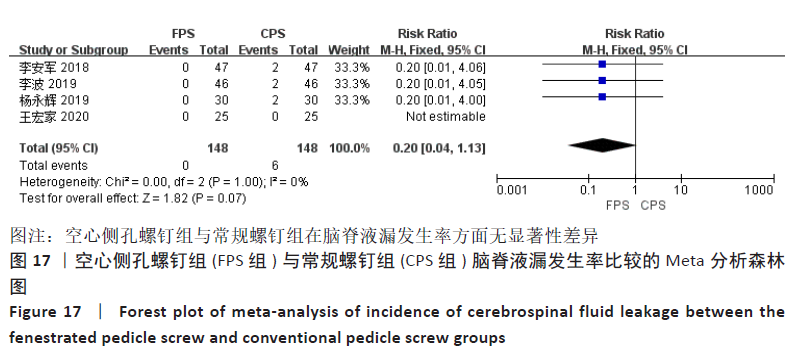
有4项研究报告了脑脊液漏发生率[13-14,16,18],空心侧孔螺钉组未发生脑脊液漏,常规螺钉组脑脊液漏发生率为4.05%,各研究间不存在异质性(P=1.00,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:空心侧孔螺钉组脑脊液漏发生率低于常规螺钉组,但两组间差异无显著性意义(RR=0.22,95%CI:0.04-1.13,P=0.07),见图17。
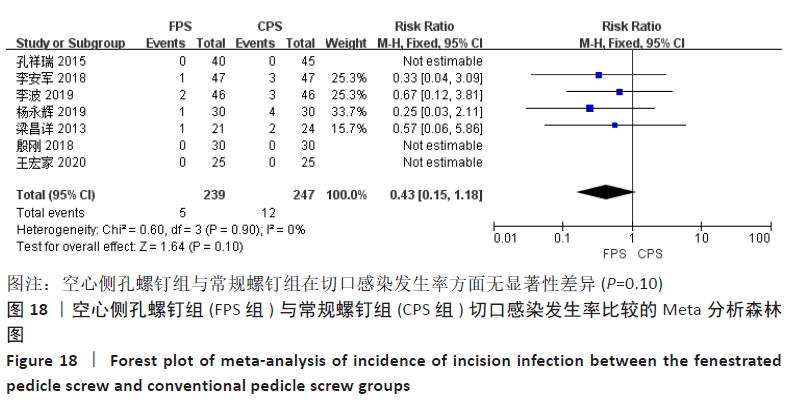
有7项研究报告了切口感染发生率[12-16,18-19],空心侧孔螺钉组切口感染发生率为2.09%,常规螺钉组发生率为4.86%,各研究间不存在异质性(P=0.90,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:空心侧孔螺钉组切口感染发生率低于常规螺钉组,但两组间差异无显著性意义(RR=0.43,95%CI:0.15-1.18,P=0.10),见图18。
2.5 敏感性分析结果 对于手术时间进行敏感性分析,逐一剔除研究后重新进行合并分析,发现异质性未发生显著变化,且两组间比较均无显著性意义,提示Meta分析结果稳定可靠。考虑不同研究者对于手术时间的衡量标准不同以及手术医生的熟练程度均可能影响手术时间,导致研究间异质性较大。
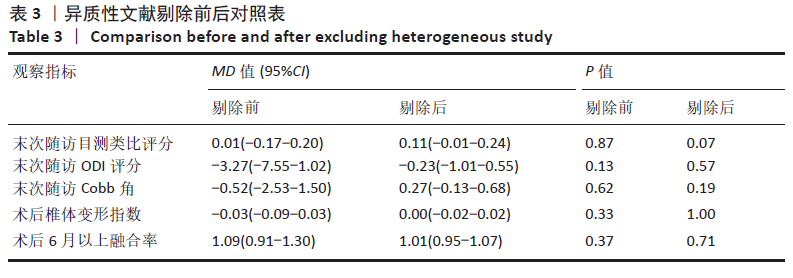
对于末次随访目测类比评分,敏感性分析提示1项研究可能为此指标异质性来源[16],剔除该项研究后结果呈现为无异质性(I2=0%),但两组间比较仍无显著性意义(P=0.07),提示Meta分析结果相对稳定可靠。异质性可能是不同医师对于术后患者的疼痛管理方案不同,如应用止痛药的时间及强度等差异造成。
对于末次随访ODI评分,敏感性分析提示1项研究可能为异质性来源[14],
剔除该项研究后结果呈现为无异质性(I2=0%),但两组间比较仍无显著性意义(P=0.57),提示Meta分析结果相对稳定可靠。其原因主要为该研究中患者术前ODI评分明显高于其他研究的患者,在改善率相近情况下,术后ODI评分仍较高。
对于末次随访Cobb角,敏感性分析提示1项研究可能为异质性来源[14],剔除该项研究后结果呈现为无异质性(I2=0%),但两组间比较仍无显著性意义(P=0.62),提示Meta分析结果相对稳定可靠。考虑到固定节段位置及数量的不同导致Cobb角大小的差异,可能造成研究间的异质性。
对于术后椎体变形指数进行敏感性分析,剔除1项研究后结果呈现为无异质性(I2=0%)[19],但两组间比较仍无显著性意义(P=1),提示Meta分析结果相对稳定可靠。椎体变形指数等参数的测量需依赖于X射线片,且成像质量、拍摄角度、测量方式及测量者个人能力均可影响测量数据,这可能是造成上述研究为异质性来源的原因。
对于术后6个月以上融合率进行敏感性分析,剔除1项研究后结果呈现为无异质性(I2=0%)[17],但两组间比较仍无显著性意义(P=0.71),提示Meta分析结果相对稳定可靠。在融合情况评价方面,CT的精确度高于X射线片,但X射线片经济快捷,故仍为首选的检查方式。上述研究随访时间虽长达1年,但融合率明显低于其他3项研究,考虑其他3项研究均采用X射线片进行评价,而该项研究可能采用了CT检查评价融合情况,从而造成研究间异质性较大。
剔除异质性来源文献前后的效应量可信区间及P值见表3。
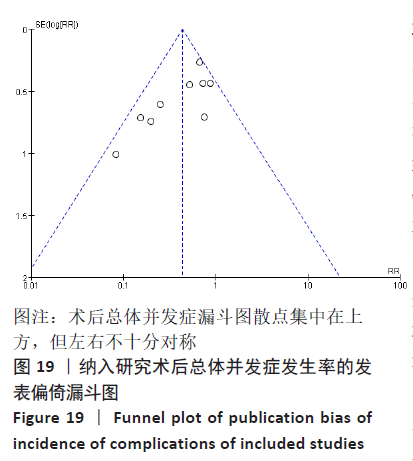
2.6 发表偏倚分析 对术后总体并发症发生率指标进行发表偏倚分析[12-16,18-23],漏斗图提示各项研究集中在漏斗图上方,但左右不十分对称,故可能存在发表偏倚,见图19。