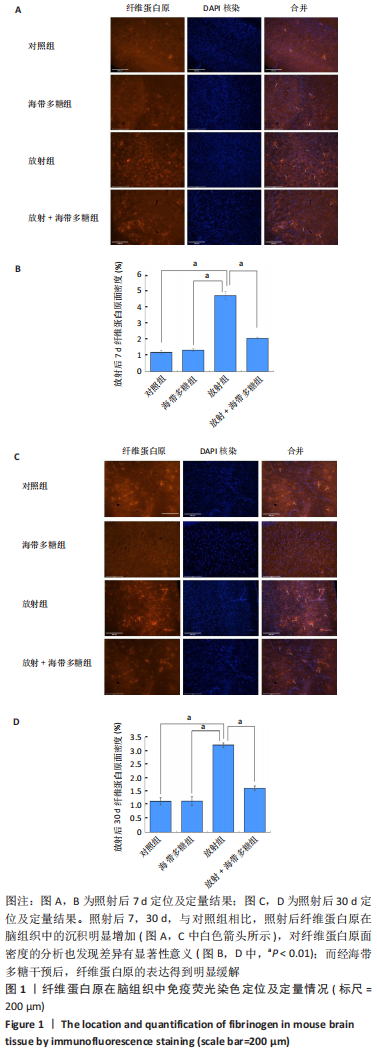
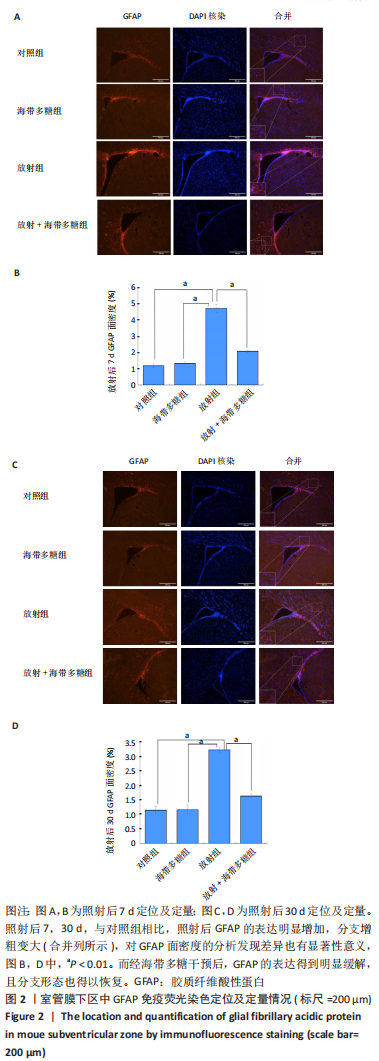
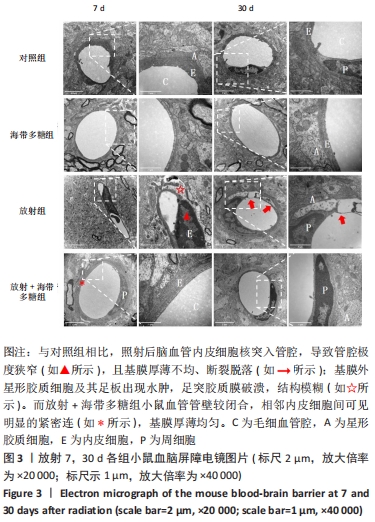
[1] BELTRAN C, NAIK M, MERCHANT TE. Dosimetric effect of target expansion and setup uncertainty during radiation therapy in pediatric craniopharyngioma. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97(3):399-403.
[2] ALI FS, AREVALO O, ZOROFCHIAN S, et al. Cerebral Radiation Necrosis: Incidence, Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Challenges, and Future Opportunities. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21(8):66.
[3] 张海博, 梁海乾, 涂悦, 等. 放射性脑损伤的研究现状[J]. 山东医药, 2014,54(26):95-97.
[4] 阮林, 韦力, 廉春蓉, 等. 全脑照射后血脑屏障改变对放射性脑损伤的影响[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志,2011,37(10):591-595.
[5] MAINPRIZE T, LIPSMAN N, HUANG Y, et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Primary Brain Tumors with Non-invasive MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound: A Clinical Safety and Feasibility Study. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1): 321.
[6] REZAI AR, RANJAN M, D’HAESE PF, et al. Noninvasive hippocampal blood-brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease with focused ultrasound . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(17):9180-9182.
[7] SANDOR N, WALTER FR, BOCSIK A, et al. Low dose cranial irradiation-induced cerebrovascular damage is reversible in mice . PLoS One. 2014; 9(11):e112397.
[8] LUMNICZKY K, SZATMÁRI T, SÁFRÁNY G. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Immune and Inflammatory Reactions in the Brain. Front Immunol. 2017;8:517.
[9] ARVANITIS CD, FERRARO GB, JAIN RK. The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(1):26-41.
[10] TIETZ S, ENGELHARDT B. Brain barriers: Crosstalk between complex tight junctions and adherens junctions . J Cell Biol. 2015;209(4):493-506.
[11] ZHAO X, GUO F, HU J, et al. Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria Japonica . Thromb Res. 2016;144:46-52.
[12] ZENG M, WU X, LI F, et al. Laminaria Japonica Polysaccharides effectively inhibited the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vivo and in vitro study. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2017;69(7):527-532.
[13] 张思琴. 海带多糖通过激活Nrf2通路保护放射诱导下颌下腺氧化应激损伤[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2019.
[14] 陈晨, 张思琴, 韦力, 等. 海带多糖调节小鼠小胶质细胞活化保护放射损伤后的海马记忆功能[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2018,34(3):327-333.
[15] 符桢琳. 海带多糖对放射诱导损伤的神经细胞、内皮细胞影响的体外研究[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2018.
[16] 柴溶, 张思琴, 刘文其, 等. 海带多糖对受照小鼠脑血管损伤的保护作用[J]. 辐射防护,2019,39(3):249-253.
[17] OBERMEIER B, DANEMAN R, RANSOHOFF RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2013; 19(12): 1584-1596.
[18] SWEENEY MD, ZHAO Z, MONTAGNE A, et al. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):21-78.
[19] LANGEN UH, AYLOO S, GU C. Development and Cell Biology of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2019;35:591-613.
[20] IADECOLA C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease. Neuron. 2017;96(1):17-42.
[21] ACHAR A, GHOSH C. Multiple hurdle mechanism and blood-brain barrier in epilepsy: glucocorticoid receptor-heat shock proteins on drug regulation. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(12):2427-2428.
[22] DAVALOS D, MAHAJAN KR, TRAPP BD. Brain fibrinogen deposition plays a key role in MS pathophysiology - Yes . Mult Scler. 2019;25(11):1434-1435.
[23] PETERSEN MA, RYU JK, AKASSOGLOU K. Fibrinogen in neurological diseases: mechanisms, imaging and therapeutics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(5):283-301.
[24] MORITA M, IKESHIMA-KATAOKA H, KREFT M, et al. Metabolic Plasticity of Astrocytes and Aging of the Brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):941.
[25] MIDDELDORP J, HOL EM. GFAP in health and disease . Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93(3):421-43.
[26] BRENNER M. Role of GFAP in CNS injuries. Neurosci Lett. 2014;565: 7-13.
[27] MCGINNIS GJ, FRIEDMAN D, YOUNG KH, et al. Neuroinflammatory and cognitive consequences of combined radiation and immunotherapy in a novel preclinical model. Oncotarget. 2017;8(6):9155-9173.
[28] NATION DA, SWEENEY MD, MONTAGNE A, et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction. Nat Med. 2019;25(2):270-276.
[29] MONTAGNE A, NATION DA, SAGARE AP, et al. APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline. Nature. 2020; 581(7806):71-76.
[30] AHN HJ, ZAMOLODCHIKOV D, CORTES-CANTELI M, et al. Alzheimer’s disease peptide beta-amyloid interacts with fibrinogen and induces its oligomerization . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(50):21812-21817.
|