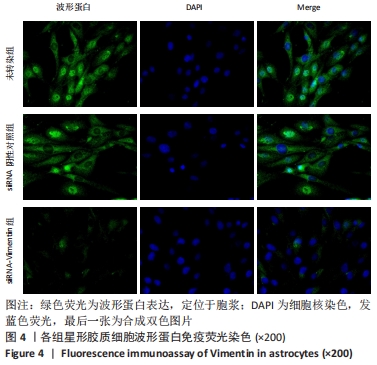
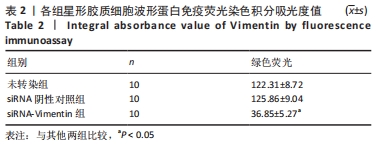
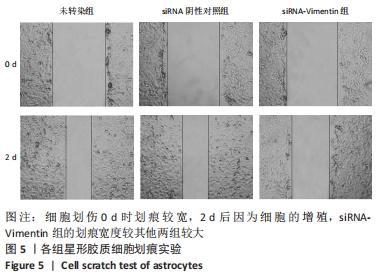
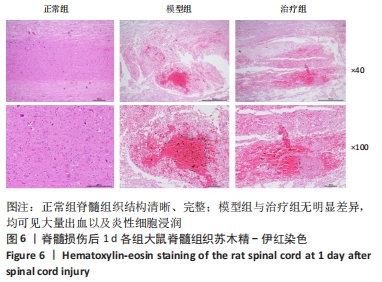
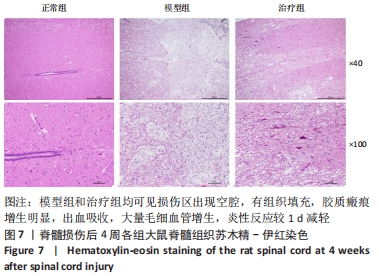
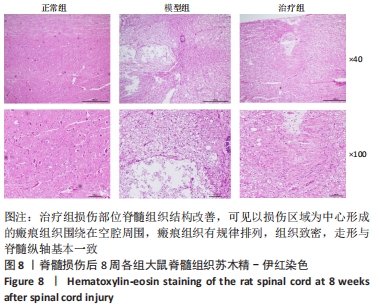
[1] KHORASANIZADEH M, YOUSEFIFARD M, ESKIAN M, et al. Neurological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;30:683-699.
[2] FAULKNER JR, HERRMANN JE, WOO MJ, et al. Reactive astrocytes protect tissue and preserve function after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2004;24(9):2143-2155.
[3] SULLIVAN PZ, ALBAYAR A, BURRELL JC, et al. Implantation of Engineered Axon Tracts to Bridge Spinal Cord Injury Beyond the Glial Scar in Rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(19-20):1264-1274.
[4] BANG M, RYU O, KIM DG, et al. Tenovin-1 Induces Senescence and Decreases Wound-Healing Activity in Cultured Rat Primary Astrocytes. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019;27(3):283-289.
[5] TAN X, CHEN C, ZHU Y, et al. Proteotoxic Stress Desensitizes TGF-beta Signaling Through Receptor Downregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(3):189-199.
[6] WILSON S, FREDERICKS DC, SAFAYI S, et al. Ovine Hemisection Model of Spinal Cord Injury. J Invest Surg. 2021;34(4):380-392.
[7] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[8] AHUJA CS, MOTHE A, KHAZAEI M, et al. The leading edge: Emerging neuroprotective and neuroregenerative cell-based therapies for spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(12):1509-1530.
[9] LI X, LI M, TIAN L, et al. Reactive Astrogliosis: Implications in Spinal Cord Injury Progression and Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:9494352.
[10] KIM YH, HA KY, KIM SI. Spinal Cord Injury and Related Clinical Trials. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):1-9.
[11] ZHENG Y, MAO YR, YUAN TF, et al. Multimodal treatment for spinal cord injury: a sword of neuroregeneration upon neuromodulation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(8):1437-1450.
[12] YILMAZ T, KAPTANOĞLU E. Current and future medical therapeutic strategies for the functional repair of spinal cord injury. World J Orthop. 2015;6(1):42-55.
[13] WILSON JR, TETREAULT LA, KWON BK, et al. Timing of Decompression in Patients With Acute Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review. Global Spine J. 2017;7(3 Suppl):95S-115S.
[14] CEKANAVICIUTE E, BUCKWALTER MS. Astrocytes: Integrative Regulators of Neuroinflammation in Stroke and Other Neurological Diseases. Neurotherapeutics. 2016;13(4):685-701.
[15] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. The Biology of Regeneration Failure and Success After Spinal Cord Injury. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(2):881-917.
[16] DYCK S, KATARIA H, ALIZADEH A, et al. Perturbing chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan signaling through LAR and PTPσ receptors promotes a beneficial inflammatory response following spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):90.
[17] WANG GY, CHENG ZJ, YUAN PW, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation alters the expression of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans and promotes axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(8):1638-1644.
[18] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533.
[19] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553.
[20] WILLIAMS A, PIATON G, LUBETZKI C. Astrocytes--friends or foes in multiple sclerosis? Glia. 2007;55(13):1300-1312.
[21] LENT R, AZEVEDO FA, ANDRADE-MORAES CH, et al. How many neurons do you have? Some dogmas of quantitative neuroscience under revision. Eur J Neurosci. 2012;35(1):1-9.
[22] LOSHAJ-SHALA A, COLZANI M, BREZOVSKA K, et al. Immunoproteomic identification of antigenic candidate Campylobacter jejuni and human peripheral nerve proteins involved in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neuroimmunol. 2018;317:77-83.
[23] TESHIGAWARA K, KUBOYAMA T, SHIGYO M, et al. A novel compound, denosomin, ameliorates spinal cord injury via axonal growth associated with astrocyte-secreted vimentin. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;168(4):903-919.
[24] DANIELSSON F, PETERSON MK, CALDEIRA ARAÚJO H, et al. Vimentin Diversity in Health and Disease. Cells. 2018;7(10):147.
[25] RAGINOV IS, CHELYSHEV IUA, SHAGIDULLIN TF. Interaction of sensory neurons and satellite cells during stimulation of the nerve regeneration. Morfologiia. 2002;122(4):37-39.
[26] BAUMANN HJ, MAHAJAN G, HAM TR, et al. Softening of the chronic hemi-section spinal cord injury scar parallels dysregulation of cellular and extracellular matrix content. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020; 110:103953.
[27] DERVAN AG, ROBERTS BL. Reaction of spinal cord central canal cells to cord transection and their contribution to cord regeneration. J Comp Neurol. 2003;458(3):293-306.
[28] TRUJILLO-CENÓZ O, REHERMANN MI, MACIEL C, et al. The ependymal cell cytoskeleton in the normal and injured spinal cord of mice. J Neurosci Res. 2021;99(10):2592-2609.
[29] POLCYN R, CAPONE M, MATZELLE D, et al. Enolase inhibition alters metabolic hormones and inflammatory factors to promote neuroprotection in spinal cord injury. Neurochem Int. 2020;139:104788.
[30] IZMIRYAN A, LI Z, NOTHIAS F, et al. Inactivation of vimentin in satellite glial cells affects dorsal root ganglion intermediate filament expression and neuronal axon growth in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2021; 115:103659.
[31] HOFSTETTER CP, SCHWARZ EJ, HESS D, et al. Marrow stromal cells form guiding strands in the injured spinal cord and promote recovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(4):2199-2204.
[32] JIN LQ, JOHN BH, HU J, et al. Activated Erk Is an Early Retrograde Signal After Spinal Cord Injury in the Lamprey. Front Neurosci. 2020; 14:580692.
|