[1] 陈谦明.口腔黏膜病学 [M]. 4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2012: 1-175.
[2] LIU N, GUAN S, WANG H, et al. The Antimicrobial Peptide Nal-P-113 Exerts a Reparative Effect by Promoting Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Cell Cycle Progression. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7349351.
[3] CHEN J, BEKALE LA, KHOMTCHOUK KM, et al. Locally administered heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor reduces radiation-induced oral mucositis in mice. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):17327.
[4] ZHAO QM, GAO J, HUANG XX, et al. Concentrated Growth Factors Extracted from Blood Plasma Used to Repair Nasal Septal Mucosal Defect After Rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020;44(2):511-516.
[5] QI L, LIU L, HU Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor promotes gingival regeneration through the AKT/Wnt/β-catenin and YAP signaling pathways. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):920-932.
[6] 张慧,王蕊,王芹,等.重组人表皮生长因子联合糖皮质激素治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓 [J]. 中国临床医生杂志,2019,47(12):1492-1494.
[7] RODELLA LF, FAVERO G, BONINSEGNA R, et al. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(8):772-777.
[8] 魏中武, 刘双喜, 陈灼庚, 等. 比较浓缩生长因子提取液和富血小板纤维蛋白提取液对成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2020,45(8):901-908.
[9] QIN J, WANG L, SUN Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor increases Schwann cell proliferation and neurotrophic factor secretion and promotes functional nerve recovery in vivo. Pubmed. 2016;37(2):493-500.
[10] ZHANG L, AI H. Concentrated growth factor promotes proliferation, osteogenic differentiation, and angiogenic potential of rabbit periosteum-derived cells in vitro. BioMed Central. 2019;14(1):146.
[11] CHEN J, JIAO D, ZHANG M, et al. Concentrated Growth Factors Can Inhibit Photoaging Damage Induced by ultraviolet A (UVA) on the Human Dermal Fibroblasts In Vitro. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:3739-3749.
[12] AGHAMOHAMADI Z, KADKHODAZADEH M, TORSHABI M, et al. A compound of concentrated growth factor and periodontal ligament stem cell-derived conditioned medium. Tissue Cell. 2020;65:101373.
[13] ÖZVERI KB, IŞıK G, ÖZDEN YM, et al. Effect of concentrated growth factor (CGF) on short-term clinical outcomes after partially impacted mandibular third molar surgery: A split-mouth randomized clinical study. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Sur. 2020;121(2):118-123.
[14] KAO CH.Use of concentrate growth factors gel or membrane in chronic wound healing: Description of 18 cases. Int Wound J. 2020;17(1):158-166.
[15] KAMAL A, SALMAN B, ABDUL RNH, et al. The Efficacy of Concentrated Growth Factor in the Healing of Alveolar Osteitis: A Clinical Study. Int J Dent. 2020;2020:9038629.
[16] 李媛姣子, 罗赛, 徐渴鑫, 等. 注射浓缩生长因子改善面部炎性衰老的临床观察 [J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志,2019,30(4):236-239.
[17] ZHAO LL, XI QC, FANG MS, et al. Observation on the Clinical Effect of Breast Augmentation by Transplanting Concentrated Growth Factor and Autologous Fat. CJPRS. 2019;1(3):18-23.
[18] HARDWICKE J, SCHMALJOHANN D, BOYCE D, et al. Epidermal growth factor therapy and wound healing--past, present and future perspectives. Surgeon. 2008;6(3):172-177.
[19] AMIN DN, HIDA K, BIELENBERG DR, et al. Tumor endothelial cells express epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but not ErbB3 and are responsive to EGF and to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2006;66(4):2173-2180.
[20] GALVEZ-CONTRERAS AY, GONZALEZ-CASTANEDA RE, CAMPOS-ORDONEZ T,et al. Phenytoin enhances the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor in the subventricular zone and promotes the proliferation of neural precursor cells and oligodendrocyte differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 2016;43(2):139-147.
[21] XU H, LIU L, CONG M, et al. EGF neutralization antibodies attenuate liver fibrosis by inhibiting myofibroblast proliferation in bile duct ligation mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 2020;154(1):107-116.
[22] 陈洁, 金绍林. 应用纳米银敷料联合表皮生长因子凝胶治疗小面积骨外露创面 [J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2021,25(1):62-65.
[23] KOZER N, CLAYTON AHA. In-cell structural dynamics of an EGF receptor during ligand-induced dimer-oligomer transition. Eur Biophys J. 2020;49(1):21-37.
[24] 刘志荣. 重组人表皮生长因子治疗口腔黏膜损伤的疗效观察 [J]. 山西医药杂志(下半月刊),2012,41(6):586-587.
[25] 王汉明, 朱晓密, 赵雅君. 口疮1号方治疗大鼠口腔溃疡的实验研究 [J].口腔医学研究,2014,30(7):627-629+634.
[26] DHARMANI P, DE SIMONE C, CHADEE K. The probiotic mixture vsl#3 accelerates gastriculcer healing by stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Plos One. 2013;8(3):e58671.
[27] 孙浩博, 吕国忠. 重组人表皮生长因子对深Ⅱ度烧伤患者创面愈合效果及相关炎症因子水平的影响 [J]. 中国美容医学,2020,29(10):75-78.
[28] 刘鹏, 徐全臣, 许晓燕,等.人牙龈成纤维细胞原代培养方法比较 [J]. 齐鲁医学杂志,2016,31(1):18-20+23.
[29] 张建伟, 徐铖, 杨慧雅, 等. 口腔黏膜色素痣4例临床及组织病理分析 [J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志,2012,26(11):993-994+996.
[30] YING J, WANG Q, JIANG M, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Promotes Cell Proliferation and Melanin Synthesis in Primary Human Epidermal Melanocytes. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33(2):61-68.
[31] PARK KY, KIM J. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the Anti-Melanogenesis Effect of Coumaric and Caffeic Acid-Conjugated Peptides in Human Melanocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:922.
[32] ANDO H, YOSHIMOTO S, YOSHIDA M, et al. Dermal Fibroblasts Internalize Phosphatidylserine-Exposed Secretory Melanosome Clusters and Apoptotic Melanocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5789.
[33] 项锦敏, 赵琼瑜, 远航, 等.乌鳖黑色素理化性质及其抗氧化活性研究 [J/OL].天然产物研究与开发:1-15[2021-01-16].
[34] BRISSETT AE, HOM DB. The effects of tissue sealants, platelet gels, and growth factors on wound healing. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2003;11(4):245-250.
[35] CHEN J, JIANG H. Clinical Application of Concentrated Growth Factor Fibrin Combined With Bone Repair Materials in Jaw Defects. CJOMS. 2020;78(7):1041.
[36] JIN R, SONG G, CHAI J, et al. Effects of concentrated growth factor on proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9:2041731418817505.
[37] MORIKAWA M, DERYNCK R, MIYAZONO K. TGF-β and the TGF-β Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. CSH Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a021873.
[38] HRUBI E, IMRE L, ROBASZKIEWICZ A, et al. Diverse effect of BMP-2 homodimer on mesenchymal progenitors of different origin. Hum Cell. 2018;31(2):139-148.
[39] MELINCOVICI CS, BOŞCA AB, ŞUŞMAN S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018;59(2):455-467.
[40] MIHAYLOVA Z, TSIKANDELOVA R, SANIMIROV P, et al. Role of PDGF-BB in proliferation, differentiation and maintaining stem cell properties of PDL cells in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;85:1-9.
[41] 江飞玉. FGF21在高糖状态下对前列腺癌细胞增殖、自噬的影响及其机制研究 [D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学,2020.
[42] ZHAO X, DAI W, ZHU H, et al. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces apoptosis in a transfected cell line expressing EGF receptor on its membrane. Cell Biol Int. 2006;30(8): 653-658.
[43] ARE A, PINAEV G, BUROVA E, et al. Attachment of A-431 cells on immobilized antibodies to the EGF receptor promotes cell spreading and reorganization of the microfilament system. Cell Motil Cytoskel. 2001;48(1):24-36.
[44] 罗雅馨, 毕浩然, 陈晓旭, 等. 细胞外基质与组织的再生与修复 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(11):1785-1790.
[45] 陈盈哲, 全知怎, 姜葳, 等. 口腔黏膜创伤修复中生长因子对牙龈成纤维细胞的影响及调节机制 [J]. 广西医科大学学报,2018,35(10): 1335-1340.
[46] 任科伟, 范卫民, 姜雪峰,等. 周期性机械应力通过激活EGFR-ERK1/2信号通路促进大鼠软骨细胞增殖和细胞外基质合成 [J]. 江苏医药,2013,39(21):2526-2528.
[47] ARıCAN G, ÖZMERIÇ A, FıRAT A, et al. Micro-ct findings of concentrated growth factors (cgf) on bone healing in masquelet’s technique-an experimental study in rabbits.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2020;10.1007/s00402-020-03596-z.
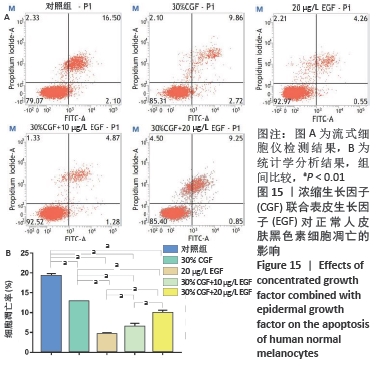
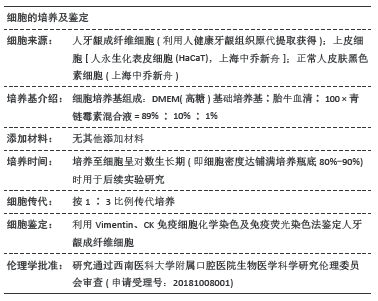
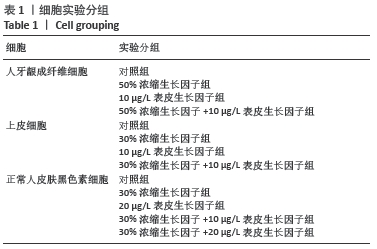
|