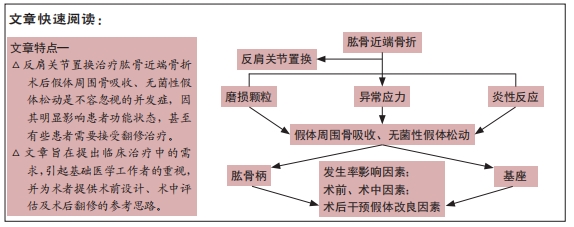
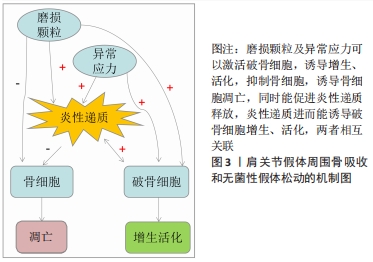
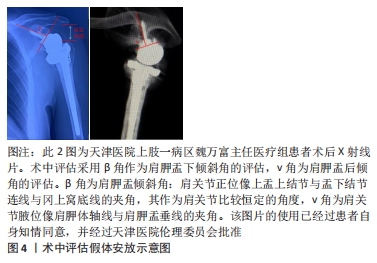
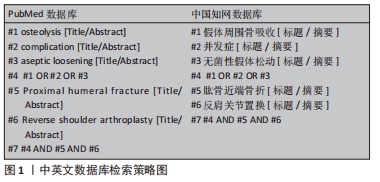
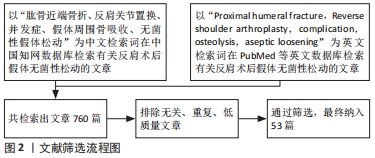
[1] MCLEAN AS, PRICE N, GRAVES S, et al. Nationwide trends in management of proximal humeral fractures: an analysis of 77,966 cases from 2008 to 2017. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(11):2072-2078.
[2] KLUG A A-O, GRAMLICH Y, WINCHERINGER D, et al. Trends in surgical management of proximal humeral fractures in adults: a nationwide study of records in Germany from 2007 to 2016. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019; 139(12):1713-1721.
[3] CHALMERS PN, BOILEAU P, ROMEO AA, et al. Revision reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(12):426-436.
[4] GREY B, RODSETH RN, ROCHE SJ. Humeral stem loosening following reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(5):e5.
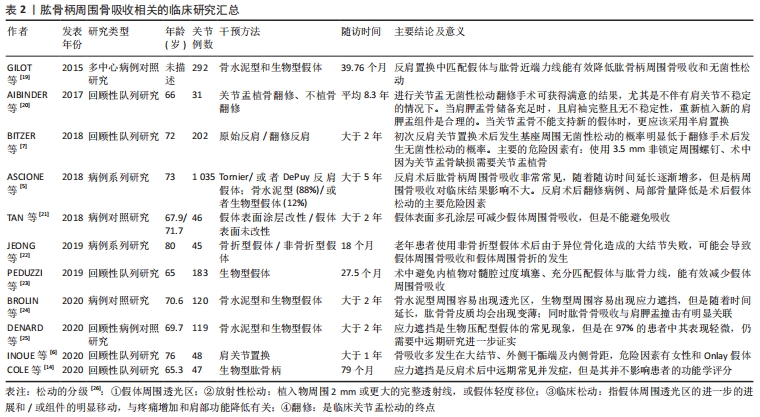
[5] ASCIONE F, DOMOS P, GUARRELLA V, et al. Long-term humeral complications after Grammont-style reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(6):1065-1071.
[6] INOUE K, SUENAGA N, OIZUMI N, et al. Humeral bone resorption after reverse shoulder arthroplasty using uncemented stem. JSES Int. 2020;4(1): 138-143.
[7] BITZER A, ROJAS J, PATTEN IS, et al. Incidence and risk factors for aseptic baseplate loosening of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(12):2145-2152.
[8] KARELSE A, VAN TONGEL A, VAN ISACKER T, et al. Parameters influencing glenoid loosening. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13(8):773-784.
[9] MAGONE K, LUCKENBILL D, GOSWAMI T. Metal ions as inflammatory initiators of osteolysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(5):683-695.
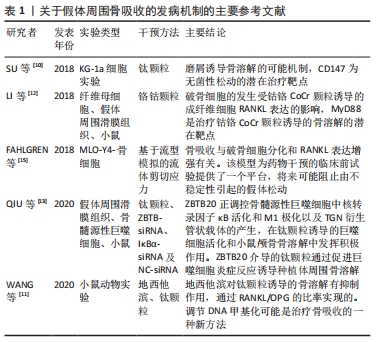
[10] SU B, LI D, XU J, et al. Wear particles enhance autophagy through up-regulation of CD147 to promote osteoclastogenesis. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(8):806-812.
[11] WANG Y, LIU H, WU J, et al. 5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine inhibits osteolysis induced by titanium particles by regulating RANKL/OPG ratio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(3):629-634.
[12] LI D, WANG H, LI Z, et al. The inhibition of RANKL expression in fibroblasts attenuate CoCr particles induced aseptic prosthesis loosening via the MyD88-independent TLR signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(2):1115-1122.
[13] QIU J, PENG P, XIN M, et al. ZBTB20-mediated titanium particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting macrophage inflammatory responses. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(11):3147-3163.
[14] COLE EW, MOULTON SG, GOBEZIE R, et al. Five-year radiographic evaluation of stress shielding with a press-fit standard length humeral stem. JSES Int. 2020;4(1):109-113.
[15] FAHLGREN A, BRATENGEIER C, SEMEINS C M, et al. Supraphysiological loading induces osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis in a novel in vitro model for bone implant loosening. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(5):1425-1434.
[16] VERONESI F, TSCHON M, FINI M. Gene expression in osteolysis:review on the identification of altered molecular pathways in preclinical and clinical studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):499.
[17] CAMUZARD O, BREUIL V, CARLE GF, et al. Autophagy involvement in aseptic loosening of arthroplasty components. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(5):466-472.
[18] EGER M, HIRAM-BAB S, LIRON T, et al. Mechanism and prevention of titanium particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2963.
[19] GILOT G, ALVAREZ-PINZON AM, WRIGHT TW, et al. The incidence of radiographic aseptic loosening of the humeral component in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(10):1555-1559.
[20] AIBINDER WR, SCHOCH B, SCHLECK C, et al. Revisions for aseptic glenoid component loosening after anatomic shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(3):443-449.
[21] TAN MT, READ JW, BOKOR DJ. Does proximal porous coating in short-stem humeral arthroplasty reduce stress shielding? Shoulder Elbow. 2019;11(2 Suppl):56-66.
[22] JEONG JJ, KONG CG, PARK SE, et al. Non-fracture stem vs fracture stem of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in complex proximal humeral fracture of asian elderly. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(12):1649-1657.
[23] PEDUZZI L, GOETZMANN T, WEIN F, et al. Proximal humeral bony adaptations with a short uncemented stem for shoulder arthroplasty:a quantitative analysis. JSES Open Access. 2019;3(4):278-286.
[24] BROLIN TJ, COX RM, HORNEFF III JG, et al. Humeral-sided radiographic changes following reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020;8(1):50-57.
[25] DENARD PJ, HAIDAMOUS G, GOBEZIE R, et al. Short-term evaluation of humeral stress shielding following reverse shoulder arthroplasty using press-fit fixation compared with cemented fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):906-912.
[26] GERALDES DM, HANSEN U, AMIS AA. Parametric analysis of glenoid implant design and fixation type. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(4):775-784.
[27] SANCHEZ-SOTELO J, O’DRISCOLL SW, TORCHIA ME, et al. Radiographic assessment of cemented humeral components in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001;10(6):526-531.
[28] INOUE K, SUENAGA N, OIZUMI N, et al. Humeral bone resorption after anatomic shoulder arthroplasty using an uncemented stem. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(11):1984-1989.
[29] KAHN T, CHALMERS PN. Proximal humeral bone loss in revision shoulder arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(1):87-95.
[30] LUNG TS, CRUICKSHANK D, GRANT HJ, et al. Factors contributing to glenoid baseplate micromotion in reverse shoulder arthroplasty:a biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(4):648-653.
[31] MARIAUX S, OBRIST R, FARRON A, et al. Is preoperative glenoid bone mineral density associated with aseptic glenoid implant loosening in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):49.
[32] NYFFELER RW, SHEIKH R, ATKINSON TS, et al. Effects of glenoid component version on humeral head displacement and joint reaction forces:an experimental study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(5):625-629.
[33] WATLING JP, SANCHEZ JE, HEILBRONER SP, et al. Glenoid component loosening associated with increased critical shoulder angle at midterm follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(3):449-454.
[34] HO JC, THAKAR O, CHAN WW, et al. Early radiographic failure of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with structural bone graft for glenoid bone loss. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(3):550-560.
[35] PATEL RJ, GULOTTA L, WRIGHT TM, et al. Effects of osteoarthritis on load transfer after cemented total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(3):407-415.
[36] LAVER L, GARRIGUES GE. Avoiding superior tilt in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a review of the literature and technical recommendations. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(10):1582-1590.
[37] MAURER A, FUCENTESE SF, PFIRRMANN CW, et al. Assessment of glenoid inclination on routine clinical radiographs and computed tomography examinations of the shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(8):1096-1103.
[38] WALCH G, BADET R, BOULAHIA A, et al. Morphologic study of the glenoid in primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(6):756-760.
[39] VIRK M, YIP M, LIUZZA L, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes with a posteriorly augmented glenoid for Walch B2, B3, and C glenoids in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):e196-e204.
[40] PLESSERS K, VERHAEGEN F, VAN DIJCK C, et al. Automated quantification of glenoid bone defects using 3-dimensional measurements. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):1050-1058.
[41] GUPTA A, THUSSBAS C, KOCH M, et al. Management of glenoid bone defects with reverse shoulder arthroplasty-surgical technique and clinical outcomes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(5):853-862.
[42] MALAHIAS MA, CHYTAS D, KOSTRETZIS L, et al. Bone grafting in primary and revision reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for the management of glenoid bone loss:A systematic review. J Orthop. 2020;20:78-86.
[43] DEBEER P, BERGHS B, POULIART N, et al. Treatment of severe glenoid deficiencies in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: the Glenius Glenoid Reconstruction System experience. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(8): 1601-1608.
[44] PATEL RJ, WRIGHT TM, GAO Y. Load transfer after cemented total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(10):1553-1562.
[45] VERHAEGEN F, CAMPOPIANO E, DEBEER P, et al. How much bone support does an anatomic glenoid component need? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020; 29(4):743-754.
[46] RIVERA MC, PERNI S, SLOAN A, et al. Anti-inflammatory drug-eluting implant model system to prevent wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:1069-1084.
[47] ALOTAIBI HF, PERNI S, PROKOPOVICH P. Nanoparticle-based model of anti-inflammatory drug releasing LbL coatings for uncemented prosthesis aseptic loosening prevention. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7309-7322.
[48] CHEVALIER Y, SANTOS I, MüLLER PE, et al. Bone density and anisotropy affect periprosthetic cement and bone stresses after anatomical glenoid replacement:A micro finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1724-1733.
[49] TERRIER A, OBRIST R, BECCE F, et al. Cement stress predictions after anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty are correlated with preoperative glenoid bone quality. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(9):1644-1652.
[50] CASP AJ, MONTGOMERY SR JR, CANCIENNE JM, et al. Osteoporosis and implant-related complications after anatomic and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(3):121-127.
[51] SMITH JM, CANCIENNE JM, BROCKMEIER SF, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and total shoulder arthroplasty complications. Shoulder Elbow. 2021;13(1):99-105.
[52] WANG P, SHANG GQ, XIANG S, et al. Zoledronic acid and teriparatide have a complementary therapeutic effect on aseptic loosening in a rabbit model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):580.
[53] HSU JE, HACKETT DJ JR, VO KV, et al. What can be learned from an analysis of 215 glenoid component failures? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(3):478-486.
|