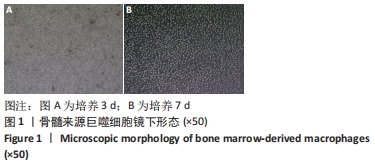
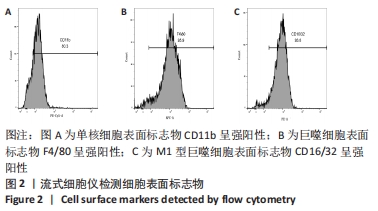
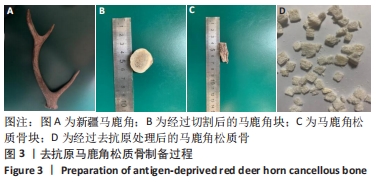
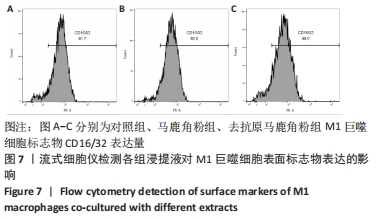
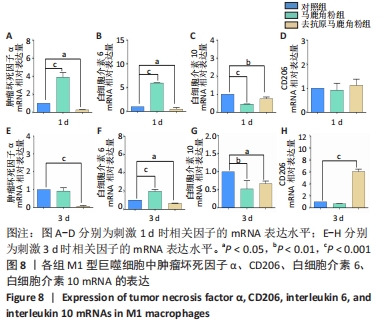
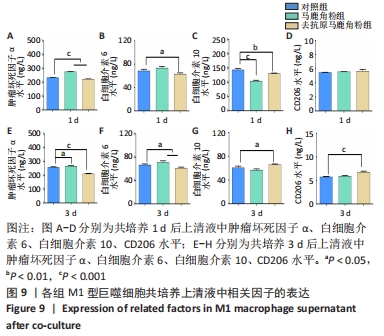
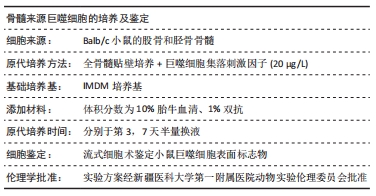
[1] 贺唯,樊瑜波,李晓明,等.骨修复材料活性机制和应用的最新研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(9):1107-1115.
[2] MONTERO J, BECERRO A, PARDAL-PELÁEZ B, et al. Main 3D Manufacturing Techniques for Customized Bone Substitutes. A Systematic Review. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(10):2524.
[3] SWETHA S, LAVANYA K, SRUTHI R, et al. An insight into cell-laden 3D-printed constructs for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(43):9836-9862.
[4] PARK SA, LEE HJ, KIM KS, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffold Implantation Combined with β-TCP Powder for Alveolar Bone Augmentation in a Beagle Defect Model. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(2):238.
[5] BELLO YD, DI DOMENICO MB, MAGRO LD, et al. Bond strength between composite repair and polymer-infiltrated ceramic-network material: Effect of different surface treatments. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2019;31(3):275-279.
[6] KHAN MUA, ABD RAZAK SI, MEHBOOB H, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver-Coated Polymeric Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: Antibacterial and In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility. ACS Omega. 2021; 6(6):4335-4346.
[7] KLOPFLEISCH R, JUNG F. The pathology of the foreign body reaction against biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):927-940.
[8] JAYASINGAM SD, CITARTAN M, THANG TH, et al. Evaluating the Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue: Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice. Front Oncol. 2020;9:1512.
[9] CHU C, LIU L, WANG Y, et al. Macrophage phenotype in the epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)-modified collagen determines foreign body reaction. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(6):1499-1507.
[10] GUILLIAMS M, MILDNER A, YONA S. Developmental and Functional Heterogeneity of Monocytes. Immunity. 2018;49(4):595-613.
[11] HU Z, MA C, RONG X, et al. Immunomodulatory ECM-like Microspheres for Accelerated Bone Regeneration in Diabetes Mellitus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(3):2377-2390.
[12] 赵小琦. 3D打印马鹿角粉组织工程骨支架的体外及体内实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2019.
[13] 赵小琦,丁刘闯,韩祥祯,等.3D打印鹿角粉/聚乙烯醇支架与纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架的性能比较[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(9):1011-1015.
[14] MENG S, ZHANG X, XU M, et al. Effects of deer age on the physicochemical properties of deproteinized antler cancellous bone: an approach to optimize osteoconductivity of bone graft. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(3):035006.
[15] 陈毓,李锋涛,钱大玮,等.马鹿角及梅花鹿角脱盘中无机元素分析与评价[J].中成药,2014,36(12):2577-2582.
[16] PICAVET PP, BALLIGAND M. Organic and mechanical properties of Cervidae antlers: a review. Vet Res Commun. 2016;40(3-4):141-147.
[17] 张亚楠,严霞,孟增东.Zn、Mg增强羟基磷灰石骨修复材料临床应用与机制:生物活性及成骨诱导的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):606-611.
[18] HU T, XU H, WANG C, et al. Magnesium enhances the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting activated macrophage-induced inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3406.
[19] 胡涂.镁通过调控巨噬细胞极化影响间充质干细胞软骨分化的研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2018.
[20] ALMEIDA JC, WACHA A, GOMES PS, et al. A biocompatible hybrid material with simultaneous calcium and strontium release capability for bone tissue repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;62:429-438.
[21] LIU E, LI Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Hepcidin Induces M1 Macrophage Polarization in Monocytes or THP-1 Derived Macrophages. Iran J Immunol. 2019;16(3):190-199.
[22] ROCHELSON B, DOWLING O, SCHWARTZ N, et al. Magnesium sulfate suppresses inflammatory responses by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HuVECs) through the NFkappaB pathway. J Reprod Immunol. 2007;73(2):101-107.
[23] LI B, CAO H, ZHAO Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo responses of macrophages to magnesium-doped titanium. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42707.
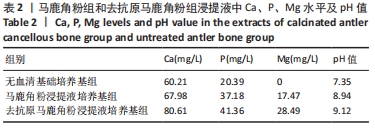
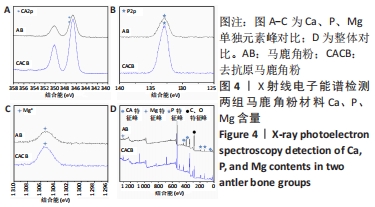
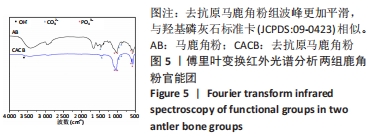
[24] 孟松,张学慧,邓旭亮.煅烧鹿角松质骨浸提液对BMSCs成骨分化的影响[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2015,29(3):129-132.
[25] HE C, LARSON-CASEY JL, GU L, et al. Cu,Zn-Superoxide Dismutase-Mediated Redox Regulation of Jumonji Domain Containing 3 Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55(1):58-71.
[26] WU H, ZHAO G, JIANG K, et al. Plantamajoside ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;35:315-322.
[27] ZHOU X, YANG W, LI J. Ca2+- and protein kinase C-dependent signaling pathway for nuclear factor-kappaB activation, inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(42):31337-31347.
[28] GAO F, DING B, ZHOU L, et al. Magnesium sulfate provides neuroprotection in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia by inhibiting NF-κB pathway. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2):944-950.
|