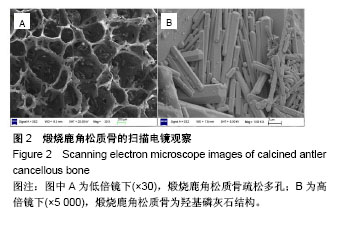
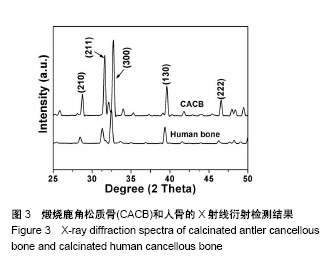
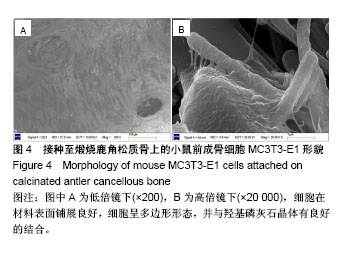
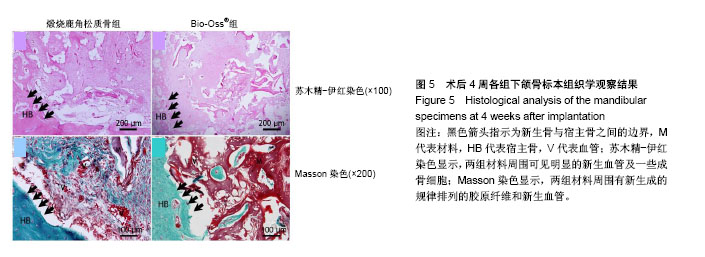
| [1] Hesse E,Kluge G,Atfi A,et al Repair of a segmental long bone defect in human by implantation of a novel multiple disc graft. Bone.2010;46:1457-1463. [2] Parikh SN.Bone graft substitutes in modern orthopedics. Orthopedics.2002;25(11):1301-1309. [3] Torroni A.Engineered bone grafts and bone flaps for maxillofacial defects: state of the art.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67:1121-1127. [4] Muschler GF,Nakamoto C,Griffith LG.Engineering principles of clinical cell-based tissue engineering.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(7):1541-1558.[5] Liu T,Wu G,Wismeijer D,et al.Deproteinized bovine bone functionalized with the slow delivery of BMP-2 for the repair of critical-sized bone defects in sheep.Bone. 2013;56(1):110-118.[6] Carmagnola D,Adriaens P,Berglundh T.Healing of human extraction sockets filled with Bio-Oss®. Clin Oral Implants Res.2003;14:137-143. [7] Park SA,Shin JW,Yang YI,et al.In vitro study of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells on heat-treated porcine trabecular bone blocks.Biomaterials. 2004;25(3): 527-535. [8] Zitzmann NU,Scharer P,Marinello CP,et al.Alveolar ridge augmentation with Bio-Oss®: a histologic study in humans.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2001;21(3):289-295. [9] Briem D,Linhart WL,Lehmann W,et al.Long-term results after application of a porous hydroxyapatite ceramic (Endobon) in proximal tibia fractures.Unfallchirurg. 2002; 105:128-133. [10] Figueiredo M,Henriques J,Martins G,et al.Physicochemical characterization of biomaterials commonly used in dentistry as bone substitutes—comparison with human bone.J Biomed Mater Res B.2010; 92(B):409-419. [11] Chen PY,Stokes AG,Mckittrick J.Comparison of the structure and mechanical properties of bovine femur bone and antler of the North American elk(Cervus elaphus canadensis).Acta Biomater.2009;5(2):693-706.[12] Zhang X,Cai Q,Liu H,et al.Osteoconductive effectiveness of bone graft derived from antler cancellous bone: an experimental study in the rabbit mandible defect model.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41(11):1330-1337.[13] Zhang X,Xu M,Song L,et al.Effects of compatibility of deproteinized antler cancellous bone with various bioactive factors on their osteogenic potential.Biomaterials. 2013; 34(36):9103-9114.[14] Wei J,Xu M,Zhang X,et al.Enhanced Osteogenic Behavior of ADSCs Produced by Deproteinized Antler Cancellous Bone and Evidence for Involvement of ERK Signaling Pathway. Tissue Eng Part A.2015; 21:1810-1821.[15] Grellier M,Bordenave L,Amédée J.Cell-to-cell communication between osteogenic and endothelial lineages: implications for tissue engineering.Trends Biotechnol.2009;27(10):562-571.[16] Griffith LG,Naughton G.Tissue engineering--current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science. 2002;295 (5557):1009-1014.[17] Otfinowski J.Heterotopic Indution of osteogenesis in the course of neural injury.J Patol Pol.1993;44(3):133-168.[18] Hara-Irie F,Amizuka N,Ozawa H.Immunohistoehemieal and ultrastructural localization of CGRP-Positive nerve fibers at the epiphyseal trabeeules facing the growth Plate of rat femurs. Bone.1996;18(1):29-39.[19] Develioglu H,Saraydin SU,Kartal U.The bone-healing effect of a xenograft in a rat calvarial defect model.Dent Mater J. 2009,28(4):396-400. [20] Develioglu H,Saraydin SU,Kartal U,et al.Evaluation of the long-term results of rat cranial bone repair using a particular xenograft.J Oral Implantol.2010;36(3):167-173. [21] Landete-Castillejos T,Estevez JA,Martínez A,et al.Does chemical composition of antler bone reflect the physiological effort made to grow it?Bone.2007;40(4):1095-1102.[22] Wu F,Li H,Jin L,et al.Deer antler base as a traditional Chinese medicine: A review of its traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol.2013;145(2):403-415. [23] Ooi CY,Hamdi M,Ramesh S.Properties of hydroxyapatite produced by annealing of bovine bon.Ceramic Int. 2007; 33(7):1171-1177.[24] Figueiredo M,Fernando A,Martins G,et al.Effect of the calcination temperature on the composition and microstructure of hydroxyapatite derived from human and animal bone.Ceramic Int.2010;36(8): 2383-2393.[25] Meng S,Zhang X,Xu M,et al.Effects of deer age on the physicochemical properties of deproteinized antler cancellous bone: an approach to optimize osteoconductivity of bone graft.Biomed Mater.2015;10(3):035006.[26] Kasten P,Beyen I,Niemeyer P,et al.Porosity and pore size of beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold can influence protein production and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: an in vitro and in vivo study.Acta Biomater.2008;4(6):1904-1915.[27] Karageorgiou V,Kaplan D.Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis.Biomaterials.2005; 26(27):5474-5491.[28] van Steenberghe D,Callens A,Geers L,et al.The clinical use of deproteinized bovine bone mineral on bone regeneration in conjunction with immediate implant installation.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(3):210-216.[29] Laurencin C,Khan Y,Elamin SF.Bone graft substitutes.Expert Rev Med Devices.2006;3(1):49-57.[30] Linsley CS,Wu BM,Tawil B.Mesenchymal stem cell growth on and mechanical properties of fibrin-based biomimetic bone scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(12):2945-2953.[31] Goss TP,Cox QG,Jinnah RH.History and current application of bone transplantation. Orthopedics.1993;16(8):895-900.[32] Kirkeby OJ,Nordsletten L,Skjeldal S,et al.Circulation in corticocancelous bone grafts measured with laser Doppler flowmettry. An experimental study in rats.Stand J Plast Reconstr Sury Hand Sury.1994;28(4):249-254.[33] Burder SP,Fox BS.Tissue engineering of bone. Cell based strategies.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1999;(367 Suppl):S68-83.[34] Griller M,Ferreira-Tojais N,Bourget C,et al.Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the communication between human osteoprogenitors and endothelial cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(3): 390-398. [35] Villars F,Bordenave L,Bareille R,et al.Effect of human endothelial cells on human bone marrow stromal cell phenotype: role of VEGF?J Cell Biochem. 2000;79(4): 672-685. [36] Aguirre A,Planell JA,Engel E.Dynamics of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell/mesenchymal stem cell interaction in co-culture and its implications in angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;400(2): 284-291. [37] Stein H,Perren SM,Cordey J,et al.The muscle bed--a crucial factor for fracture healing: a physiological concept. Orthopedics. 2002;25(12):1379-1383.[38] 鲍小刚,许国华.工程骨的快速血管化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(7):1063-1069.[39] Mastrogiacomo M,Corsi A,Francioso E,et al.Reconstruction of extensive long bone defects in sheep using resorbable bioceramics based on silicon stabilized tricalcium phosphate.Tissue Eng Part A.2006;12(5):1261-1273.[40] Geiger F,Bertram H,Berger I,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor gene-activatedmatrix (VEGF165-GAM) enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in large segmental bone defects.J BoneMiner Res.2005;20(11):2028-2035.[41] 余希杰,杨志明,马骏荣.成骨细胞的细胞社会学特征[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,1998,12(6):350-354.[42] Das A,Botchwey E.Evaluation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2011; 17(6):403-414.[43] Kaigler D,Krebsbach PH,Polverini PJ,et al.Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone marrow stromal cell modulation of endothelial cells.Tissue Eng.2003;9(1):95-103.[44] Chandra VS,Baskar G,Suganthi RV,et al.Blood compatibility of iron-doped nanosize hydroxyapatite and its drug release. ACS Appl Mater Inter.2012;4:1200-1210. |
.jpg)

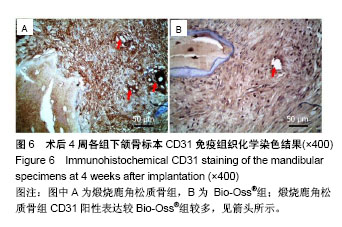
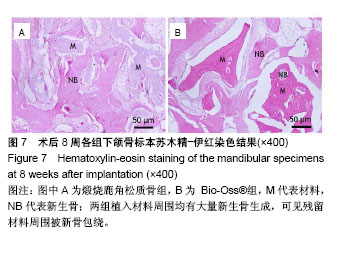
.jpg)