[1] PEREZ JR, KOUROUPIS D, LI DJ, et al. Tissue Engineering and Cell-Based Therapies for Fractures and Bone Defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018; 6:105.
[2] 杨楠,何惠宇,胡杨,等.复合骨髓间充质干细胞同种异体支架骨修复羊髂骨极限缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16):2859-2868.
[3] WANG W, YEUNG KWK. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact Mater. 2017;2(4):224-247.
[4] LEE SH, NOH SH, CHUN KC, et al. A case of bilateral revision total knee arthroplasty using distal femoral allograft-prosthesis composite and femoral head allografting at the tibial site with a varus-valgus constrained prosthesis: ten-year follow up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):69.
[5] KUBOSCH EJ, BERNSTEIN A, WOLF L, et al. Clinical trial and in-vitro study comparing the efficacy of treating bony lesions with allografts versus synthetic or highly-processed xenogeneic bone grafts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:77.
[6] 杨川博,何惠宇.牙槽骨缺损修复治疗新进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2012,5(3):182-185.
[7] DE WITTE TM, FRATILA-APACHITEI LE, ZADPOOR AA, et al. Bone tissue engineering via growth factor delivery: from scaffolds to complex matrices. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(4):197-211.
[8] 赵小琦,丁刘闯,韩祥祯,等.3D打印马鹿角粉/聚乙烯醇支架与纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架的性能比较[J].口腔医学研究,2018, 34(9):1011-1015.
[9] WU F, LI H, JIN L, et al. Deer antler base as a traditional Chinese medicine: a review of its traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;145(2):403-415.
[10] DEHGHAN-MANSHADIA N, FATTAHIA S, HADIZADEHA M, et al.The influence of elastomeric polyurethane type and ratio on the physicochemical properties of electrospun polyurethane/silk fibroin hybrid nanofibers as potential scaffolds for soft and hard tissue engineering. European Polymer Journal. 2019;12(121):109294.
[11] VANAWATI N, BARLIAN A, TABATA Y, et al. Comparison of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells biocompatibility data growth on gelatin and silk fibroin scaffolds. Data Brief. 2019;27:104678.
[12] 刘小元,张凯,韩祥祯,等.3D打印复合PVA骨组织工程支架研究现状[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(1):52-55.
[13] AN L, SHI Q, FAN M, et al. Benzo[a]pyrene injures BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through AhR reducing BMPRII. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;203:110930.
[14] YORUKOGLU AC, KITER AE, AKKAYA S, et al. A Concise Review on the Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cell Sheet-Based Tissue Engineering with Special Emphasis on Bone Tissue Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2374161.
[15] THE MINISTRY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals.2006-09-30.
[16] 周琦琪.3D打印组织工程骨支架的骨改建机制研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2017.
[17] 赵小琦,周琦琪,韩祥祯,等.马鹿角粉复合支架与纳米级羟基磷灰石复合支架的性能比较[J].口腔医学,2017,37(9):791-795.
[18] 丁刘闯,赵小琦,韩祥祯,等.3D打印PVA/nHA支架与SF(丝素蛋白)/PVA/nHA支架的性能比较[J].口腔医学,2018,38(7):598-602.
[19] 赵小琦.3D打印马鹿角粉组织工程骨支架的体外及体内实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2019.
[20] PAZ AG, MAGHAIREH H, MANGANO FG. Stem Cells in Dentistry: Types of Intra- and Extraoral Tissue-Derived Stem Cells and Clinical Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:4313610.
[21] OK JS, SONG SB, HWANG ES. Enhancement of Replication and Differentiation Potential of Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells by Nicotinamide Treatment. Int J Stem Cells. 2018;11(1):13-25.
[22] NISHIMURA A, NAKAJIMA R, TAKAGI R, et al. Fabrication of tissue-engineered cell sheets by automated cell culture equipment. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(12):2246-2255.
[23] PARK JY, PARK CH, YI T, et al. rhBMP-2 Pre-Treated Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Sheets Regenerate a Mineralized Layer Mimicking Dental Cementum. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3767.
[24] CHEN G, QI Y, NIU L, et al. Application of the cell sheet technique in tissue engineering. Biomed Rep. 2015;3(6):749-757.
[25] MOUTHUY PA, EL-SHERBINI Y, CUI Z, et al. Layering PLGA-based electrospun membranes and cell sheets for engineering cartilage-bone transition. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(4):E263-274.
[26] 张文静. BMP-2及FGF-2诱导BMSCs膜片复合马鹿角粉支架构建组织工程骨的实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2020.
[27] JEON OH, PANICKER LM, LU Q, et al. Human iPSC-derived osteoblasts and osteoclasts together promote bone regeneration in 3D biomaterials. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26761.
[28] HAN H, LI Z, QU N, et al. Synthesis and Promotion of the Osteoblast Proliferation Effect of Morroniside Derivatives. Molecules. 2018;23(6):1412.
[29] SULJIC EM, MEHICEVIC A, MAHMUTBEGOVIC N. Effect of Long-term Carbamazepine Therapy on Bone Health. Med Arch. 2018;72(4):262-266.
[30] DROSSE I, VOLKMER E, CAPANNA R, et al. Tissue engineering for bone defect healing: an update on a multi-component approach. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 2: S9-20.
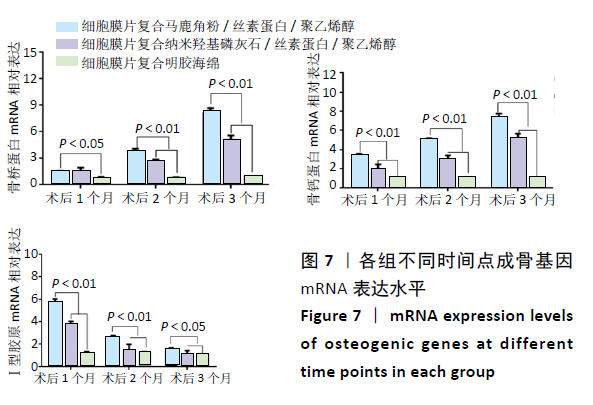
|