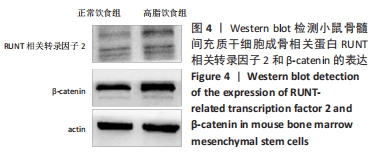
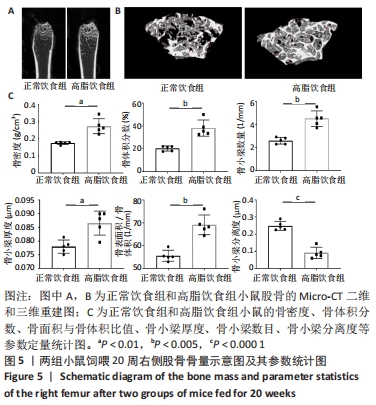
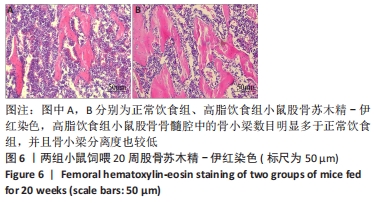
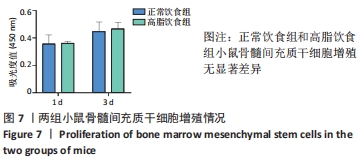
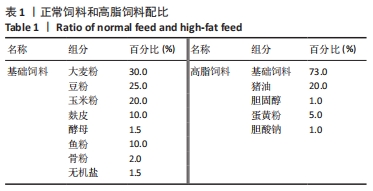
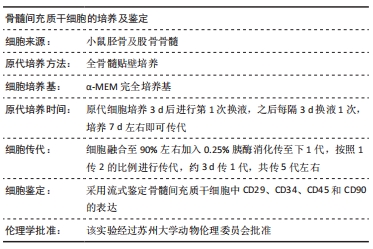
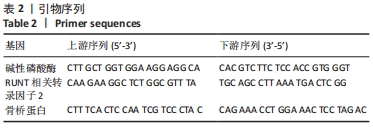
[1] GBD 2015 OBESITY COLLABORATORS, AFSHIN A, FOROUZANFAR MH, et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years.N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):13-27.
[2] GREGG EW, SHAW JE. Global Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):80-81.
[3] 董虹孛,闫银坤,米杰.儿童肥胖与骨量的双重性关系[J].中华骨质疏松症和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):406-412.
[4] 王烁,董彦会,王政和,等. 1985—2014 年中国7~18 岁学生超重与肥胖流行趋势[J].中华预防医学杂志,2017,51(4):300-305.
[5] EVANS AL, PAGGIOSI MA, EASTELL R, et al. Bone density, microstructure and strength in obese and normal weight men and women in younger and older adulthood. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(5):920-928.
[6] ARMSTRONG ME, SPENCER EA, CAIRNS BJ, et al. Body mass index and physical activity in relation to the incidence of hip fracture in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(6):1330-1338.
[7] ARMSTRONG ME, CAIRNS BJ, BANKS E, et al. Different effects of age, adiposity and physical activity on the risk of ankle, wrist and hip fractures in postmenopausal women. Bone. 2012;50(6):1394-1400.
[8] PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, PREMAOR MO, FINA AVILÉS F, et al. The association between fracture and obesity is site-dependent: a population-based study in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(2):294-300.
[9] PREMAOR MO, COMPSTON JE, FINA AVILÉS F, et al. The association between fracture site and obesity in men: a population-based cohort study. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(8):1771-1777.
[10] DE LAET C, KANIS JA, ODÉN A, et al. Body mass index as a predictor of fracture risk: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(11):1330-1338.
[11] JOHANSSON H, KANIS JA, ODÉN A, et al. A meta-analysis of the association of fracture risk and body mass index in women. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(1):223-233.
[12] GNUDI S, SITTA E, LISI L. Relationship of body mass index with main limb fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(4):479-484.
[13] BECK TJ, PETIT MA, WU G, et al. Does obesity really make the femur stronger? BMD, geometry, and fracture incidence in the women’s health initiative-observational study. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(8): 1369-1379.
[14] COMPSTON JE, WATTS NB, CHAPURLAT R, et al. Obesity is not protective against fracture in postmenopausal women: GLOW. Am J Med. 2011;124(11):1043-1050.
[15] ESTRADA A, RAMNITZ MS, GAFNI RI. Bone densitometry in children and adolescents. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;26(5):339-346.
[16] BRONCKERS AL, SASAGURI K, ENGELSE MA. Transcription and immunolocalization of Runx2/Cbfa1/Pebp2alphaA in developing rodent and human craniofacial tissues: further evidence suggesting osteoclasts phagocytose osteocytes. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;61(6):540-548.
[17] HORWITZ EM, LE BLANC K, DOMINICI M, et al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2005;7(5):393-395.
[18] QADIR A, LIANG S, WU Z, et al. Senile Osteoporosis: The Involvement of Differentiation and Senescence of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(1):349.
[19] GAO J, XIANG S, WEI X, et al. Icariin Promotes the Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Regulating Sclerostin and Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6666836.
[20] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(7):1929-1937.
[21] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, DE GRAAFF B, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of utility-based quality of life for osteoporosis-related conditions. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(8):1987-1997.
[22] ZHOU W, LIN J, ZHAO K, et al. Single-Cell Profiles and Clinically Useful Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Adipose and Bone Marrow Origin. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(7):1722-1733.
[23] DELANOIS RE, ETCHESON JI, SODHI N, et al. Biologic Therapies for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4):801-813.
[24] FROST HM. The mechanostat: a proposed pathogenic mechanism of osteoporoses and the bone mass effects of mechanical and nonmechanical agents. Bone Miner. 1987;2(2):73-85.
[25] FROST HM. Bone’s mechanostat: a 2003 update. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2003;275(2):1081-1101.
[26] KINDLER JM, LEWIS RD, HAMRICK MW. Skeletal muscle and pediatric bone development. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2015;22(6): 467-474.
[27] VAN LEEUWEN J, KOES BW, PAULIS WD, et al. Differences in bone mineral density between normal-weight children and children with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2017;18(5):526-546.
[28] CLARK EM, NESS AR, TOBIAS JH. Adipose tissue stimulates bone growth in prepubertal children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(7):2534-2541.
[29] UUSI-RASI K, LAAKSONEN M, MIKKILÄ V, et al. Overweight in childhood and bone density and size in adulthood. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(4): 1453-1461.
[30] WHITING SJ, VATANPARAST H, BAXTER-JONES A, et al. Factors that affect bone mineral accrual in the adolescent growth spurt. J Nutr. 2004;134(3):696S-700S.
[31] MAÏMOUN L, COSTE O, MURA T, et al. Specific bone mass acquisition in elite female athletes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(7):2844-2853.
[32] BAILEY DA, MCKAY HA, MIRWALD RL, et al. A six-year longitudinal study of the relationship of physical activity to bone mineral accrual in growing children: the university of Saskatchewan bone mineral accrual study. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(10):1672-1679.
[33] BONJOUR JP, THEINTZ G, BUCHS B, et al. Critical years and stages of puberty for spinal and femoral bone mass accumulation during adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991;73(3):555-563.
[34] HENRY YM, FATAYERJI D, EASTELL R. Attainment of peak bone mass at the lumbar spine, femoral neck and radius in men and women: relative contributions of bone size and volumetric bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(4):263-273.
[35] VILJAKAINEN H, IVASKA KK, PALDÁNIUS P, et al. Suppressed bone turnover in obesity: a link to energy metabolism? A case-control study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(6):2155-2163.
[36] KANG C, LEROITH D, GALLAGHER EJ. Diabetes, Obesity, and Breast Cancer. Endocrinology. 2018;159(11):3801-3812.
[37] PROTANI M, COORY M, MARTIN JH. Effect of obesity on survival of women with breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123(3):627-635.
[38] IKEDA K, TAKESHITA S. The role of osteoclast differentiation and function in skeletal homeostasis. J Biochem. 2016;159(1):1-8.
[39] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89.
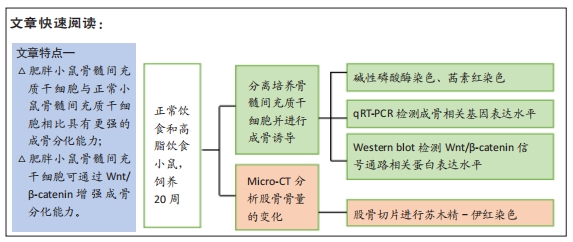
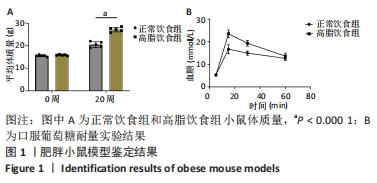
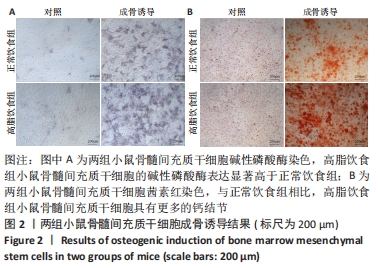
|