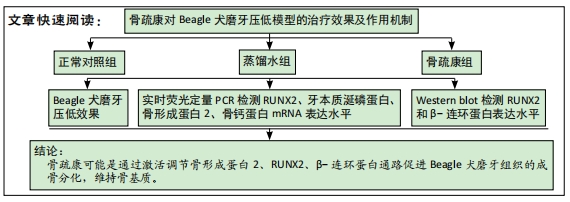
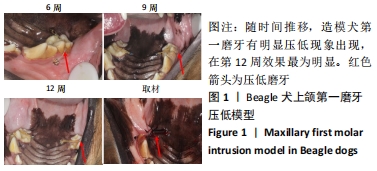
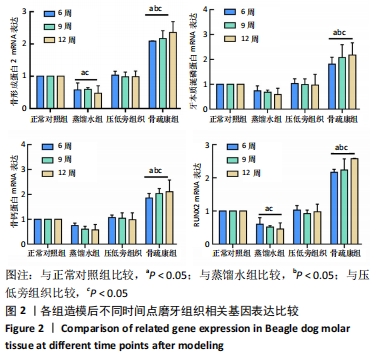
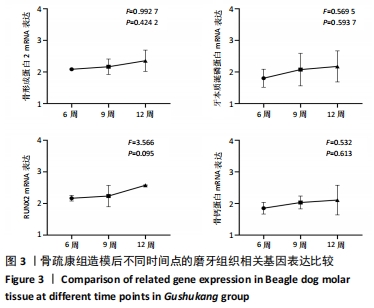
[1] 邹双双,温兴涛,徐卓,等.微种植支抗压低成年人上颌伸长磨牙的CBCT分析[J].口腔医学,2019,39(5):436-438.
[2] 张春利.微型种植钉支抗在口腔正畸中的临床应用效果[J].口腔医学研究,2018,10(3):135-137.
[3] 李翀乾,刘继光.正畸治疗中牙根吸收影响因素的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2018,26(3):178-181.
[4] 许辉明,陈雪芬,孙晓峰.微型种植体支抗在正畸治疗中的疗效观察[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2018,28(12):724-732.
[5] 田青鹭,赵志河.微型种植体在口腔正畸中稳定性的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(2):212-218.
[6] 吴也可,郜然然,左渝陵,等.影响微种植体正畸治疗成功率的因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):538-543.
[7] LOSSDÖRFER S, YILDIZ F, GÖTZ W, et al. Anabolic effect of intermittent PTH (1 -34) on the local microenvironment during the late phase of periodontal repair in a rat model of tooth root resorption. Clin Oral Investig. 2010;14(1):89-98.
[8] HUANG H, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Bone resorption deficiency affects tooth root development in RANKL mutant mice due to attenuated IGF-1 signaling in radicular odontoblasts. Bone. 2018;114:161-171.
[9] TAN L, ZHANG Y, HUANG Y, et al. Preservation of alveolar ridge after tooth extraction with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein in a dog model. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(4):2913-2920.
[10] 肖聪,葛伶伶,赵同平,等.微种植体支抗压低上颌磨牙的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(2):397-400.
[11] 成洁,王颖,吉健华,等.骨疏康胶囊治疗肾阳虚型骨质疏松症疗效及对患者骨代谢影响[J].陕西中医,2019,40(9):1232-1234,1250.
[12] 侍方,李欣,张蕊,等.骨疏康胶囊联合鲑鱼降钙素、戊酸雌二醇对绝经后骨质疏松患者的临床疗效[J]. 中成药,2020,42(12):3188-3192.
[13] 郑志坚,舒冰,赵世天,等.骨疏康颗粒对去卵巢小鼠骨质疏松模型骨丢失和破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(7): 3647-3651.
[14] EL-BIALY T, HAZAN MOLINA H, AIZENBUD Y, et al. Effects of Intraligamentary Injection of Osteogenic-Induced Gingival Fibroblasts on Cementum Thickness in the Dog Model of Tooth Root Resorption. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1289:107-114.
[15] 黄林,方威苏,曹君.IL-1β、MMP-2在大鼠牙根吸收组织中的表达及意义[J].口腔正畸学研究,2019,39(6):604-607.
[16] 梁昌富,陈国新,肖秀凤,等.正畸治疗对下颌髁突肥大术后颞下颌关节的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(8):870-875.
[17] 林若慧,陈赛楠,叶云金,等.基于TMT蛋白质组学分析骨疏康胶囊治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5141-5147.
[18] SCHWARTZ AM. Tissue changes incidental to tooth movement. Int J Orthod. 1992;18(5):331-352.
[19] ABOALNAGA AA, SALAH FAYED MM, EL-ASHMAWI NA, et al. Effect of micro-osteoperforation on the rate of canine retraction: a split-mouth randomized controlled trial. Prog Orthod. 2019;20(1):21.
[20] ALQADASI B, ALDHORAE K, HALBOUB E, et al. The effectiveness of micro-osteoperforations during canine retraction: a three-dimensional randomized clinical trial. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019;9(6): 637-645.
[21] BABANOURI N, AJAMI S, SALEHI P. Effect of mini-screw-facilitated micro-osteoperforation on the rate of orthodontic tooth movement: a single-center, split-mouth, randomized, controlled trial. Prog Orthod. 2020; 21(1):7.
[22] LI Y, JACOX LA, LITTLE SH, et al. Orthodontic tooth movement: The biology and clinical implications Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34(4):207-214.
[23] MOON CH, WEE JU, LEE HS. Intrusion of overerupted molars by corticotomy and orthodontic skeletal anchorage. Angle Orthod. 2007; 77(6):1119-1125.
[24] 喻凤,邓锋,张翼,等.骨皮质切开术对比格犬前磨牙压入移动影响的三维形态学研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2016,34(3):267-271.
[25] 费晓娟,金美林,卢曾奎,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2(BMP2)基因的生理功能和信号通路研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2021,57(3):1-6.
[26] LIN YC, NICETA M, MUTO V, et al. SCUBE3 loss-of-function causes a recognizable recessive developmental disorder due to defective bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108(1): 115-133.
[27] KIM MJ, CHA JK, PAENG KW, et al. Immediate versus delayed application of bone morphogenetic protein-2 solution in damaged extraction sockets: a preclinical in vivo investigation. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(1):275-282.
[28] RAKIAN A, YANG WC, GLUHAK-HEINRICH J, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene controls tooth root development in coordination with formation of the periodontium. Int J Oral Sci. 2013;5(2):75-84.
[29] NEWTON AH, PASK AJ. Evolution and expansion of the RUNX2 QA repeat corresponds with the emergence of vertebrate complexity. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):771.
[30] LI S, KONG H, YAO N, et al. The role of runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) in the late stage of odontoblast differentiation and dentin formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;410(3):698-704.
[31] MURODUMI H, SHIGEISHI H, KATO H, et al. Melatonin‑induced miR‑181c‑5p enhances osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of human jawbone‑derived osteoblastic cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020; 22(4):3549-3558.
[32] LIU J, WU M, FENG G, et al. Downregulation of LINC00707 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating DKK1 via targeting miR-103a-3p. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(3):1029-1038.
[33] SASE T, SUZUKI T, MIURA K, et al. Runt-related transcription factor 2 in human colon carcinoma: a potent prognostic factor associated with estrogen receptor. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(10):2284-2293.
[34] ZHANG G, LI H, ZHAO W, et al. miR-205 regulates bone turnover in elderly female patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus through targeted inhibition of Runx2. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):1557-1565.
[35] 张麟,向楠,周广文,等.补肾化痰方对去势骨质疏松大鼠BMP2/Smad/RUNX2信号通路及钙沉积的影响[J].中医药导报,2018, 24(18):20-24.
[36] 秦凡,周述作,罗金英,等.β-catenin对人牙周膜干细胞应力成骨调控作用的研究[J].局解手术学杂志,2017,26(3):162-166.
[37] 任小华,韩红娟,吴浩.下颌单颗后牙即刻种植负载后种植体周围龈沟液TNF-α、IL-1β、TGFα及骨钙蛋白的变化及意义[J].四川医学, 2018,39(8):904-908.
[38] 陈聚秀,黄正蔚.Ⅱ型牙本质发育不全患者DSPP基因突变的研究进展[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(1):66-70.
[39] CHEN XJ, SHEN YS, HE MC, et al. Polydatin promotes the osteogenic differentia- tion of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating the BMP2-Wnt/beta -catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108746.
[40] SHEN YS, CHEN XJ, WURI SN, et al. Polydatin improves osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by stimulating TAZ expression via BMP2-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;27;11(1):204.
[41] KUSHWAHA P, KHEDGIKAR V, GAUTAM J, et al. A novel therapeutic approach with Caviunin-based isoflavonoid that en routes bone marrow cells to bone formation via BMP2/Wnt-β-catenin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(9):e1422.
|