[1] ULRICH-VINTHER M, MALONEY MD, SCHWARZ EM, et al. Articular cartilage biology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(6):421-430.
[2] MOBASHERI A, MATTA C, ZAKANY R, et al. Chondrosenescence: definition, hallmarks and potential role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Maturitas. 2015;80(3):237-244.
[3] GOBBI A, DALLO I, KUMAR V. Editorial commentary: biological cartilage repair technique-an “effective, accessible, and safe” surgical solution for an old difficult biological problem. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(3):859-861.
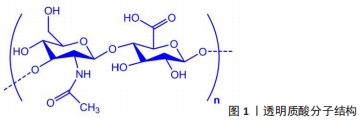
[4] HORKAY F. Interactions of cartilage extracellular matrix macromolecules. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 2012;50(24):1699-1705.
[5] WANG AT, ZHANG QF, WANG NX, et al. Cocktail of hyaluronic acid and human amniotic mesenchymal cells effectively repairs cartilage injuries in sodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis rats. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:87.
[6] 付力伟,杨振,李浩,等.亲和肽在软骨组织工程中应用的新策略和问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(16):2569-2574.
[7] OLSON A, GRAVER A, GRANDE D. Scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2012;22(3):219-227.
[8] FU N, DONG T, MENG A, et al. Research progress of the types and preparation techniques of scaffold materials in cartilage tissue engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):583-590.
[9] ZASLAV K, MCADAMS T, SCOPP J, et al. New frontiers for cartilage repair and protection. Cartilage. 2012;3(1 Suppl):77S-86S.
[10] SIEGEL MG, LUBOWITZ JH, BRAND JC, et al. Articular cartilage restoration requires cells, scaffolds, growth factors, and mechanical stimulation. Arthroscopy. 2021; 37(5):1359-1360.
[11] KALKAN R, NWEKWO CW, ADALI T. The use of scaffolds in cartilage regeneration. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2018;28(4):343-348.
[12] MAKRIS EA, GOMOLL AH, MALIZOS KN, et al. Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34.
[13] SHA’BAN M, AHMAD RADZI MA. Scaffolds for cartilage regeneration: to use or not to use? Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1249:97-114.
[14] SACHLOS E, CZERNUSZKA JT. Making tissue engineering scaffolds work. Review: the application of solid freeform fabrication technology to the production of tissue engineering scaffolds. Eur Cell Mater. 2003;5:29-39.
[15] FRASER JR, LAURENT TC, LAURENT UB. Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J Intern Med. 1997;242(1):27-33.
[16] ABBRUZZESE F, BASOLI F, COSTANTINI M, et al. Hyaluronan: an overview. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017 Dec 27;31(4 Suppl 2):9-22.
[17] LAURENT TC, LAURENT UB, FRASER JR. The structure and function of hyaluronan: an overview. Immunol Cell Biol. 1996;74(2):A1-A7.
[18] ABATANGELO G, VINDIGNI V, AVRUSCIO G, et al. Hyaluronic acid: redefining its role. Cells. 2020;9(7):1743.
[19] BOWMAN S, AWAD ME, HAMRICK MW, et al. Recent advances in hyaluronic acid based therapy for osteoarthritis. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7(1):6.
[20] OLIVEIRA I, CARVALHO AL, RADHOUANI H, et al. Promising biomolecules. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059:189-205.
[21] FALLACARA A, BALDINI E, MANFREDINI S, et al. Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(7):701.
[22] BRUN P, ZAVAN B, VINDIGNI V, et al. In vitro response of osteoarthritic chondrocytes and fibroblast-like synoviocytes to a 500-730 kDa hyaluronan amide derivative. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(8):2073-2081.
[23] VETRANO M, RANIERI D, NANNI M, et al. Hyaluronic acid (HA), platelet-rich plasm and extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) promote human chondrocyte regeneration in vitro and ESWT-mediated increase of CD44 expression enhances their susceptibility to HA treatment. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218740.
[24] KATOH S, YOSHIOKA H, SENTHILKUMAR R, et al. Enhanced expression of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis-affected knee-cartilage chondrocytes during three-dimensional in vitro culture in a hyaluronic-acid-retaining polymer scaffold. Knee. 2021;29:365-373.
[25] WANG T, LAI JH, YANG F. Effects of hydrogel stiffness and extracellular compositions on modulating cartilage regeneration by mixed populations of stem cells and chondrocytes in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(23-24):1348-1356.
[26] 张晓鸥,吕旸,毛华,等.透明质酸支架材料:应用研究与产品转化前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2):294-302.
[27] 刘效仿,张健,侯蕾,等.透明质酸促进关节软骨缺损修复的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(24):2271-2276.
[28] CHEN J, YANG J, WANG L, et al. Modified hyaluronic acid hydrogels with chemical groups that facilitate adhesion to host tissues enhance cartilage regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(6):1689-1698.
[29] LOPEZ-RUIZ E, JIMENEZ G, ÁLVAREZ DE CIENFUEGOS L, et al. Advances of hyaluronic acid in stem cell therapy and tissue engineering, including current clinical trials. Eur Cell Mater. 2019;37:186-213.
[30] GUPTA RC, LALL R, SRIVASTAVA A, et al. Hyaluronic acid: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic trajectory. Front Vet Sci. 2019;6:192.
[31] BULPITT P, AESCHLIMANN D. New strategy for chemical modification of hyaluronic acid: preparation of functionalized derivatives and their use in the formation of novel biocompatible hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;47(2):152-169.
[32] KIM IL, MAUCK RL, BURDICK JA. Hydrogel design for cartilage tissue engineering: a case study with hyaluronic acid. Biomaterials. 2011;32(34):8771-8782.
[33] 魏健,刘建建,黄思玲,等.透明质酸交联衍生物的研究进展[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2017,33(10):183-190.
[34] BENCHERIF SA, SRINIVASAN A, HORKAY F, et al. Influence of the degree of methacrylation on hyaluronic acid hydrogels properties. Biomaterials. 2008; 29(12):1739-1749.
[35] TIWARI S, BAHADUR P. Modified hyaluronic acid based materials for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;121:556-571.
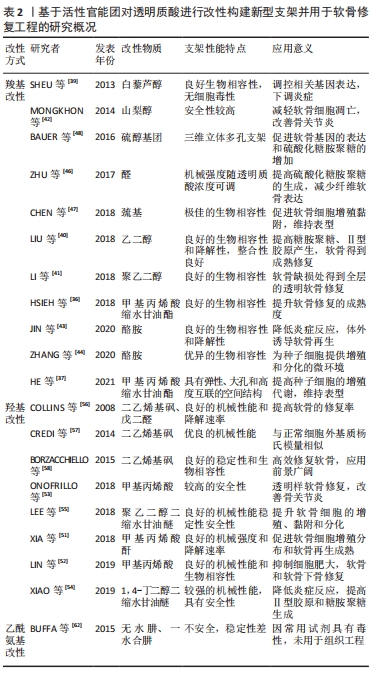
[36] HSIEH YH, SHEN BY, WANG YH, et al. Healing of osteochondral defects implanted with biomimetic scaffolds of poly(ε-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite and glycidyl-methacrylate-modified hyaluronic acid in a minipig. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4): 1125.
[37] HE T, LI B, COLOMBANI T, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based shape-memory cryogel scaffolds for focal cartilage defect repair. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(11-12):748-760.
[38] WANG T, LAI JH, HAN LH, et al. Modulating stem cell-chondrocyte interactions for cartilage repair using combinatorial extracellular matrix-containing hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(47):7641-7650.
[39] SHEU SY, CHEN WS, SUN JS, et al. Biological characterization of oxidized hyaluronic acid/resveratrol hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(12):3457-3466.
[40] LIU C, LIU D, WANG Y, et al. Glycol chitosan/oxidized hyaluronic acid hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix particles and incorporating BMSCs for cartilage repair. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):721-732.
[41] LI J, HUANG Y, SONG J, et al. Cartilage regeneration using arthroscopic flushing fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in a one-step rapid cross-linked hydrogel. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:202-215.
[42] MONGKHON JM, THACH M, SHI Q, et al. Sorbitol-modified hyaluronic acid reduces oxidative stress, apoptosis and mediators of inflammation and catabolism in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2014;63(8):691-701.
[43] JIN Y, KOH RH, KIM SH, et al. Injectable anti-inflammatory hyaluronic acid hydrogel for osteoarthritic cartilage repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;115:111096.
[44] ZHANG Y, CAO Y, ZHAO H, et al. An injectable BMSC-laden enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking collagen-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for cartilage repair and regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(19):4237-4244.
[45] JOOYBAR E, ABDEKHODAIE MJ, ALVI M, et al. An injectable platelet lysate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel supports cellular activities and induces chondrogenesis of encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;83:233-244.
[46] ZHU D, WANG H, TRINH P, et al. Elastin-like protein-hyaluronic acid (ELP-HA) hydrogels with decoupled mechanical and biochemical cues for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2017;127:132-140.
[47] CHEN Y, SUI J, WANG Q, et al. Injectable self-crosslinking HA-SH/Col I blend hydrogels for in vitro construction of engineered cartilage. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;190:57-66.
[48] BAUER C, BERGER M, BAUMGARTNER RR, et al. A novel cross-linked hyaluronic acid porous scaffold for cartilage repair: an in vitro study with osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Cartilage. 2016;7(3):265-273.
[49] KHUNMANEE S, JEONG Y, PARK H. Crosslinking method of hyaluronic-based hydrogel for biomedical applications. J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417726464.
[50] FAKHARI A, BERKLAND C. Applications and emerging trends of hyaluronic acid in tissue engineering, as a dermal filler and in osteoarthritis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7081-7092.
[51] XIA H, ZHAO D, ZHU H, et al. Lyophilized scaffolds fabricated from 3D-printed photocurable natural hydrogel for cartilage regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(37):31704-31715.
[52] LIN H, BECK AM, SHIMOMURA K, et al. Optimization of photocrosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid hybrid scaffold for the repair of cartilage defect. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(8):1418-1429.
[53] ONOFRILLO C, DUCHI S, O’CONNELL CD, et al. Biofabrication of human articular cartilage: a path towards the development of a clinical treatment. Biofabrication. 2018;10(4):045006.
[54] XIAO SP, TANG LS, CHEN JY, et al. Effect of cross-linked hyaluronate scaffold on cartilage repair: an in vivo study. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(4):679-689.
[55] LEE HY, HWANG CH, KIM HE, et al. Enhancement of bio-stability and mechanical properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogels by tannic acid treatment. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;186:290-298.
[56] COLLINS MN, BIRKINSHAW C. Physical properties of crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(11):3335-3343.
[57] CREDI C, BIELLA S, DE MARCO C, et al. Fine tuning and measurement of mechanical properties of crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels as biomimetic scaffold coating in regenerative medicine. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;29:309-316.
[58] BORZACCHIELLO A, RUSSO L, MALLE BM, et al. Hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 871218.
[59] ZHANG W, MU H, DONG D, et al. Alteration in immune responses toward N-deacetylation of hyaluronic acid. Glycobiology. 2014;24(12):1334-1342.
[60] SEDLACEK J, HERMANNOVA M, MRAZEK J, et al. Insight into the distribution of amino groups along the chain of chemically deacetylated hyaluronan. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;225:115156.
[61] SEDLACEK J, HERMANNOVA M, ŠATINSKY D, et al. Current analytical methods for the characterization of N-deacetylated hyaluronan: a critical review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;249:116720.
[62] BUFFA R, ŠEDOVA P, BASARABOVA I, et al. α, β-Unsaturated aldehyde of hyaluronan--Synthesis, analysis and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;134: 293-299.
[63] LIU Y, YANG J, LUO Z, et al. Development of an injectable thiolated icariin functionalized collagen/hyaluronic hydrogel to promote cartilage formation in vitro and in vivo. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(17):2845-2854.
[64] YANG J, LIU Y, HE L, et al. Icariin conjugated hyaluronic acid/collagen hydrogel for osteochondral interface restoration. Acta Biomater. 2018;74:156-167.
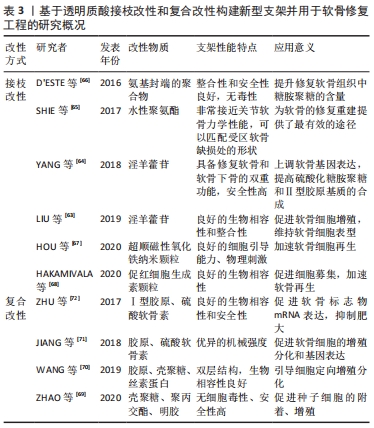
[65] SHIE MY, CHANG WC, WEI LJ, et al. 3D printing of cytocompatible water-based light-cured polyurethane with hyaluronic acid for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(2):136.
[66] D’ESTE M, SPRECHER CM, MILZ S, et al. Evaluation of an injectable thermoresponsive hyaluronan hydrogel in a rabbit osteochondral defect model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6):1469-1478.
[67] HOU KT, LIU TY, CHIANG MY, et al. Cartilage tissue-mimetic pellets with multifunctional magnetic hyaluronic acid-graft-amphiphilic gelatin microcapsules for chondrogenic stimulation. polymers (basel). 2020;12(4):785.
[68] HAKAMIVALA A, SHUXIN Li, ROBINSON K, et al. Recruitment of endogenous progenitor cells by erythropoietin loaded particles for in situ cartilage regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(1):142-152.
[69] ZHAO W, DU Z, FANG J, et al. Synthetic/natural blended polymer fibrous meshes composed of polylactide, gelatin and glycosaminoglycan for cartilage repair. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(11):1437-1456.
[70] WANG J, WANG Y, SUN X, et al. Biomimetic cartilage scaffold with orientated porous structure of two factors for cartilage repair of knee osteoarthritis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1710-1721.
[71] JIANG X , LIU J , LIU Q , et al . Therapy for cartilage defects: functional ectopic cartilage constructed by cartilage-simulating collagen, chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid (CCH) hybrid hydrogel with allogeneic chondrocytes. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(6):1616-1626.
[72] ZHU M, FENG Q, SUN Y, et al. Effect of cartilaginous matrix components on the chondrogenesis and hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in hyaluronic acid hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(8):2292-2300.
|