中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 3108-3116.doi: 10.12307/2022.394
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
少突胶质细胞的功能与脱髓鞘疾病
宋聖姣,李 娟,吴文成,肖 赟,廖宝莹,李 星
- 陕西师范大学 生命科学学院,西北濒危药材资源开发国家工程实验室 药用资源与天然药物化学教育部重点实验室,陕西省西安市 710119
-
收稿日期:2021-06-02修回日期:2021-07-22接受日期:2021-08-09出版日期:2022-07-08发布日期:2021-12-29 -
通讯作者:李星,博士,教授,硕士生导师,陕西师范大学 生命科学学院,西北濒危药材资源开发国家工程实验室 药用资源与天然药物化学教育部重点实验室,陕西省西安市 710119 -
作者简介:宋聖姣,女,1998年生,陕西省渭南市人,汉族,陕西师范大学在读硕士,主要从事干细胞、外泌体对脱髓鞘疾病治疗的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金-面上基金项目(31970771),项目负责人:李星;陕西省重点产业创新链(群)-社会发展领域(2021ZDLSF03-09),项目负责人:李星;中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(2021CSZL008),项目负责人:宋聖姣;中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(TD2020039Y),项目负责人:吴文成;中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(2021CSZL009),项目负责人:廖宝莹
Function of oligodendrocytes and demyelinating disease
Song Shengjiao, Li Juan, Wu Wencheng, Xiao Yun, Liao Baoying, Li Xing
- National Engineering Laboratory for Resource Development of Endangered Crude Drugs in Northwest China, Key Laboratory of Medicinal Resources and Natural Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710119, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-02Revised:2021-07-22Accepted:2021-08-09Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-29 -
Contact:Li Xing, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, National Engineering Laboratory for Resource Development of Endangered Crude Drugs in Northwest China, Key Laboratory of Medicinal Resources and Natural Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710119, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Song Shengjiao, Master candidate, National Engineering Laboratory for Resource Development of Endangered Crude Drugs in Northwest China, Key Laboratory of Medicinal Resources and Natural Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710119, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China-General Fund Project, No. 31970771 (to LX); Shaanxi Province Key Industrial Innovation Chain (Group)-Social Development Field, No. 2021ZDLSF03-09 (to LX); The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 2021CSZL008 (to SSJ); The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. TD2020039Y (to WWC); The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 2021CSZL009 (to LBY)
摘要:
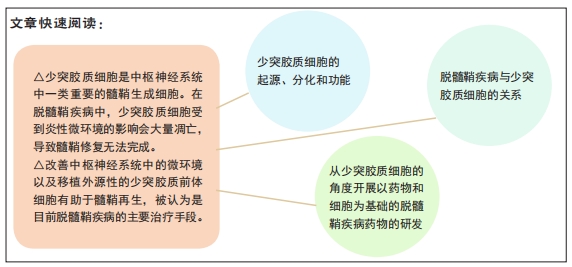
文题释义:
脱髓鞘疾病:中枢神经系统脱髓鞘疾病是一类同时涉及脑、脊髓和周围神经等多个部位的疾病。脱髓鞘是其整个病理过程中最具特征性的表现,该类疾病因为具有发病机制复杂、临床表现多样、对治疗药物反应的个体差异性较大等特点,在临床治疗过程中具有极大的挑战性。
少突胶质细胞:是中枢神经系统内形成髓鞘的细胞,由少突胶质前体细胞分化形成。主要功能是在中枢神经系统中包绕轴突、形成绝缘的髓鞘结构、协助生物电信号的跳跃式高效传递并维持和保护神经元的正常功能。
背景:脱髓鞘疾病是以神经髓鞘脱失为主、神经元胞体及轴突相对损伤较轻为特征的一种疾病。正常生理条件下,髓鞘脱失后机体会自发地进行髓鞘再生,但在病理条件下,该过程会因多种因素被抑制,导致髓鞘再生不完全或失败,使脱髓鞘发展,病情持续加重。
目的:文章强调了少突胶质细胞在髓鞘再生过程中的重要性,以及如何从少突胶质细胞的角度开展以药物和细胞为基础的脱髓鞘疾病药物的研发,以期为脱髓鞘疾病的药物开发提供新的途径。
方法:利用PubMed、GeenMedical和中国知网等数据库检索、筛选与少突胶质细胞和脱髓鞘疾病相关或涉及少突胶质前体细胞、少突胶质细胞相关功能以及髓鞘再生方面的文献,英文检索词为“oligodendrocyte, demyelinating disease”,中文检索词为“少突胶质细胞、脱髓鞘疾病”,检索时间从各数据库建库至2021-05-01,共纳入参考文献142篇。
结果与结论:①少突胶质细胞在脱髓鞘疾病中对于髓鞘再生的作用至关重要,炎性微环境中,少突胶质细胞的功能会受到损伤并损害轴突传导,维持少突胶质细胞在中枢神经系统中的功能对于脱髓鞘疾病的治疗至关重要。②目前,针对脱髓鞘疾病新的治疗策略层出不穷,主要以预防炎症为主。如通过生物信息技术手段筛选出可用的小分子化合物或经美国食品和药物管理局批准的药物为筛选对象开发出可以靶向调节髓鞘再生不同阶段内在或外在信号的药物,以及移植具有分化为少突胶质细胞能力的中枢神经系统干细胞至病灶区域的细胞疗法。现行研究的治疗切入点各有千秋,研发出低成本、低不良反应、高药物疗效、高效益的治疗策略还将面临艰巨的挑战。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0742-1364 (李星)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
宋聖姣, 李 娟, 吴文成, 肖 赟, 廖宝莹, 李 星. 少突胶质细胞的功能与脱髓鞘疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(19): 3108-3116.
Song Shengjiao, Li Juan, Wu Wencheng, Xiao Yun, Liao Baoying, Li Xing. Function of oligodendrocytes and demyelinating disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3108-3116.

少突胶质细胞这个概念是由RíO HORTEGA于1921年提出的,最早被用来描述在碳酸银浸染法中几乎没有突起的神经胶质细胞[4]。少突胶质细胞是中枢神经系统的髓鞘形成细胞,起源于少突胶质前体细胞(oligodendrocyte progenitor cell,OPC),少突胶质前体细胞可以根据环境分化为少突胶质细胞或星形胶质细胞[8]。少突胶质前体细胞分化为少突胶质细胞阶段时先会延伸出多个单独包裹轴突的突起,继而产生同心层修饰的细胞膜包裹形成髓鞘[9]。在人类中,白质区域约占大脑的50%,白质区域轴突密集分布,因而白质是髓鞘形成的主要区域,但灰质中也有少量的少突胶质细胞存在。脊髓和脑干的髓鞘形成较早,而其他区域,如端脑、内嗅皮质、海马和杏仁核的髓鞘形成较晚,髓鞘成熟后在胼胝体、一些皮质区域和海马中富集[10]。
少突胶质细胞是在中枢神经系统轴突周围延伸髓鞘的胶质细胞,在有髓节段之间的无髓轴突区域被称为郎飞氏结,参与动作电位产生的钠通道聚集在该区域。作为典型的脊椎动物神经纤维,这种精细的结构对于电脉冲沿着轴突进行的跳跃式传导至关重要,因此完整的髓鞘帮助中枢神经系统实现了神经细胞网络之间的快速通信[11]。除了通过生成髓鞘来提高轴突传导速度外,还分泌维持神经元存活的生长因子,并为神经元提供营养支持,特别是对于不能单独从轴突内运输获得足够支持的长轴突可提供充分的营养供给[12-14]。因此,发育中或受损中脑的髓鞘形成障碍会影响少突胶质细胞功能并且损害轴突的正常功能[15],这一系列损伤都与神经元变性有关[16],所以少突胶质细胞在维持中枢神经系统的正常功能方面不可或缺。
少突胶质细胞的研究历程,见图4。

2.1.1 少突胶质细胞的形成 少突胶质细胞源自侧脑室室管膜下区的胚胎神经上皮干细胞即神经祖细胞,经历前少突胶质细胞祖细胞和少突胶质前体细胞两个阶段后最终分化完成。神经祖细胞是一种能够“自我更新”和分化成为中枢神经系统主要类型细胞的干细胞群,前少突胶质细胞祖细胞呈圆形,表面较为光滑,分裂增殖能力强。少突胶质前体细胞为圆形或椭圆形细胞,胞体常呈两极或三极突起,仍具有一定的分裂增殖能力[17]。
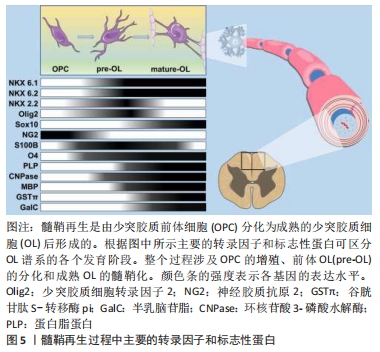
更进一步地说,少突胶质前体细胞是一种可增殖、能够分化为少突胶质细胞或是可分化中枢神经系统髓鞘形成细胞的少突胶质细胞前体细胞,有分化为神经元的潜能[18]。按照时间顺序,在哺乳动物中的分化主要有3个阶段,整个过程受到多种信号通路及转录因子的调控。在分化中的后续迁移过程中,少突胶质前体细胞依旧保持着增殖能力。在特定发育阶段后,大多数少突胶质前体细胞分化为成熟的少突胶质细胞形成髓鞘,而极少部分(大约占人脑总细胞数3%)仍以前体细胞的形式存在着,对髓鞘受损后的再生起关键作用[19]。
少突胶质前体细胞在面对裸露轴突的情况下,会增加其增殖速度,并主动迁移到缺乏髓鞘的区域,分化为成熟的有髓少突胶质细胞[20]。在分化及成熟过程中,血小板源性生长因子受体α(platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha,PDGFRα)和神经胶质抗原2 (neuron-glial actigen 2,NG2)的表达逐渐下调,转而倾向于表达未成熟状态的少突胶质细胞标志物O4[21-22]。在向完全成熟的少突胶质细胞表型发展的过程中,未成熟的少突胶质细胞下调O4,并开始表达髓鞘特异性蛋白,如蛋白脂蛋白1(proteolipid protein 1,PLP1)、髓鞘碱性蛋白(myelin basic protein,MBP)、环核苷酸3-磷酸水解酶(2’,3’-Cyclic Nucleotide 3’ phosphodiesterase,CNPase)、谷胱甘肽S-转移酶pi(glutathione S-Transferase Pi 1,GSTπ)和半乳脑苷脂(galactosylceramidase,GalC)[23]。随着细胞按照少突胶质细胞谱系发展,它们的形态也会发生变化,从未激活的少突胶质前体细胞阶段的双极或三极形状发展到成熟后期的多极、分枝状。
2.1.2 少突胶质前体细胞的激活、募集及分化 少突胶质前体细胞的激活是少突胶质细胞促进髓鞘再生过程的第一步,少突胶质前体细胞的激活过程涉及表型的转换,祖细胞在没有接触促分化因子的情况下,会由静止状态转为有丝分裂状态,进而实现大量增殖[24]。在体外培养中,常用血小板衍生生长因子[25]、成纤维细胞生长因子[26]、胰岛素样生长因子[27]、表皮生长因子以及血管内皮生长因子等生长因子用于促进少突胶质前体细胞的增殖[28-29]。神经营养因子3(neurotrophin 3,NT-3)[30]、睫状节神经营养因子[31]、音猬因子、Noggin[32]、三碘甲状腺原氨酸(triiodothyronine,T3)等促分化因子促进少突胶质前体细胞分化为成熟少突胶质细胞[33],最终形成髓鞘,见表1。

少突胶质前体细胞的激活是一个复杂的过程,来自血液的免疫细胞在浸润到脑实质后激活小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞,同时触发少突胶质细胞的脱髓鞘和炎症反应[34-37]。在脱髓鞘区域,活化的小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞可以分泌大量的炎性因子以激活少突胶质前体细胞。在这一阶段,少突胶质前体细胞的激活被认为是对活化的小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的响应,而不是对炎症本身的反应[38]。有研究表明,在没有脱髓鞘的情况下,少突胶质前体细胞也可能被激活[39],血液来源的炎性细胞浸润诱导的脱髓鞘将刺激小胶质细胞和反应性星形胶质细胞以及浸润的巨噬细胞,这些细胞会分泌各种有丝分裂原和细胞因子从而激活少突胶质前体细胞,这是少突胶质前体细胞进入细胞周期的先决条件。
少突胶质前体细胞的募集即指的是少突胶质前体细胞向髓鞘再生区域进行定向迁移[50],这一过程的核心是免疫反应,即在炎症微环境下,生长因子、细胞因子和基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)被大量释放,这些被分泌的因子通过增加少突胶质前体细胞的增殖速率或促进祖细胞的迁移将活化的少突胶质前体细胞募集到脱髓鞘区域。研究表明,免疫介导的脱髓鞘损伤导致局部病灶出现少突胶质前体细胞的大量增殖,这一现象经常出现在脱髓鞘后的数天之内,并且少突胶质前体细胞的募集主要依靠活化的小胶质细胞分泌的细胞因子。
少突胶质细胞的具体分化过程受多种分子调节,涉及转录因子、神经递质,生长因子,激素和其他小分子,信号通路复杂。在发育过程中参与少突胶质前体细胞向少突胶质细胞分化的几个基因也在髓鞘再形成的激活阶段被上调,比如包括NG2[51]、碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋转录因子1/2(bHLH1/bHLH2)和同源结构域转录因子2.2(NK2 homeobox 2,Nkx2.2)[52-53]。少突胶质前体细胞激活期间不仅涉及表型转换也涉及形态变化,少突胶质前体细胞一旦被激活,细胞的尺寸将增加,并延伸出更多的分枝以便于与轴突进行接触。总之,以T淋巴细胞浸润诱导的脱髓鞘损伤会引发强烈的炎症反应,这种反应包括巨噬细胞增殖和髓鞘碎片清除速度的增加[54-55],以及巨噬细胞、小胶质细胞和反应性星形胶质细胞释放有丝分裂原和细胞因子的增加[56]。有丝分裂原和细胞因子上调少突胶质前体细胞内关键转录因子的表达,使少突胶质前体细胞重新进入细胞周期并进入髓鞘再形成的募集阶段。因此,髓鞘再生过程中,少突胶质前体细胞的激活高度依赖于机体对脱髓鞘的先天免疫反应,适当调节这一激活过程对髓鞘再生至关重要。
综上,在中枢神经系统发育成髓鞘的过程中,少突胶质前体细胞增殖并迁移到最终目的地,最终分化为成熟的少突胶质细胞随后由其形成髓鞘包裹轴突。少突胶质细胞谱系进展和终末分化受到严格的转录和转录后控制,新出现的少突胶质细胞谱系细胞表达转录因子NK6 homeobox 1(Nkx 6.1)、NK6 homeobox 2(Nkx 6.2)、NK2 homeobox 2(NKX 2.2)和少突胶质细胞转录因子2(oligodendrocyte Transcription Factor 2, Olig2)[57]。Olig2和Nkx2.2是少突胶质细胞分化的重要决定因素,两者严格的共同表达是分化发生的先决条件。此外,Olig2直接诱导SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 10(SOX10)的表达,直到最近,后者才被认为是少突胶质细胞最终分化的主要决定因素[58]。Sox10作为少突胶质细胞成熟所必需的蛋白,是几个对髓鞘化过程至关重要的基因的直接激活物,包括髓鞘调节因子[59-60]。一旦髓鞘调节因子被激活,将调节未成熟的少突胶质细胞由前髓鞘形成细胞状态转化为成熟的少突胶质细胞,即髓鞘生成细胞[61],见图5。
2.1.3 少突胶质细胞的功能 少突胶质细胞以一种特定的方式在轴突周围延伸髓鞘,相邻的有髓节段或节间由郎飞氏结隔开,形成无髓轴突的间歇性间隙。这种精妙的结构可以将电压门控钠通道限制在郎飞氏结节点上[62-63]。而脱髓鞘病理条件下,离子通道的分布被破坏,使得钠通道和钾通道沿着轴突重新分布,进而导致结区的蛋白结构域和结旁区的蛋白结构域重叠[64-65]。离子通道的扩散和髓鞘丢失会使得膜电容增加从而导致脱髓鞘轴突的阻抗失配,最终造成神经信号低效传导[66-67]。在多发性硬化症,脉冲传导受损通常与功能和认知障碍有关,进一步印证了中枢神经系统轴突周围完整的髓鞘对调节神经网络之间有效沟通的重要性[68- 69]。
近期有研究表明少突胶质细胞除了对髓鞘形成具有重要的作用外,在维持轴突完整性方面也起着关键作用[70-72]。例如,PLP1或CNPase(髓鞘中发现的主要少突胶质细胞蛋白)缺陷的小鼠,髓鞘没有明显的结构异常,但轴突传导受损[73-75]。此外,靶向清除小鼠体内的少突胶质细胞会导致轴突的病理性损伤[76-77],但目前对于如何使少突胶质细胞维持轴突的完整性仍不清楚。已有研究基础表明,在多发性硬化脱髓鞘病变和实验性自身免疫脑脊髓炎(experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,EAE)模型脱髓鞘后,轴突中的线粒体密度显著增加,表明髓鞘或少突胶质细胞的存在可对调节轴突能量代谢起重要作用[78-81],其原因可能是少突胶质细胞为轴突提供代谢因子以满足其高能量需求,缺乏少突胶质细胞的支持可能使神经元更容易受到氧化损伤导致细胞死亡[82]。事实上,近期研究发现,乳酸向神经元的运输对于维持神经元的健康和存活至关重要[83],少突胶质细胞中乳酸转运蛋白——单羧酸盐转运蛋白1 (MCT1)的下调使得乳酸转运受损,导致神经元功能障碍和变性[84]。
少突胶质细胞还具有产生神经营养因子以调节神经元存活的能力。研究表明,少突胶质细胞主要表达脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子和NT-3等生长因子[85-90],由少突胶质细胞分泌的这些神经营养因子可通过增加胆碱乙酰转移酶(ChAT)的表达来增强体外培养的基底前脑神经元的功能[91-92]。此外,少突胶质细胞还可以表达胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和胰岛素样生长因子1,这两种神经营养因子都可以有效增强皮质神经元的存活[93-94]。然而,这些研究大多是在体外进行的,因此需要进一步研究神经营养因子在体内经少突胶质细胞介导的对神经元存活的作用。
2.2 脱髓鞘疾病与少突胶质细胞 脱髓鞘疾病是指以神经髓鞘脱失为特征的神经系统疾病,可发生于周围神经系统(许旺细胞是周围神经系统的成髓鞘胶质细胞)和中枢神经系统。脱髓鞘疾病主要涉及少突胶质细胞的功能障碍或凋亡,可导致髓鞘损伤,这类疾病包括成人获得性髓鞘障碍,如多发性硬化[95]、白质中风[96]、脑瘫[97]、帕金森症[98]、脊髓损伤和视神经脊髓炎等[99-100]。脱髓鞘疾病是神经学中最普遍和致残率最高的疾病之一,仅多发性硬化在年轻人中的发病率就显著高于其他神经系统疾病[101-102]。然而,由于炎症反应往往对神经系统造成了不可逆的损伤,同时也损伤了少突胶质前体细胞的分化,如多发性硬化病理通常与少突胶质细胞的活化以及少突胶质前体细胞的损伤有关,少突胶质细胞的激活会刺激促炎细胞因子的表达,如白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α等,损伤了少突胶质前体细胞的分化[103]。但是炎症反应并不会直接影响少突胶质前体细胞的分化,白细胞介素1α等炎症因子甚至可以促进少突胶质前体细胞的分化[104]。目前针对诸如多发性硬化等脱髓鞘疾病的治疗手段还是以预防炎症为主[105],且尚未开发出有效的治疗方案[106-107]。
多发性硬化被认为是一种最为典型的脱髓鞘疾病,与患者自身免疫有关、以中枢神经系统白质炎性脱髓鞘病变为主要特点,可分为临床前、复发-缓解临床及进展性临床三个阶段[108-109],病理包括血脑屏障的破坏、少突胶质细胞丢失、轴突变性等,影响因素较为复杂,环境因素和生活习惯也有一定的影响概率[110],如青少年肥胖[111]、暴露于有机溶剂[112]、夜间工作[113]、吸烟[114]、饮酒[115]、紫外线[116]、维生素D等对多发性硬化均具有一定促进作用[117]。目前的治疗策略主要是使用免疫调节剂类药物,大多通过阻断炎症反应来间接抑制髓鞘损伤。然而仅部分有效,因为丢失的髓鞘很难修复,同时在自身免疫介导下,脱髓鞘的反复发作,中枢神经系统髓鞘受损,导致髓鞘再生失败,因此针对诸如多发性硬化等脱髓鞘疾病尚未开发出有效的治疗方案[109-110]。
由于髓鞘损伤和髓鞘再生障碍导致了一系列的疾病,而少突胶质细胞是来源于少突胶质前体细胞的一类细胞群体,因此使用少突胶质前体细胞替代疗法被认为是治疗脱髓鞘疾病的一种最为合适的策略之一[118]。原因在于,其一是成熟少突胶质细胞作为分化成熟的细胞,其生存力要明显弱于少突胶质前体细胞,并且成熟少突胶质细胞自身缺乏增殖和迁移能力,所以利用成熟少突胶质细胞治疗具有很大的局限性。其二是在动物模型和人类中少突胶质细胞生成能力存在明显差异,在人类中,少突胶质前体细胞以及少突胶质细胞在青少年个体内产生数量最多,在儿童早期下降并趋于稳定数量,然后在成年期及之后基本保持稳定[110]。而在动物模型中,成年动物的髓鞘生成速度相较于人类更为迅速,但成熟少突胶质细胞的数量同样趋于稳定,且成熟少突胶质细胞髓鞘化效率较低,但是小鼠体内新生少突胶质细胞有助于髓鞘再生,且在脱髓鞘动物模型中通过各种手段如调控信号通路可促进髓鞘再生。与动物相比,人体内新生成的少突胶质细胞在髓鞘再生中不发挥主要作用[119]。考虑到啮齿动物和人类之间少突胶质细胞生成动力学存在差异,多发性硬化症的动物模型也可能无法最佳地反映人类疾病及其细胞反应。所以同样一种疗法在动物模型中可能疗效明显,但在临床实践中却难以再现动物实验中的高疗效,动物模型和人类之间的这些差异限制了它们在细胞治疗中的实际应用。相比之下,少突胶质前体细胞拥有成熟少突胶质细胞所不具备的一些优点,比如少突胶质前体细胞在体内扩散和成熟后具有高度的迁移性、活跃的增殖能力、机械耐受力和强大的髓鞘形成能力。因此,在脱髓鞘疾病模型的脑和脊髓髓鞘再生治疗领域,少突胶质前体细胞作为潜在的治疗方式已经成为一大研究热点。此外,以人类诱导多能干细胞为基础,通过在体外利用转录因子或小分子化合物的处理诱导分化少突胶质前体细胞,有希望成为一种更易于在临床开展用于治疗各类脱髓鞘疾病的治疗方式[120]。但细胞疗法依然存在一些需要被解决的问题,如周期长,操作复杂,无法高效获得有效、充足的移植细胞等;除此之外,还不能排除由诱导性多能干细胞(iPSC)分化而来的少突胶质前体细胞有成瘤的风险[19]。
目前,鉴于对于少突胶质细胞分化的信号通路有了一定的研究基础,故也可直接在患者体内借药物治疗以活化少突胶质前体细胞,促进其分化和髓鞘生成。如少突胶质细胞表达Olig2、MBP、PDGFRα多肽等标志蛋白,脑源性神经营养因子/酪氨酸激酶受体B (BDNF/TrkB)、神经调节蛋白1/表皮生长因子受体(NRG-1/Erb-B2)、酪氨酸激酶Fyn(tyrosine kinase Fyn)及其相应的信号通路是促进少突胶质细胞分化和髓鞘形成及再生的正性调节机制,Notch、骨形成蛋白4 (BMP4)及其相应的信号通路则是负性调节机制[121]。此外,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白(PI3K/AKT-mTor)通路也参与少突胶质细胞的分化、髓鞘形成和髓鞘再生相关的信号转导过程,这些分子和通路对脱髓鞘疾病的治疗和调控有重要意义,可作为治疗脱髓鞘及相关疾病的靶点[122]。
2.3 脱髓鞘疾病的治疗
2.3.1 开发髓鞘再生药物 鉴于对髓鞘再生机制的认识不断扩大,开发用于多发性硬化和其他脱髓鞘疾病髓鞘再形成的药物疗法是脱髓鞘疾病基础研究与转化医学的当务之急。目前主要有两种研究者较为认可的方法来筛选靶向少突胶质前体细胞活化、迁移以及分化不同阶段的小分子或抗体类药物。
第一种方法是靶向调节髓鞘再生不同阶段的特定内在或外在信号。通过这种方法,研究人员筛选了大量潜在的药物和作用靶点,并首次开展了用于治疗多发性硬化症的促进髓鞘再生的临床试验。尽管针对LINGO的人源化单克隆抗体在视神经脊髓炎的早期试验中表现良好[123],但在多发性硬化的第二阶段试验中未能达到预期效果[124]。目前还有一些其他候选物正处于临床前的研究探索阶段。但实际上,多发性硬化作为一种多因素诱发的炎性诱导的脱髓鞘疾病模型,其发病机制复杂多变,至今仍缺乏一个与人类疾病高度相似的动物模型来进行模拟研究,因此极大的限制了对于该类疾病的药物开发[125]。目前的解决方法是结合小分子或生物制剂针对单一疾病因素开发一种可用于临床前的测试药物。即便如此,这种针对单因素诱导的模型的方法增加了潜在药物和靶点在临床试验中失败的风险,部分原因是在这种单因素模型(如EAE、铜腙诱导的脱髓鞘模型和溶血卵磷脂诱导的脱髓鞘模型等)下进行的研究无法解决炎症、髓鞘再生和神经退化这一系列复杂过程之间的相互作用[106]。
选择合适的临床前候选药物的关键在于有效甄别出在多发性硬化髓鞘再生失败过程中的影响因素,即使已有的药物具有促进少突胶质前体细胞分化的能力,但是在微环境下可能存在其他干扰因素阻断髓鞘再生从而使得该药物失去原有的治疗效果[106]。
然而,从神经组织病理学研究的结论来看,可以明确多发性硬化的病变是异质性的。在过去的20年里,经权威研究已经定义了多发性硬化病变中不同的炎症模式[126],近期针对髓鞘再生的研究进一步明确了多发性硬化的病变异质性。一个聚焦于促进少突胶质细胞分化的研究项目的结果为:30%患者的病理切片显示在病灶部位缺乏足够数量的少突胶质前体细胞来促使髓鞘再生;而在其余的病变中,尽管存在足够的少突胶质前体细胞,但是在分化和髓鞘形成的后期,仍旧无法完成髓鞘再生[127]。这项研究表明,针对少突胶质细胞分化的治疗可能只对70%的病变有效,其余的患者则需要促进祖细胞激活和迁移的疗法。如果这70%的人在髓鞘再生过程中,少突胶质前体细胞的分化进程被阻断,则表现出进一步的异质性,那么只针对该过程的临床治疗药物的治愈率会进一步降低,而针对性阻断每个特定的阶段的联合疗法则将具有更明确的应用前景。因此,下一步药物开发的重点工作应聚焦于对髓鞘再生过程进行更为详细的神经病理学研究。目前随着新技术的应用,如将单细胞RNA测序等技术应用于病人样本,将有望明确病变过程内的细胞类型及其所处的分化阶段。
第二种方法则是使用高通量药物筛选技术,以小分子化合物库或经美国食品和药物管理局批准的药物作为筛选对象,测试少突胶质细胞对这些药物的反应。这种筛查方法已经在诱导性多能干细胞的原代细胞或少突胶质前体细胞中进行了测试,这项研究以MBP表达水平为检测指标评估少突胶质细胞的分化程度,并筛选出美国食品和药物管理局批准的药物咪康唑和氯倍他索[128-129]。已知这两种药物能够激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)和糖皮质激素受体信号通路,但对于少突胶质细胞的信号通路影响尚不明确。药物苯托品和氯马司汀这两类药物调控少突胶质细胞分化的新途径在实验研究中已被证实[130]。这些候选药物目前已获美国食品和药物管理局批准,临床试验的进展较其他药物更为顺利,如氯马斯汀的一期临床试验已经完成,其结果表明患者的视觉通路传导速度明显改善,该小分子化合物在临床试验的成功在髓鞘再生药物领域代表了一个里程碑式的进步[131]。
2.3.2 细胞疗法 另一种促进髓鞘再生的方法是细胞移植,有实验证据表明,通过细胞移植可以恢复髓鞘再生。LACHAPELLE
等[132]在将野生型细胞移植到Shiverer突变小鼠模型(这种小鼠的MBP基因突变导致缺乏正常的髓鞘结构)中后,观察到了髓鞘再生的现象。此外,在溶血卵磷脂(LPC)诱导的脱髓鞘模型小鼠中,移植髓鞘形成细胞到病灶区域也可观察到髓鞘再生现象[133-134],并且这种修复作用是非特异的。因此移植相应的细胞均可以实现中枢神经系统髓鞘再生[135-137]。
然而,利用移植细胞治疗多发性硬化时,如何将细胞移植到多个病灶区域仍旧是一大障碍,加之每个病灶区域都存在慢性炎症和潜在的不利环境,因此细胞移植面临的另一个挑战是经此方法治疗后如果髓鞘生成过少,会造成白质营养不良。目前已有一项临床研究,在患有佩梅病的儿童身上使用具有分化为少突胶质细胞能力的人中枢神经系统干细胞进行移植试验,该疾病是由于PLP1基因突变而引起的严重脑白质营养不良[138]。尽管这4例儿童没有表现出不良反应,但与动物模型研究中观察到的髓鞘再生程度相比,核磁共振影像结果显示细胞注射部位附近只有少量的髓鞘再生现象,推测有两个因素可能影响了髓鞘再生的程度:首先,啮齿类动物和人脑体积大小差异显著,而移植细胞的迁移能力是有限的,因此限制了移植的细胞迁移到病灶区域的数量;其次,临床试验中使用的细胞需要进行长期测试,需要制订一套标准化的操作规程减少细胞受到其他外来因素的影响。目前用于制备少突胶质前体细胞的方案相对于骨髓细胞或T细胞较为落后,有可能影响移植细胞本身的活力[139-140]。
2.3.3 震荡电场刺激疗法 外加电场刺激于脱髓鞘部位可清除内源性的损伤电流,减少轴突的退变和萎缩,促进轴突的再生和髓鞘的再形成,能够有效抑制星形胶质细胞的增生,抑制脊髓损伤断端的瘢痕形成,可以缓解四肢肌肉的痉挛,避免肌肉出现不必要的萎缩,以提高功能的恢复,同时可改善脊髓损伤后的膀胱收缩功能,促进排尿,从而改善脊髓损伤的预后,同时电场刺激阴、阳两极的方向变化对脱髓鞘损伤后的神经再生起着举足轻重的作用[141]。
2.3.4 激素冲击疗法 激素冲击疗法是采用短期内大剂量应用激素迅速控制病情恶化的一种静脉给药方法。在脱髓鞘急性期,通常以大剂量激素冲击治疗为主,甲基强的松龙可直接作用于脱髓鞘轴突,迅速减轻炎症和水肿,减少神经细胞的死亡,改善轴索传导,对脱髓鞘区受损的传导性神经纤维有效,以免发生不可逆的病变[142]。

| [1] RUDOLF V. Ueber das granulirte Aussehen der Wandungen der Gehirnventrikel. Allg Z Psychiat. 1856;3:242-250. [2] RIO-HORTEGA PD. Tercera aportacion al conocimiento morfologicoe interpretacion funcional de la oligodendroglia. Mem Real Soc Espan Hist Nat. 1928;14:40-122. [3] TIANE A, SCHEPERS M, ROMBAUT B, et al. From OPC to Oligodendrocyte: An Epigenetic Journey. Cells. 2019;8(10):1236. [4] RIO-HORTEGA PD. Histogenesis y evolucion normal; exodo y distribucion regional de la microglia. Memor Real Soc Esp Hist Nat. 1921;11:213-268. [5] PEFEROEN L, KIPP M, VAN DER VALK P, et al. Amor, Oligodendrocyte-microglia cross-talk in the central nervous system. Immunology. 2014; 141(3):302-313. [6] DELPECH JC, HERRON S, BOTROS MB, aet al. Neuroimmune Crosstalk through Extracellular Vesicles in Health and Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2019; 42(5):361-372. [7] LINNERBAUER M, WHEELER MA, QUINTANA FJ. Astrocyte Crosstalk in CNS Inflammation. Neuron. 2020;108(4):608-622. [8] ZHANG Y, LU XY, CASELLA G, et al. Generation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells From Mouse Bone Marrow Cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:247. [9] SHERMAN DL, BROPHY PJ. Mechanisms of axon ensheathment and myelin growth. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(9):683-690. [10] MARQUES S, ZEISEL A, CODELUPPI S, et al. Oligodendrocyte heterogeneity in the mouse juvenile and adult central nervous system. Science. 2016; 352(6291):1326-1329. [11] BHATT A, FAN LW, PANG Y. Strategies for myelin regeneration: lessons learned from development. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(14):1347-1350. [12] NAVE KA. Myelination and the trophic support of long axons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(4):275-283. [13] FÜNFSCHILLING U, SUPPLIE LM, MAHAD D, et al. Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity. Nature. 2012;485(7399):517-521. [14] LEE Y, MORRISON BM, LI Y, et al. Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nature. 2012;487(7408):443-448. [15] WAXMAN SG. Axonal conduction and injury in multiple sclerosis: the role of sodium channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(12):932-941. [16] HAINES JD, INGLESE M, CASACCIA P. Axonal damage in multiple sclerosis. Mt Sinai J Med. 2011;78(2):231-243. [17] 谢登峰,邱小燕,熊春霞,等.哺乳动物少突胶质细胞分化、成熟和功能化的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(8):1443-1456. [18] KUHN S, GRITTI L, CROOKS D, et al. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells. 2019;8(11):1424. [19] 张冠宇,孙平新,李文林.少突胶质细胞前体细胞移植治疗中枢神经系统脱髓鞘疾病的研究进展[J]. 第二军医大学学报,2017,38(1):7-14. [20] DE LA FUENTE AG, QUEIROZ RML, GHOSH T, et al. Changes in the Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Proteome with Ageing. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020;19(8):1281-1302. [21] NISHIYAMA A. Polydendrocytes: NG2 cells with many roles in development and repair of the CNS. Neuroscientist. 2007;13(1):62-76. [22] TAUPIN P. Thirteen compounds promoting oligodendrocyte progenitor cell differentiation and remyelination for treating multiple sclerosis: WO2010054307. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2010;20(12):1767-1773. [23] GOLDMAN SA, KUYPERS NJ. How to make an oligodendrocyte. Development. 2015;142(23):3983-3995. [24] LONG KLP, BRETON JM, BARRAZA MK, et al. Hormonal Regulation of Oligodendrogenesis I: Effects across the Lifespan. Biomolecules. 2021;11(2): 283. [25] PRINGLE NP, MUDHAR HS, COLLARINI EJ, et al. PDGF receptors in the rat CNS: during late neurogenesis, PDGF alpha-receptor expression appears to be restricted to glial cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage. Development. 1992;115(2):535-551. [26] FURUSHO M, ISHII A, BANSAL R. Signaling by FGF Receptor 2, Not FGF Receptor 1, Regulates Myelin Thickness through Activation of ERK1/2-MAPK, Which Promotes mTORC1 Activity in an Akt-Independent Manner. J Neurosci. 2017;37(11):2931-2946. [27] CUI QL, ALMAZAN G. IGF-I-induced oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation requires PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK, and Src-like tyrosine kinases. J Neurochem. 2007;100(6):1480-1493. [28] YANG J, CHENG X, QI J, et al. EGF Enhances Oligodendrogenesis from Glial Progenitor Cells. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:106. [29] HAYAKAWA K, PHAM LD, SOM AT, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates the migration of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. J Neurosci. 2011; 31(29):10666-10670. [30] JEAN I, LAVIALLE C, BARTHELAIX-POUPLARD A, et al. Neurotrophin-3 specifically increases mature oligodendrocyte population and enhances remyelination after chemical demyelination of adult rat CNS. Brain Res. 2003;972(1-2):110-118. [31] TALBOTT JF, CAO Q, BERTRAM J, et al. CNTF promotes the survival and differentiation of adult spinal cord-derived oligodendrocyte precursor cells in vitro but fails to promote remyelination in vivo. Exp Neurol. 2007; 204(1):485-489. [32] KONDO T, RAFF MC. A role for Noggin in the development of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Dev Biol. 2004;267(1):242-251. [33] FRANCO PG, SILVESTROFF L, SOTO EF, et al. Thyroid hormones promote differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and improve remyelination after cuprizone-induced demyelination. Exp Neurol. 2008;212(2):458-467. [34] KUCHAROVA K, STALLCUP WB. Dissecting the multifactorial nature of demyelinating disease. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):628-632. [35] CLEMENTE D, ORTEGA MC, MELERO-JEREZ C, et al. The effect of glia-glia interactions on oligodendrocyte precursor cell biology during development and in demyelinating diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:268. [36] GENSEL JC, ZHANG B. Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2015;1619:1-11. [37] RAWJI KS, YOUNG AMH, GHOSH T, et al. Niacin-mediated rejuvenation of macrophage/microglia enhances remyelination of the aging central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;139(5):893-909. [38] FERNANDEZ-CASTANEDA A, GAULTIER A. Adult oligodendrocyte progenitor cells - Multifaceted regulators of the CNS in health and disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;57:1-7. [39] THOMAS L, PASQUINI LA. Galectin-3-Mediated Glial Crosstalk Drives Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and (Re)myelination. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:297. [40] COUMANS JV, LIN TT, DAI HN, et al. Axonal regeneration and functional recovery after complete spinal cord transection in rats by delayed treatment with transplants and neurotrophins. J Neurosci. 2001;21(23): 9334-9344. [41] NESS JK, MITCHELL NE, WOOD TL. IGF-I and NT-3 signaling pathways in developing oligodendrocytes: differential regulation and activation of receptors and the downstream effector Akt. Dev Neurosci. 2002;24(5):437-445. [42] YANG J, YAN Y, XIA Y, et al. Neurotrophin 3 transduction augments remyelinating and immunomodulatory capacity of neural stem cells. Mol Ther. 2014;22(2):440-450. [43] STAHL N, YANCOPOULOS GD. The tripartite CNTF receptor complex: activation and signaling involves components shared with other cytokines. J Neurobiol. 1994;25(11):1454-1466. [44] STANKOFF B, AIGROT MS, NOEL F, et al. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) enhances myelin formation: a novel role for CNTF and CNTF-related molecules. J Neurosci. 2002;22(21):9221-9227. [45] WU M, HERNANDEZ M, SHEN S, et al. Differential modulation of the oligodendrocyte transcriptome by sonic hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein 4 via opposing effects on histone acetylation. J Neurosci. 2012; 32(19):6651-6664. [46] FERENT J, ZIMMER C, DURBEC P, et al. Sonic Hedgehog signaling is a positive oligodendrocyte regulator during demyelination. J Neurosci. 2013; 33(5):1759-1772. [47] MERCHAN P, BRIBIAN A, SANCHEZ-CAMACHO C, et al., Sonic hedgehog promotes the migration and proliferation of optic nerve oligodendrocyte precursors. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007;36(3):355-368. [48] IZRAEL M, ZHANG P, KAUFMAN R, et al. Human oligodendrocytes derived from embryonic stem cells: Effect of noggin on phenotypic differentiation in vitro and on myelination in vivo. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007;34(3):310-323. [49] YOUNES-RAPOZO V, BERENDONK J, SAVIGNON T, et al. Thyroid hormone deficiency changes the distribution of oligodendrocyte/myelin markers during oligodendroglial differentiation in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2006; 24(7):445-453. [50] GHORBANI S, YONG VW. The extracellular matrix as modifier of neuroinflammation and remyelination in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2021: awab059. [51] SARASWAT D, WELLIVER RR, RAVICHANDAR R, et al. Heparanome-Mediated Rescue of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Quiescence following Inflammatory Demyelination. J Neurosci. 2021;41(10):2245-2263. [52] KREMER D, CUI QL, GÖTTLE P, et al. CXCR7 Is Involved in Human Oligodendroglial Precursor Cell Maturation. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146503. [53] XU X, YU Q, FANG M, et al. Stage-specific regulation of oligodendrocyte development by Hedgehog signaling in the spinal cord. Glia. 2020;68(2): 422-434. [54] WYLOT B, MIECZKOWSKI J, NIEDZIOLKA S, et al. Csf1 Deficiency Dysregulates Glial Responses to Demyelination and Disturbs CNS White Matter Remyelination. Cells. 2019;9(1):99. [55] CIGNARELLA F, FILIPELLO F, BOLLMAN B, et al. TREM2 activation on microglia promotes myelin debris clearance and remyelination in a model of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140(4):513-534. [56] HORIUCHI M, SUZUKI-HORIUCHI Y, AKIYAMA T, et al. Differing intrinsic biological properties between forebrain and spinal oligodendroglial lineage cells. J Neurochem. 2017;142(3):378-391. [57] ELBAZ B, POPKO B. Molecular Control of Oligodendrocyte Development. Trends Neurosci. 2019;42(4):263-277. [58] KÜSPERT M, HAMMER A, BÖSL MR, et al. Olig2 regulates Sox10 expression in oligodendrocyte precursors through an evolutionary conserved distal enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(4):1280-1293. [59] DUNCAN GJ, PLEMEL JR, ASSINCK P, et al. Myelin regulatory factor drives remyelination in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134(3):403-422. [60] APRATO J, SOCK E, WEIDER M, et al. Myrf guides target gene selection of transcription factor Sox10 during oligodendroglial development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(3):1254-1270. [61] EMERY B, AGALLIU D, CAHOY JD, et al. Myelin gene regulatory factor is a critical transcriptional regulator required for CNS myelination. Cell. 2009; 138(1):172-185. [62] FLETCHER JL, MAKOWIECKI K, CULLEN CL, et al. Oligodendrogenesis and myelination regulate cortical development, plasticity and circuit function. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021:S1084-9521(21)00064-1. [63] CULLEN CL, PEPPER RE, CLUTTERBUCK MT, et al. Periaxonal and nodal plasticities modulate action potential conduction in the adult mouse brain. Cell Rep. 2021;34(3):108641. [64] KAWAGASHIRA Y, KOIKE H, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Aberrant Expression of Nodal and Paranodal Molecules in Neuropathy Associated With IgM Monoclonal Gammopathy With Anti-Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein Antibodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020;79(12):1303-1312. [65] GALLEGO-DELGADO P, JAMES R, BROWNE E, et al. Neuroinflammation in the normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) of the multiple sclerosis brain causes abnormalities at the nodes of Ranvier. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(12): e3001008. [66] PFEIFFER F, FROMMER-KAESTLE G, FALLIER-BECKER P. Structural adaption of axons during de- and remyelination in the Cuprizone mouse model. Brain Pathol. 2019;29(5):675-692. [67] FAIVRE-SARRAILH C. Molecular organization and function of vertebrate septate-like junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020;1862(5): 183211. [68] KASTRITI ME, SARGIANNIDOU I, KLEOPA KA, et al. Differential modulation of the juxtaparanodal complex in Multiple Sclerosis. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015;67:93-103. [69] GOPALASINGAM G, BARTLETT CA, MCGONIGLE T, et al. The effects of a combination of ion channel inhibitors on pathology in a model of demyelinating disease. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;34:1-8. [70] LAOUAREM Y, KASSOUSSI A, ZAHAF A, et al. Functional cooperation of the hedgehog and androgen signaling pathways during developmental and repairing myelination. Glia. 2021;69(6):1369-1392. [71] BERGAGLIO T, LUCHICCHI A, SCHENK GJ. Engine Failure in Axo-Myelinic Signaling: A Potential Key Player in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:610295. [72] DUNCAN GJ, SIMKINS TJ, EMERY B. Neuron-Oligodendrocyte Interactions in the Structure and Integrity of Axons. Front Cell Dev Bio. 2021;9:653101. [73] RAJKOWSKA G, MAHAJAN G, MACIAG D, et al. Oligodendrocyte morphometry and expression of myelin - Related mRNA in ventral prefrontal white matter in major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;65:53-62. [74] LIU M, XU P, GUAN Z, et al. Ulk4 deficiency leads to hypomyelination in mice. Glia. 2018;66(1):175-190. [75] SNAIDERO N, VELTE C, MYLLYKOSKI M, et al. Antagonistic Functions of MBP and CNP Establish Cytosolic Channels in CNS Myelin. Cell Rep. 2017; 18(2):314-323. [76] GHOSH A, MANRIQUE-HOYOS N, VOIGT A, et al. Targeted ablation of oligodendrocytes triggers axonal damage. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22735. [77] GRITSCH S, LU J, THILEMANN S, et al. Oligodendrocyte ablation triggers central pain independently of innate or adaptive immune responses in mice. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5472. [78] ADIELE RC, ADIELE CA. Metabolic defects in multiple sclerosis. Mitochondrion. 2019;44:7-14. [79] CORREALE J, MARRODAN M, YSRRAELIT MC. Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration and Axonal Dysfunction in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Biomedicines. 2019;7(1):14. [80] SEKYI MT, LAUDERDALE K, ATKINSON KC, et al. Alleviation of extensive visual pathway dysfunction by a remyelinating drug in a chronic mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2021;31(2):312-332. [81] NAVE KA, WERNER HB. Ensheathment and Myelination of Axons: Evolution of Glial Functions. Annu Rev Neurosci.2021:44:197-219. [82] SPAAS J, VAN VEGGEL L, SCHEPERS M, et al. Schreiber, and T. Vanmierlo, Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021; 78(10):4615-4637. [83] JHA MK, MORRISON BM. Lactate Transporters Mediate Glia-Neuron Metabolic Crosstalk in Homeostasis and Disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:589582. [84] PHILIPS T, MIRONOVA YA, JOUROUKHIN Y, et al. MCT1 Deletion in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells Causes Late-Onset Hypomyelination and Axonal Degeneration. Cell Rep. 2021;34(2):108610. [85] CHENG J, SHEN W, JIN L, et al. Treadmill exercise promotes neurogenesis and myelin repair via upregulating Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathways in the juvenile brain following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(5):1447-1463. [86] POURNAJAF S, VALIAN N, MOHAGHEGH SHALMANI L, et al. Fingolimod increases oligodendrocytes markers expression in epidermal neural crest stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173502. [87] LANGHNOJA J, BUCH L, PILLAI P. Potential role of NGF, BDNF, and their receptors in oligodendrocytes differentiation from neural stem cell: An in vitro study. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(2):432-446. [88] XU Z, JIANG J, XU S, et al. Nerve Growth Factor is a Potential Treated Target in Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020: doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00993-1. [89] BRANDI R, FABIANO M, GIORGI C, et al. Nerve Growth Factor Neutralization Promotes Oligodendrogenesis by Increasing miR-219a-5p Levels. Cells. 2021;10(2):405. [90] FRESSINAUD C, THOMAS O, UMERSKA AM, et al. Lipid Nanoparticles Vectorized with NFL-TBS.40-63 Peptide Target Oligodendrocytes and Promote Neurotrophin-3 Effects After Demyelination In Vitro. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(11):2732-2748. [91] MCCARTNEY AM, ABEJUELA VL, ISAACSON LG. Characterization of trkB immunoreactive cells in the intermediolateral cell column of the rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 2008;440(2):103-108. [92] DAI X, LERCHER LD, CLINTON PM, et al. The trophic role of oligodendrocytes in the basal forebrain. J Neurosci. 2003;23(13):5846-5853. [93] DE PAULA ML, CUI QL, HOSSAIN S, et al. The PTEN inhibitor bisperoxovanadium enhances myelination by amplifying IGF-1 signaling in rat and human oligodendrocyte progenitors. Glia. 2014;62(1):64-77. [94] KUROWSKA Z, BRUNDIN P, SCHWAB ME, et al. Intracellular Nogo-A facilitates initiation of neurite formation in mouse midbrain neurons in vitro. Neuroscience. 2014;256:456-466. [95] LI X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG WF, et al. P7C3 attenuates CNS autoimmunity by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(6):1565-1567. [96] WANG X, LI R, ZACHAREK A, et al. Administration of Downstream ApoE Attenuates the Adverse Effect of Brain ABCA1 Deficiency on Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3368. [97] RUMAJOGEE P, ALTAMENTOVA S, LI L, et al. Exogenous Neural Precursor Cell Transplantation Results in Structural and Functional Recovery in a Hypoxic-Ischemic Hemiplegic Mouse Model. eNeuro. 2018;5(5):ENEURO.0369-0318. 2018. [98] AHMED Z, ASI YT, LEES AJ, et al. Identification and quantification of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2013;23(3):263-273. [99] NORI S, KHAZAEI M, AHUJA CS, et al. Human Oligodendrogenic Neural Progenitor Cells Delivered with Chondroitinase ABC Facilitate Functional Repair of Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;11(6): 1433-1448. [100] ZHU W, ZHANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Monoclonal Antibody-Based Treatments for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: From Bench to Bedside. Neurosci Bull. 2020;36(10):1213-1224. [101] MATHYS H, DAVILA-VELDERRAIN J, PENG Z, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2019;570(7761):332-337. [102] ROSATI G. The prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the world: an update. Neurol Sci. 2001;22(2):117-139. [103] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, LATZ E. Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(7):463-477. [104] 孙薇.白细胞介素-1α和白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂与多发性硬化病的相关性研究[J].中国现代医生,2021,59(14):45-48. [105] LI X, ZHANG Y, YAN Y, et al. Neural Stem Cells Engineered to Express Three Therapeutic Factors Mediate Recovery from Chronic Stage CNS Autoimmunity. Mol Ther. 2016;24(8):1456-1469. [106] FRANKLIN RJM, FFRENCH-CONSTANT C. Regenerating CNS myelin - from mechanisms to experimental medicines. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(12): 753-769. [107] PLEMEL JR, LIU WQ, YONG VW. Remyelination therapies: a new direction and challenge in multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(9):617-634. [108] LECCA D, ABBRACCHIO MP, FUMAGALLI M. Purinergic Receptors on Oligodendrocyte Progenitors: Promising Targets for Myelin Repair in Multiple Sclerosis? Front Pharmacol. 2021;11:629618. [109] UITDEHAAG BM, BARKHOF F, COYLE PK, et al. The changing face of multiple sclerosis clinical trial populations. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27(8):1529-1537. [110] BAECHER-ALLAN C, KASKOW BJ, WEINER HL. Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms and Immunotherapy. Neuron. 2018;97(4):742-768. [111] RICCIO P, ROSSANO R. Nutrition facts in multiple sclerosis. ASN Neuro. 2015; 7(1):1759091414568185. [112] NAPIER MD, POOLE C, SATTEN GA, et al. Heavy metals, organic solvents, and multiple sclerosis: An exploratory look at gene-environment interactions. Arch Environ Occup Health. 2016;71(1):26-34. [113] MAGRINI A, PIETROIUSTI A, COPPETA L, et al. Shift work and autoimmune thyroid disorders. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006;19(4 Suppl):31-36. [114] WINGERCHUK DM. Smoking: effects on multiple sclerosis susceptibility and disease progression. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2012;5(1):13-22. [115] QUESNEL S, FEINSTEIN A. Multiple sclerosis and alcohol: a study of problem drinking. Mult Scler. 2004;10(2):197-201. [116] LUCAS RM, BYRNE SN, CORREALE J, et al. Ultraviolet radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2015;5(5):413-424. [117] MUNGER KL, LEVIN LI, HOLLIS BW, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis. JAMA. 2006;296(23):2832-2838. [118] GOLDMAN SA, NEDERGAARD M, WINDREM MS. Glial progenitor cell-based treatment and modeling of neurological disease. Science. 2012; 338(6106):491-495. [119] YEUNG MSY, DJELLOUL M, STEINER E, et al. Dynamics of oligodendrocyte generation in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 2019;566(7745):538-542. [120] FOX IJ, DALEY GQ, GOLDMAN SA, et al. Stem cell therapy. Use of differentiated pluripotent stem cells as replacement therapy for treating disease. Science. 2014;345(6199):1247391. [121] 牛红妹,王明洋,李林.中枢神经系统髓鞘形成和再生调控机制研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2020,34(6):451-459. [122] 玛娜璐璐. 利用STZ损伤OLN93细胞拟AD模型从PI3K/AKT-mTOR通路探讨参枝苓髓鞘保护机制[D].北京:北京中医药大学, 2019. [123] CADAVID D, BALCER L, GALETTA S, et al. Safety and efficacy of opicinumab in acute optic neuritis (RENEW): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(3):189-199. [124] Medicine Us National Library Of. Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of BIIB033 in Participants With Relapsing Forms of Multiple Sclerosis When Used Concurrently With Avonex 2017. [125] HUANG JK, JARJOUR AA, NAIT OUMESMAR B, et al. Retinoid X receptor gamma signaling accelerates CNS remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14(1): 45-53. [126] LUCCHINETTI C, BRÜCK W, PARISI J, et al. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann Neurol. 2000;47(6):707-717. [127] BOYD A, ZHANG H, WILLIAMS A. Insufficient OPC migration into demyelinated lesions is a cause of poor remyelination in MS and mouse models. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;125(6):841-859. [128] DESHMUKH VA, TARDIF V, Lyssiotis CA, et al. A regenerative approach to the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Nature. 2013;502(7471):327-332. [129] MEI F, MAYORAL SR, NOBUTA H, et al. Identification of the Kappa-Opioid Receptor as a Therapeutic Target for Oligodendrocyte Remyelination. J Neurosci. 2016;36(30):7925-7935. [130] Medicine Us National Library Of. Assessment of Clemastine Fumarate as a Remyelinating Agent in Multiple Sclerosis 2018. [131] GREEN AJ, GELFAND JM, CREE BA, et al. Clemastine fumarate as a remyelinating therapy for multiple sclerosis (ReBUILD): a randomised, controlled, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet. 2017;390(10111):2481-2489. [132] LACHAPELLE F, GUMPEL M, BAULAC M, et al. Transplantation of CNS fragments into the brain of shiverer mutant mice: extensive myelination by implanted oligodendrocytes. I. Immunohistochemical studies. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(6):325-334. [133] BLAKEMORE WF, FRANKLIN RJ. Transplantation of glial cells into the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1991;14(8):323-327. [134] BLAKEMORE WF, CRANG AJ. The use of cultured autologous Schwann cells to remyelinate areas of persistent demyelination in the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1985;70(2):207-223. [135] WANG S, BATES J, LI X, et al. Human iPSC-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cells can myelinate and rescue a mouse model of congenital hypomyelination. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(2):252-264. [136] WINDREM MS, NUNES MC, RASHBAUM WK,et al. Fetal and adult human oligodendrocyte progenitor cell isolates myelinate the congenitally dysmyelinated brain. Nat Med. 2004;10(1):93-97. [137] WINDREM MS, SCHANZ SJ, GUO M, et al. Neonatal chimerization with human glial progenitor cells can both remyelinate and rescue the otherwise lethally hypomyelinated shiverer mouse. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(6):553-565. [138] GUPTA N, HENRY RG, STROBER J, et al. Neural stem cell engraftment and myelination in the human brain. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(155):155ra137. [139] PIAO J, MAJOR T, AUYEUNG G, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitors remyelinate the brain and rescue behavioral deficits following radiation. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(2):198-210. [140] HARRISINGH MC, FFRENCH-CONSTANT C. Can the irradiated brain be salvaged by oligodendrocyte precursor transplantation? Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(2):113-114. [141] 田大胜.振荡电场刺激对受损脊髓少突胶质前体细胞的活化作用及相关研究[D].济南:山东大学,2014. [142] 赵媛,陈小虎,王晓莉,等.激素冲击疗法治疗特发性脱髓鞘视神经病变的远期疗效[J].国际眼科杂志,2013,13(2):322-323. |
| [1] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 周 倩, 张 强, 陈 秋. 人体唾液成分与骨质疏松/骨量低下[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | 金 涛, 刘 林, 朱晓燕, 史宇悰, 牛建雄, 张同同, 吴树金, 杨青山. 骨关节炎与线粒体异常[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | 张立创, 徐 浩, 马迎辉, 熊梦婷, 韩海慧, 鲍嘉敏, 翟伟韬, 梁倩倩. 免疫调控淋巴回流功能治疗类风湿关节炎的机制及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 张 强, 刘 静, 邵 明. 针刺治疗帕金森病:动物实验显示的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | 吴玮玥, 郭晓东, 包崇云. 工程化外泌体在骨修复再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [7] | 周洪琴, 吴丹丹, 杨 琨, 刘 琪. 传递特定miRNA的外泌体可调控成骨并促进成血管[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [8] | 张璟琳, 冷 敏, 朱博恒, 汪 虹. 干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [9] | 黄晨玮, 费彦亢, 朱梦梅, 李鹏昊, 于 兵. 谷胱甘肽在干细胞“干性”及调控中的重要作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [10] | 惠小珊, 白 京, 周思远, 王 阶, 张金生, 何庆勇, 孟培培. 中医药调控干细胞诱导分化的理论机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [11] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | 范一鸣, 刘方煜, 张洪宇, 李 帅, 王岩松. 脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | 郭 嘉, 丁琼桦, 刘 泽, 吕思懿, 周泉程, 高玉花, 白春雨. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体的生物学特性及免疫调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [14] | 许 磊, 韩晓强, 张锦涛, 孙海飚. 关节软骨细胞周围透明质酸产生、转化和功能特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [15] | 李嘉骏, 夏 天, 刘佳敏, 陈 锋, 陈豪特, 卓映宏, 吴炜锋. 淫羊藿苷调控成骨信号相关通路治疗激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
早在18世纪,VIRCHOW就已描述了除神经元之外的细胞,他认为这类细胞组成了大脑的结缔组织,称之为“神经胶(Nervenkitt)”[1],即神经胶质细胞。胶质细胞的分类最初是通过显微镜观察在不同染色方法下的不同形态特征来完成的。RAMON最初通过改良的铬酸盐-硝酸银染法观察到神经细胞中的星形胶质细胞。随后,RIO HORTEGA通过碳酸银浸染的方法发现了另外两种细胞类型,一种是少突胶质细胞(Oligodendrocyte),最初被称为束间胶质细胞[2],占总神经胶质群的5%-10%[3];另一种是与星形胶质细胞与少突胶质细胞具有明显形态差异的细胞,被称之为小胶质细胞(Microglia)[4],见图1,占总神经胶质群的10%-20%[5]。
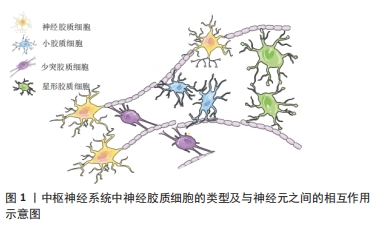
近年来,研究者对胶质细胞在中枢神经系统中的功能认知取得了重大进展。胶质细胞对于神经元的功能正常发育和成熟是必不可少的,其对细胞内外环境变化的反应能力以及对神经系统的功能至关重要。此外,越来越多的研究表明胶质细胞可能通过神经胶质网络传递信号,具有与神经元互补的信号传递能力[6-7]。目前,有关神经元和神经胶质细胞的特化及其持续的相互作用的发现不断更新,这也为神经系统疾病的病理结果分析提供了新的见解,而少突胶质细胞除了具有与髓鞘形成和维持相关的功能外,可能还具有很多未知功能等待被深入研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间范围为各数据库建库至2021-05-01。
1.1.3 检索数据库 ①PubMed数据库(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/),PubMed 是一个免费的搜寻引擎,提供生物医学方面的论文搜寻以及摘要的数据库,它的数据库来源为MEDLINE,其核心主题为医学,但它同时也提供对于相关生物医学资讯上相当全面的资源,该搜寻引擎是由美国国立医学图书馆提供,作为 Entrez 资讯检索系统的一部分。②GeenMedical(https://www.geenmedical.com/),GeenMedical是基于Sci-Hub和其他免费文献资源提供英文文献免费下载的网站,支持Sci-Hub文献下载所使用的DOI和PMID,而且还支持关键词搜索,是一个全能型的文献下载网站。③中国知网(https://www.cnki.net/),中国知网是中国学术期刊(光盘版)电子杂志社和同方知网(北京)技术有限公司共同主办的出版网站,是CNKI各类知识信息内容的数字出版平台和知识服务平台。
1.1.4 检索词 包括英文及中文检索词、检索词的逻辑组配等。英文关键检索词为“Oligodendrocyte,Demyelinating disease”,中文关键检索词为“少突胶质细胞,脱髓鞘疾病”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 期刊文献,研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 中英文数据库检索策略,见图2。
1.1.7 检索文献量 根据数据库搜索初步检索得到相关文献435篇。
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:观点新颖、切入点创新的涉及少突胶质细胞和脱髓鞘疾病的相关研究,涉及少突胶质前体细胞、少突胶质细胞相关功能以及髓鞘再生方面的文献,以及收录脱髓鞘疾病治疗方向的文献入参考库。
排除标准:不涉及此篇综述研究目的的文献,重复性观点研究文献,质量较低且观点过时的文献,继而排除中英文重复性观点和研究文献。
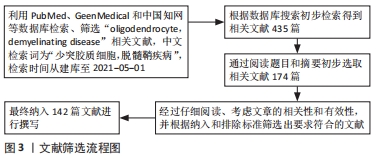
1.3 数据提取 经过中英文数据库初步检索获得相关文献435篇,通过粗略阅读摘要和结果进一步选取相关文献174篇,后经过仔细阅读、考虑文章的相关性和参考价值,并根据纳入和排除标准共筛选出相关参考文献142篇,检索流程见图3。
局限性:从宏观到微观,髓鞘形成和髓鞘再生过程十分复杂,受到年龄、遗传、环境、表观遗传调控、炎症微环境、转录因子、神经营养因子等多因素影响。实现脱髓鞘疾病的有效治疗,对髓鞘再生机制的深层次研究和对这些影响因素的进一步挖掘和探究仍然至关重要。以少突胶质细胞的功能、分化、髓鞘再生机制等为基础深入探索,努力发掘内外影响因素、新的信号通路、细胞与环境的相互作用等,剖析其规律,寻找可靠切入点,新的信号分子、更多表观遗传及其他调控因素有望被发现从而作为新兴的疾病治疗靶点。随着药物来源的拓展、生产成本的降低,在目前初步成熟但效果欠佳、有待深入完善的治疗基础上,研发出低成本、低不良反应、高药物疗效、高效益的治疗策略是当务之急。
研究前景:尽管小分子药物、细胞疗法展现出了极大的治疗潜力,不管是在技术、设备还是使用方式上,在运用过程中不断被优化和迭代,但细胞疗法的精准性和长效性仍需不断完善。学术研究变成真正临床应用需要不断用实验去验证、修正或推翻已有研究基础,这是一个极为漫长的过程,要不断探索、去获取可靠实验数据的支撑。进一步为脱髓鞘疾病治疗带来非常广阔的前景,实现对脱髓鞘疾病的有效治疗,为临床治疗奠定基础,产生更新颖、更有价值的研究假设。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
脱髓鞘疾病:中枢神经系统脱髓鞘疾病是一类同时涉及脑、脊髓和周围神经等多个部位的疾病。脱髓鞘是其整个病理过程中最具特征性的表现,该类疾病因为具有发病机制复杂、临床表现多样、对治疗药物反应的个体差异性较大等特点,在临床治疗过程中具有极大的挑战性。
少突胶质细胞:是中枢神经系统内形成髓鞘的细胞,由少突胶质前体细胞分化形成。主要功能是在中枢神经系统中包绕轴突、形成绝缘的髓鞘结构、协助生物电信号的跳跃式高效传递并维持和保护神经元的正常功能。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
少突胶质细胞的形成:少突胶质细胞源自侧脑室室管膜下区的胚胎神经上皮干细胞即神经祖细胞,经历前少突胶质细胞祖细胞和少突胶质前体细胞两个阶段后最终分化完成。神经祖细胞是一种能够“自我更新”和分化成为中枢神经系统主要类型细胞的干细胞群,前少突胶质细胞祖细胞呈圆形,表面较为光滑,分裂增殖能力强。少突胶质前体细胞为圆形或椭圆形细胞,胞体常呈两极或三极突起,仍具有一定的分裂增殖能力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||