中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (34): 5427-5431.doi: 10.12307/2021.234
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
不同配方新型牙用玻璃陶瓷的显微结构与力学性能
任世鹏1,陈新民2,青 松1,喻 洁1,杨 婷1,唐婉容1
- 1川北医学院附属医院口腔科,四川省南充市 637000;2四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610000
Microstructure and mechanical properties of the new dental glass ceramics with different formulations
Ren Shipeng1, Chen Xinmin2, Qing Song1, Yu Jie1, Yang Ting1, Tang Wanrong1
- 1Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
玻璃陶瓷:玻璃是一种具有无规则结构的非晶态固体,或称玻璃态物质,而玻璃陶瓷又称微晶玻璃,是将特定组成的基础玻璃在加热过程中通过控制晶化而制成的一类大量含微晶相和玻璃相的多晶固体材料。
二硅酸锂:是金属锂与硅酸根结合形成的化合物。二硅酸锂晶体本身具有高强、高韧性能,使得二硅酸锂微晶玻璃是生物陶瓷中机械性能和生物性能都比较突出的一类陶瓷材料。
背景:通过调整基础玻璃的成分和工艺制度可以得到各种符合预定性能的微晶玻璃。
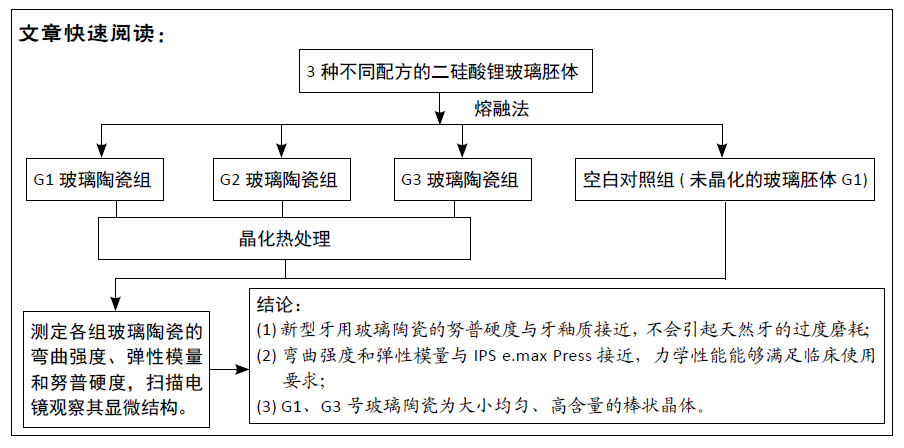
目的:通过不同配方制取以二硅酸锂为主晶相的玻璃陶瓷,晶化后对其力学性能和显微结构进行测定。
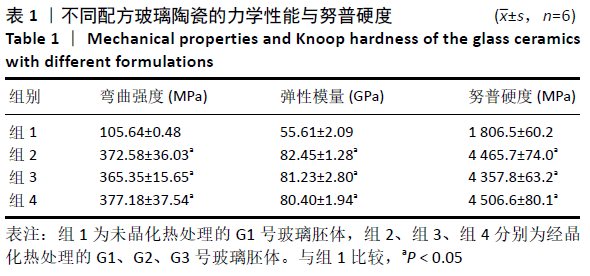
方法:以二硅酸锂为主晶相,通过熔融法制备不同配方的G1、G2、G3号玻璃胚体,打磨、抛光,相对面互相平行。将G1、G2、G3号玻璃胚体进行晶化热处理(以10 ℃/min升温至606 ℃保温30 min,继续升温至880 ℃保温30 min),打磨、抛光、干燥,以未晶化热处理的G1号玻璃胚体为空白对照。测定各组玻璃陶瓷的弯曲强度、弹性模量、努普硬度及显微结构。
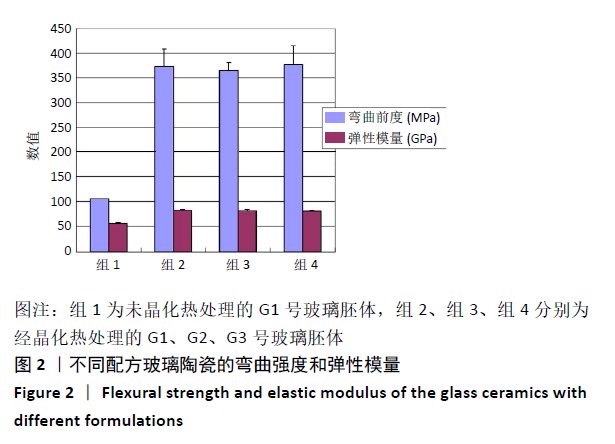
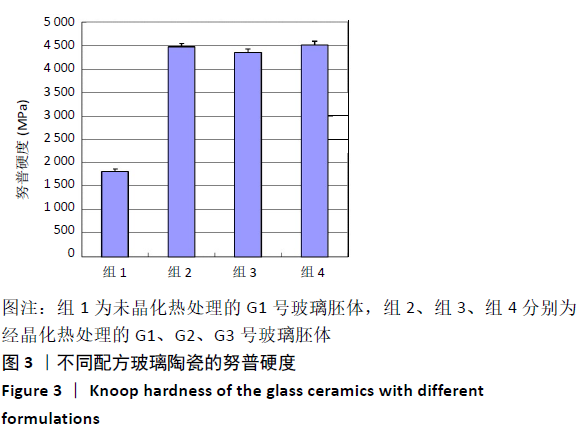
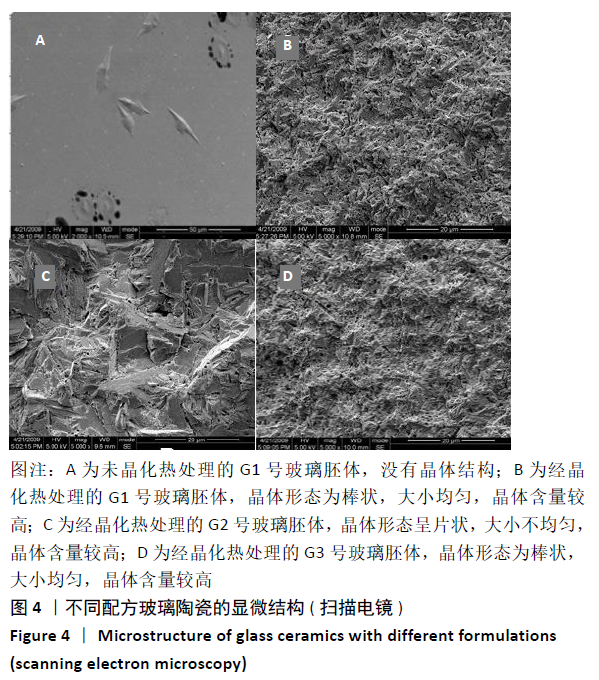
结果与结论:①G1、G2、G3号玻璃陶瓷的弯曲强度和弹性模量均高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),G1、G2、G3号玻璃陶瓷的弯曲强度和弹性模量比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②G1、G2、G3号玻璃陶瓷的努普硬度均高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),G1、G2、G3号玻璃陶瓷的努普硬度比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③扫描电镜显示,G1、G2、G3号玻璃陶瓷的主晶相均为二硅酸锂,但配方的改变导致其微观结构出现差异,G1、G3号玻璃陶瓷的显微结构相似,晶体形态为棒状,大小均匀,晶体含量较高;G2号玻璃陶瓷晶体形态呈片状,大小不均匀,晶体含量较高;④结果表明,该新型玻璃陶瓷的力学性能与IPS e.max Press接近,是一种有开发前景的修复材料。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4053-4299 (任世鹏)
中图分类号: