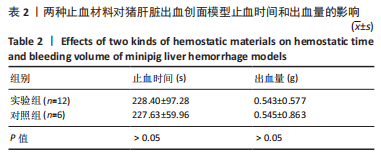
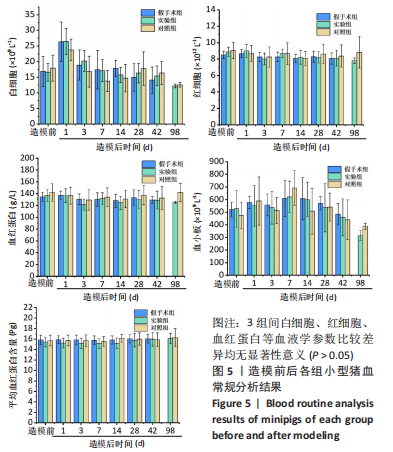
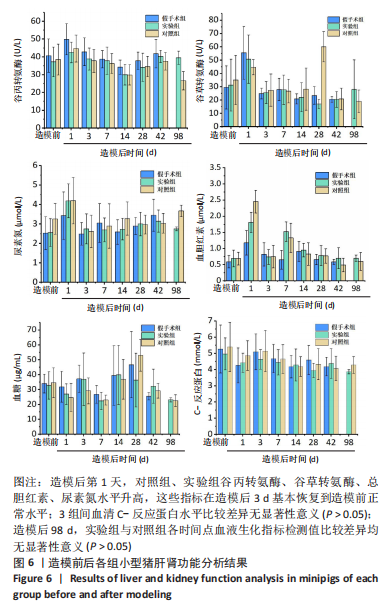
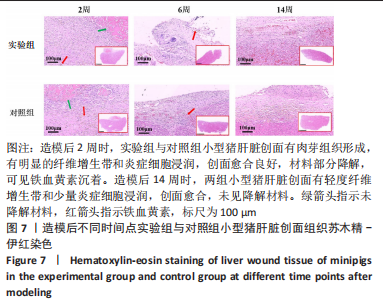
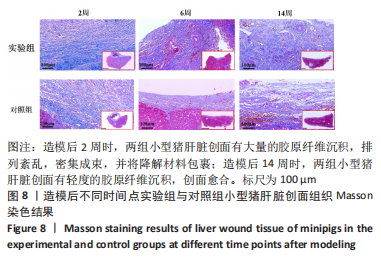
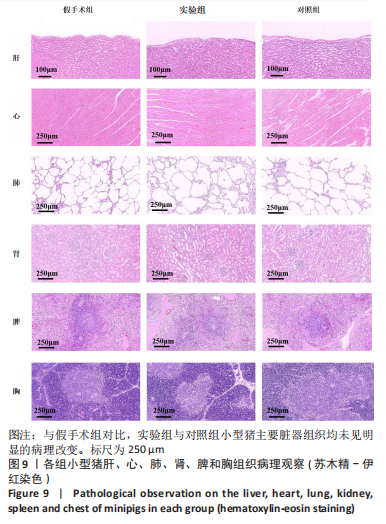
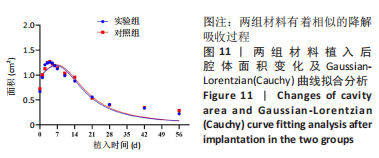
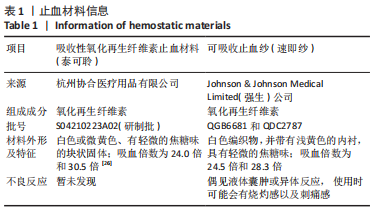
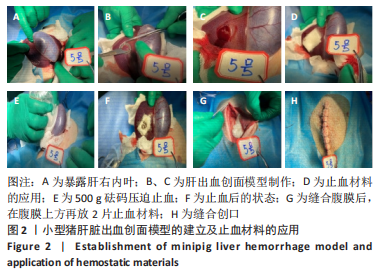
[1] BEHRENS AM, SIKORSKI MJ, KOFINAS P. Hemostatic strategies for traumatic and surgical bleeding. Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2014; 102(11):4182-4194.
[2] WANG J, ZHANG HL, WANG JK, et al. Efficacy of New Zeolite-based Hemostatic Gauze in a Gunshot Model of Junctional Femoral Artery Hemorrhage in Swine. J Surg Res. 2021;(263):176-185.
[3] CHEN H, SHANG XQ, YU LS, et al. Safety evaluation of a low-heat producing zeolite granular hemostatic dressing in a rabbit femoral artery hemorrhage model. J Biomater Appl. 2020;34(7):988-997.
[4] CHENG Y, HU Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Sponges of carboxymethyl chitosan grafted with collagen peptides for wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(16):3890.
[5] MAEVSKAIA EN, DRESVYANINA EN, SHABUNIN AS, et al. Preparation and Study of Hemostatic Materials Based on Chitosan and Chitin Nanofibrils. Nanotechnol Russ. 2020;15(7-8):466-475.
[6] JALAL R, MOJTABA K, HONG C, et al. Novel chitosan/gelatin/oxidized cellulose sponges as absorbable hemostatic agents. Cellulose. 2021; 28:3663-3675.
[7] AHMAD M, JAFARSADEGH M, SEYEDHOSEIN J, et al. Biodegradable cellulose-based superabsorbent as potent hemostatic agent. Chem Eng J. 2021;418(1):129252.
[8] 胡鸣,毕大鹏,汪颖峰,等. 医用可吸收止血材料的临床应用与研究进展[J]. 踝外科电子杂志,2020,7(3):58-62.
[9] 王璐璐.局部可吸收止血材料的应用现状及其研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2018,31(1):109-112.
[10] LIU L, HU WL, YU K, et al. Recent advances in materials for hemostatic management. Biomater Sci-Uk. 2021;9(22):7343-7378.
[11] 冯靖祎,黄进,吴航.医疗机构止血材料管理专家共识[J].中国医院建筑与装备,2021,22(7):19-28.
[12] 张爽,叶红,朱玉,等.纤维素类可吸收止血材料体外效果评价方法[J].中国医药生物技术,2022,17(2):176-182.
[13] 喻炎,马凤森,陆佳骏,等.纤维素类可吸收止血材料的体外细胞毒性评价[J]. 材料导报,2018,32(3):874-880.
[14] 李伟,王玲爽,孙伟庆.纤维素类止血材料的临床应用及作用机理的研究[J].当代医药论丛,2019,17(22):13-15.
[15] 张爽,徐庆华,童琳,等.可吸收止血材料的研究现状与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1628-1634.
[16] GABRIELA J, NADA P, VLADIMIR S, et al. Microdispersed Oxidized Cellulose as a novel potential substancewith hypolipidemic properties. Nutrition. 2008;24(11-12):1174-1181.
[17] MOMIN M, MISHRA V, GHARAT S, et al. Recent advancements in cellulose-based biomaterials for management of infected wounds. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021;18(11):1741-1760.
[18] 俞文峰,徐金明,盛宏旭,等.可吸收再生氧化纤维素在肺癌手术中的临床效果评价[J].中国肺癌杂志,2020,23(6):492-495.
[19] PATERNÒ VA, BISIN A, ADDIS A. Comparison of the efficacy of five standard topical hemostats: a study in porcine liver and spleen models of surgical bleeding. BMC Surg. 2020;20(1):215.
[20] 崔国栋,陶宇,顾强,等.液态可吸收生物止血材料的安全性及有效性研究[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2020,25(11):512-516.
[21] CHENG WL, HE JM, WU YD, et al. Preparation and characterization of oxidized regenerated cellulose film for hemostasis and the effect of blood on its surface. Cellulose. 2013;20(5):2547-2558.
[22] 唐新雯,简祖琴.氧化再生纤维素纱布的止血作用[J].母婴世界, 2015(10):417-418.
[23] 仲光勇,郭佩利,宋延平,等.吸收性氧化纤维素止血胶囊的止血作用研究[J].西北药学杂志,2016,31(3):274-276.
[24] PALM MD, ALTMAN JS. Topical hemostatic agents: a review. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34(4):431-445.
[25] ASHTON WH. Oxidized cellulose product and method for preparing the same. US Paten. 3364200,1968.
[26] 王玲爽,童健星,赵哲哲,等.一种可吸收止血纤丝的有效性和安全性评价[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2021,50(5):633-641.
[27] GALGUT PN. Oxide cellulose mesh.I.Biodegradable membrane in periodontal surgery. Biomaterials. 1990;11(8):561-564.
[28] 郭鑫.不同材质及形态的纤维素类可吸收止血材料的止血性能评价[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2021.
[29] 崔智慧,张雅菲,田田,等.国产氧化纤维素可吸收止血纱布对大鼠皮肤伤口愈合影响的机制研究[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2019, 40(10):1193-1196.
[30] KRÍZOVÁ P, MÁSOVÁ L, SUTTNAR J, et al. The influence of intrinsic coagulation pathway on blood platelets activation by oxidized cellulose. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;82(2):274-280.
[31] 喻炎.氧化再生纤维素可降解材料及其降解产物的生物学评价[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2017.
[32] 林媛媛.氧化再生纤维素钠盐可吸收止血纱的降解机制研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2013.
|