[1] CRABTREE JH, CHOW KM. Peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion. Semin nephrol. 2017;37(1):17-29.
[2] PYART R, DONOVAN K, CARRINGTON C, et al. Peritoneal dialysis: turning choice into reality. Perit Dial int. 2018;38(5):328-333.
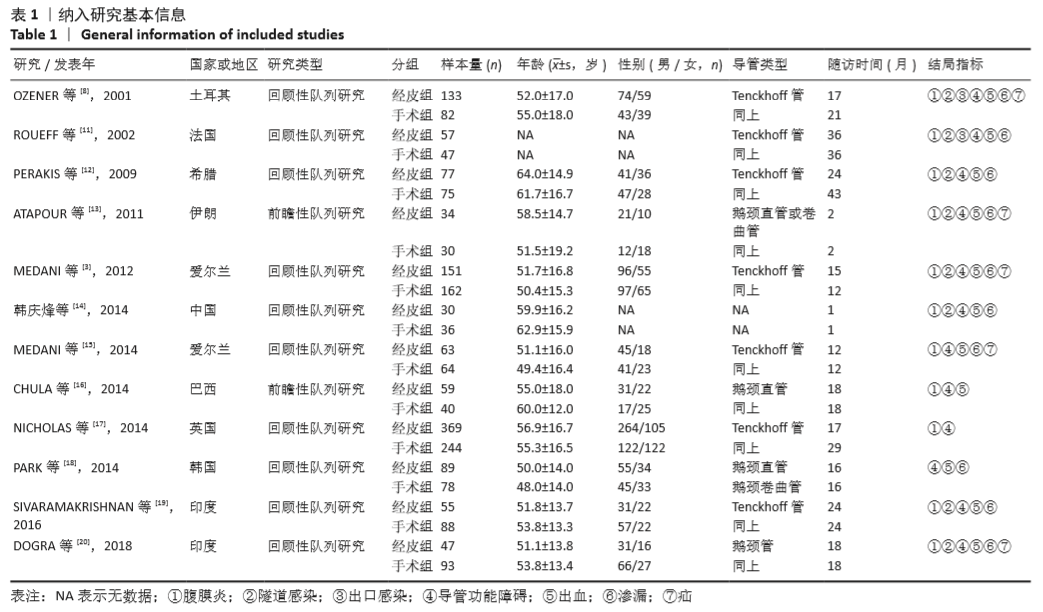
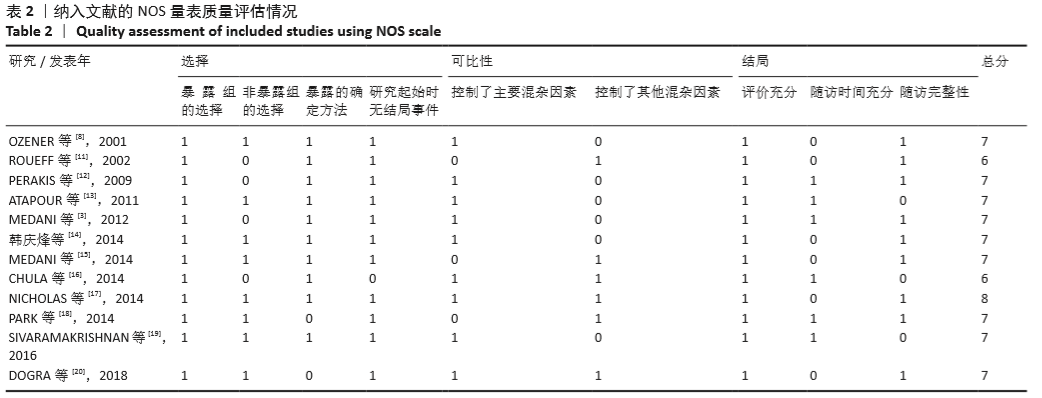
[3] MEDANI S, SHANTIER M, HUSSEIN W, et al. A comparative analysis of percutaneous and open surgical techniques for peritoneal catheter placement. Perit Dial Int. 2012;32(6):628-635.
[4] OUYANG CJ, HUANG FX, YANG QQ, et al. Comparing the incidence of catheter-related complications with straight and coiled tenckhoff catheters in peritoneal dialysis patients-a single-center prospective randomized trial. Perit Dial Int. 2015;35(4):443-449.
[5] SHANMUGALINGAM R, MAKRIS A, HASSAN HC, et al. The utility of sonographic assessment in selecting patients for percutaneous insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter. Perit Dial Int. 2017;37(4):434-442.
[6] SALGAONKAR HP, BEHERA R R, SHARMA PC, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for salvage of malfunctioning peritoneal dialysis catheters. J Minim Access Surg. 2019;15(1):19-24.
[7] PERL J, PIERRATOS A, KANDASAMY G, et al. Peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation by nephrologists is associated with higher rates of peritoneal dialysis utilization: a population-based study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(2):301-309.
[8] OZENER C, BIHORAC A, AKOGLU E. Technical survival of CAPD catheters: comparison between percutaneous and conventional surgical placement techniques. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(9):1893-1899.
[9] 中国超重/肥胖医学营养治疗专家共识编写委员会.中国超重/肥胖医学营养治疗专家共识(2016年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2016,8(9): 525-540.
[10] COOK DA, REED DA. Appraising the quality of medical education research methods: the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale-Education. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1067-1076.
[11] ROUEFF S, PAGNIEZ D, MORANNE O, et al. Simplified percutaneous placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters: comparison with surgical placement. Perit Dial Int. 2002;22(2):267-269.
[12] PERAKIS KE, STYLIANOU KG, KYRIAZIS JP, et al. Long-term complication rates and survival of peritoneal dialysis catheters: the role of percutaneous versus surgical placement. Seminars in Dialysis. 2009;22(5): 569-575.
[13] ATAPOUR A, ASADABADI H R, KARIMI S, et al. Comparing the outcomes of open surgical procedure and percutaneously peritoneal dialysis catheter (PDC) insertion using laparoscopic needle: a two month follow-up study. J Res Med Sci. 2011;16(4):463-468.
[14] 韩庆烽,孙玲华,聂建东,等.经皮穿刺腹膜透析置管术的临床应用[J].中国血液净化,2014, 13(10):686-688.
[15] MEDANI S, HUSSEIN W, SHANTIER M, et al. Comparison of percutaneous and open surgical techniques for first-time peritoneal dialysis catheter placement in the unbreached peritoneum. Perit Dial Int. 2015;35(5):576-585.
[16] CHULA DC, CAMPOS RP, DE ALCANTARA MT, et al. Percutaneous and surgical insertion of peritoneal catheter in patients starting in chronic dialysis therapy: a comparative study. Semin Dial. 2014; 27(3):E32-E37.
[17] NICHOLAS J, THOMAS M, ADKINS R, et al. Percutaneous and surgical peritoneal dialysis catheter placements have comparable outcomes in the modern era. Perit Dial Int. 2014;34(5):552-556.
[18] PARK YS, MIN SI, KIM DK, et al. The outcomes of percutaneous versus open placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters. World J Surg. 2014; 38(5):1058-1064.
[19] SIVARAMAKRISHNAN R, GUPTA S, AGARWAL SK, et al. Comparison of outcomes between surgically placed and percutaneously placed peritoneal dialysis catheters: a retrospective study. Indian J Nephrol. 2016;26(4):268-274.
[20] DOGRA PM, HOODA AK, SHANMUGRAJ G, et al. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion technique: a comparative study of percutaneous versus surgical insertion. Indian J Nephrol. 2018;28(4):291-297.
[21] KIM YS, KIM Y, SHIN SJ, et al. Current state of dialysis access management in Korea. J Vasc Access. 2019; 20(1-suppl):15-19.
[22] LEE YK, YANG PS, PARK KS, et al. Modified peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion: comparison with a conventional method. Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56(4):981-986.
[23] BRIGGS V, PITCHER D, BRADDON F, et al. UK Renal Registry 15th annual report: Chapter 8 UK multisite peritoneal dialysis access catheter audit for first PD catheters 2011. Nephron Clin Pract. 2013;123(Suppl 1):165-181.
[24] GEORGE N, ALEXANDER S, DAVID VG, et al. Comparison of early mechanical and infective complications in first time blind, bedside, midline percutaneous tenckhoff catheter insertion with ultra-short break-in period in diabetics and non-diabetics: setting new standards. Perit Dial Int. 2016;36(6):655-661.
[25] TOKGOZ B. Clinical advantages of peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2009;29 Suppl 2:S59-61.
[26] CRABTREE J, PENNER T, ARMSTRONG S, et al. Peritoneal dialysis university for surgeons: a peritoneal access training program. Peri Dial Int. 2016;36(2):177-181.
[27] ABDEL-AAL AK, GADDIKERI S, SADDEKNI S. Technique of peritoneal catheter placement under fluroscopic guidance. Radiol Res Pract. 2011;2011:141707.
[28] VOSS D, HAWKINS S, POOLE G, et al. Radiological versus surgical implantation of first catheter for peritoneal dialysis: a randomized non-inferiority trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(11):4196-4204.
[29] TULLAVARDHANA T, AKRANURAKKUL P, UNGKITPHAIBOON W, et al. Surgical versus percutaneous techniques for peritoneal dialysis catheter placement: a meta-analysis of the outcomes. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2016;10:11-18.
[30] DE MORAES TP, CAMPOS RP, DE ALCANTARA MT, et al. Similar outcomes of catheters implanted by nephrologists and surgeons: analysis of the Brazilian peritoneal dialysis multicentric study. Semin Dialy. 2012;25(5):565-568.
|