| [1] 严嘉枫,纪文宙,周正修.肌少症之流行病学及健康促进介入之探讨[J].身心障碍研究,2015,13(1):9-25.[2] 张淑芳.老年肌少症之诊断与治疗[J].护理杂志, 2014,61(2):101-105.[3] 陈思远,张钦凯.身体活动与肌少症[J].台湾医学, 2014,18(3): 310-316.[4] Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM,et al.Sarcopenia: Euro-pean consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing.2010; 39( 4):412-423. [5] Fielding RA,Vellas B,Evans WJ,et al.Sarcopenia: an undiag-nosed condition in older adults.Current consensus definition: prev-alence,etiology,and consequences. International working group on sarcopeniaJ Am Med Dir Assoc.2011;12( 4): 249-256. [6] 吴雅汝,詹鼎正.探讨肌少症和骨质疏松症的关系[J].台北市医师公会会刊,2013,57(4):18-21.[7] 杜诗淳,蔡坤维,陈妙文,等.老年人肌少症之预防与照护[J].志为护理, 2015,14(2):62-68.[8] 张珮慈,傅麗蘭.亚洲肌少症之评估指标比较与盛行率介绍[J].台湾体育学术研究,2016.6,(60):145-160.[9] Hida T, Ishiguro N, Shimokata H, et al. High prevalence of sarcopenia and reduced leg muscle mass in Japanese patients immediately after a hip fracture. Gerontol Int.2012;13(2):413-420. [10] Kim SH, Kim TH, Hwang HJ. The relationship of physical activity(PA) and walking with sarcopenia in Korean males aged 60 years and older using the Fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(KNHANES IV-2, 3) 2008-2009. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.2013;56(3); 472-477. [11] Pongchaiyakul C, Limpawattana P, Kotruchin P, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia and associated factors among Thai population. J Bone Miner Metab.2013; 31(3):346-350. [12] Cheng Q, Zhu X, Zhang X, et al. A cross-sectional study of loss of muscle mass corresponding to sarcopenia in healthy Chinese men and women: reference values, prevalence, and association with bone mass. J Bone Miner Metab.2014;32(1):78-88. [13] 胡世莲.老年肌少症的评估及干预[J].中国临床保健杂志,2017,20(2): 113-116.[14] 周怡君,张皓翔,詹鼎正.肌少症的评估与预防[J].台湾医学.2014, 18(3):303-309.[15] 吴雅汝,周怡君,詹鼎正.肌少症与衰弱症[J].内科学志,2014,25:131-136.[16] Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, et al: Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian working group for sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc.2014;15:95-101. [17] 付素华.老年肌少症患者护理干预策略[J].当代护士,2018.4,25(10): 9-12.[18] 吴佳佳,邢学农.肌少症研究进展[J].医学综述,2016.02,22(4): 753-756.[19] 余卫,程晓光,袁凌青.肌少症的评估方法[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016.9,9(3):240-246.[20] Abellan van Kan G, Rolland Y, Andrieu S, et al: Gait speed at usual pace as a predictor of adverse outcomes in community- dwelling older people an Internationgal Academy on Nutrition and Aging (IANA) Task Force. J Nutr Health Aging.2009; 13:881-889. [21] Cederholm TE, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Schneider SM, et al. Toward a definition of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med.2011;27:341-53. [22] 张冰,李维辛.老年人糖尿病相关性肌少症的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(11):1294-1297.[23] 林泰祐,林麓娟.阻力训练对减缓老年人骨骼肌减少症的效益[J].中华体育季刊,2011,25(1):10-21.[24] Drummond MJ, Miyazaki M, Dreyer HC, et al. Expression of growth-related genes in young and older human skeletal muscle following an acute stimulation of protein synthesis. J Appl Physiol (1985).2009, 106(4):1403-1411. [25] Frontera WR,Hughes VA,FieldingRA,et al.Aging of skeletal muscle: a 12-yr longitudinal study.J Appl Physiol (1985).2000; 88(4):1321-1326. [26] 林雨薇,钱桂玉,许美智.老年人肌肉减少症的成因与影响[J].大专体育,2010.10,(110):85-91.[27] 虚佳文,陈怡茹,黄国晋.老人肌少症肥胖症[J].台湾医学,2014,18(3): 317-324.[28] Layman DK. Dietary Guidelines should reflect new under-standings about adult protein needs. Nutr Metabo.2009;6:12. [29] Buitrago CG,Arango NS,BolandRL.25(OH) 2D3-dependentmodulation of Akt in proliferating and differentiating C2C12 skele-tal muscle cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113( 4):1170-1181. [30] Schiafflno S, Dyar KA, Ciciliot S, et al. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J.2013;280(170): 4294-4314. [31] Morley JE, Malmstrom TK. Frailty, sarcopenia, and hormones. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.2013; 42:391-405. [32] Sipilä S, Narici M, Kjaer M,et al. Sex hormones and skeletal musdomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2010;95(2):639-650. [33] Cesari M, Kritchevsky SB, Baumgartner RN, et al: Sarcopenia, obesity, and inflammation- results from the Trial of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factors study. Am J Clin Nutr, 2005;82:428-34. [34] Jo E, Lee SR, Park BS, Kim JS: Potential mechanisms underlying the role of chronic in?mmation in age-related muscle wasting. Aging Clin Exp Res.2012;24:412-422. [35] Collins-Hooper H, Woolley TE, Dyson L, et al: Age-related changes in speed and mechanism of adult skeletal muscle stem cell migration. Stem Cells.2012; 30:1182-1195. [36] Wagatsuma A, Sakuma K. Vitamin D signaling in myogenesis: potential for treatment of sarcopenia.BiomedRes Int.2014;2014: 121254. [37] Dyck DJ, Heigenhauser GJ, Bruce CR: The role of adipokines as regulators of skeletal muscle fatty acid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2006;186:5-16. [38] Kim KS, Park KS, Kim MJ, et al. Type 2 diabetes is associated with low muscle mass in older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int.2014; 14(Suppl 1):115-121. [39] Akpinar TS, Tayfur M, Tufan F, et al. Uncomplicated diabetes does not accelerate age-related sarcopenia. Aging Male.2014;17(4): 205-210. [40] 江柏欣,陈昱宏.肌少症的诊断、成因与临床重要性之探讨[J].台湾家医志,2014,24:1-8.[41] Argilés JM, Busquets S, Felipe A,et al. Muscle wasting in cancer and ageing: cachexia versus sarcopenia. Adv Gerontol. 2006;18: 39-54. Review. [42] Chin SO, Rhee SY, Chon S,et al. Sarcopenia is independengtly associated with cardiovascular disease inolder Korean adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination on Survey (KNHANES) from, PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60119. [43] Yu R, Leung J, Woo J: Incremental predictive value of sarcopenia for incident fracture in an elderly Chinese cohort: results from the osteoporotic fractures in men (MrOs) study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15:551-558. [44] Fried LP, Walston JD, Ferruci L. Frailty. In: Halter JB, Ouslander JG, Tinetti ME, el al.Hazzard's Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 6th ed. New York: McGrall-Hill.2009:631-645. [45] Evans WJ, Campbell WW. Sarcopenia and age-related changes in body composition and functional capacity. J Nutr.1993;123 (2 Suppl):465-468. [46] Peterson MD, Rhea MR, Sen A, et al: Resistance exercise for muscular strength in order adults: a meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev.2010;9:226-237. [47] Peterson MD, Sen A, Gordon PM.Influence of resistance exercise on lean body mass in aging adults: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2011; 43:249-258. [48] Crocker T, Forster A, Young J, et al: Physical rehabilitation for older people in long-term care. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2:CDOO4294. [49] Abdulla H, Phillips B, Smith K, et al. Physiological mechanisms of action of incretin and insulin in regulating skeletal muscle metabolism. Curr Diabetes Rev.2014;10(5):327-335. [50] Ramel A, Arnarson A, Geirsdottir OG, et al. Glomerular filtration rate after a 12-wk resistance exercise program with post-exercise protein ingestion in community dwelling elderly. Nutrition.2013; 29:719-23. [51] Polly P,Tan TC.The role of vitamin D in skeletal and cardiac muscle fun. Front Physiol.2014;5:145. [52] Basaria S, Coviello AD, Travison TG, et al: Adverse events associated with testosterone administration. N Engl J Med.2010; 363:109-22. |
.jpg)
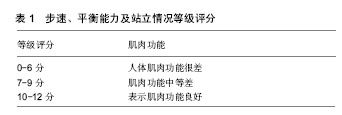
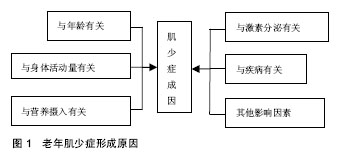
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
肌肉减少症:肌肉减少症的定义最早是由Baumgarner等提出的,是以骨骼肌肉质量指数(skeletal muscle index,SMI)作为判别标准,若SMI比年轻族群低于2个标准差,即为肌少症,即伴随骨骼肌质量的流失、及肌力或耐力的下降,以至于产生一些不良的影响,如生活功能下降、生活品质不良,甚至死亡等现象。#br#
肌少症评估方法:欧盟肌少症工作小组(EWGSOP)在2010年建立肌少症评估指标,分别为肌肉量(muscle mass)、肌力(muscle strength)、身体表现(physical performance)3项。国际上关于肌少症的评估与测量方法均在此基础上并根据切点、人种、地区等的不同,进行深化展开。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
肌肉减少症:肌肉减少症的定义最早是由Baumgarner等提出的,是以骨骼肌肉质量指数(skeletal muscle index,SMI)作为判别标准,若SMI比年轻族群低于2个标准差,即为肌少症,即伴随骨骼肌质量的流失、及肌力或耐力的下降,以至于产生一些不良的影响,如生活功能下降、生活品质不良,甚至死亡等现象。#br#
肌少症评估方法:欧盟肌少症工作小组(EWGSOP)在2010年建立肌少症评估指标,分别为肌肉量(muscle mass)、肌力(muscle strength)、身体表现(physical performance)3项。国际上关于肌少症的评估与测量方法均在此基础上并根据切点、人种、地区等的不同,进行深化展开。