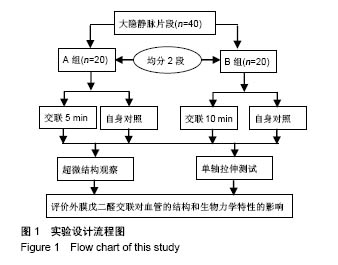
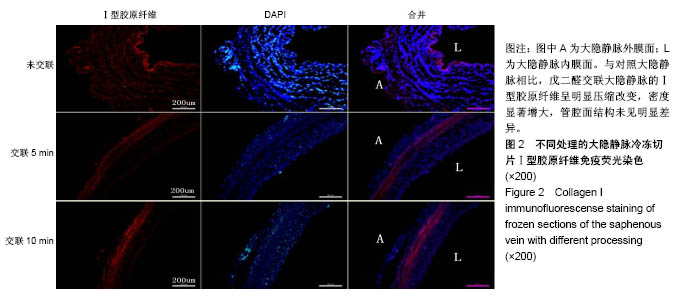
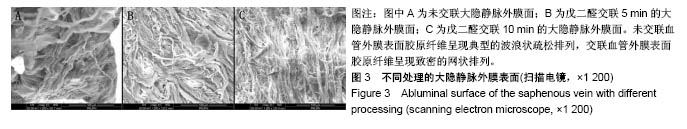
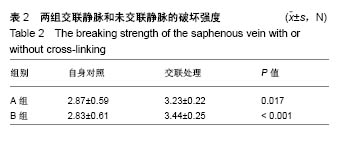
| [1] Goldman S,Zadina K,Moritz T,et al.Long-term patency of saphenous vein and left internal mammary artery grafts after coronary artery bypass surgery: results from a Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44(11):2149-2156.[2] Harskamp RE,Lopes RD,Baisden CE,et al.Saphenous vein graft failure after coronary artery bypass surgery: pathophysiology, management, and future directions.Ann Surg. 2013;257(5):824-833.[3] Gooch KJ,Firstenberg MS,Shrefler BS,et al.Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Saphenous Vein Grafts. J Biomech Eng. 2018;140(2).doi:10.1115/1.34038705.[4] Parsonnet V,Lari AA,Shah IH.New Stent for Support of Veins in Arterial Grafts.Arch Surg. 1963;87:696-702.[5] Taggart DP,Ben Gal Y,Lees B,et al.A Randomized Trial of External Stenting for Saphenous Vein Grafts in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(6): 2039-2045.[6] Angelini GD,Lloyd C,Bush R,et al.An external, oversized, porous polyester stent reduces vein graft neointima formation, cholesterol concentration, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 expression in cholesterol-fed pigs.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;124(5):950-956.[7] Goldstone RN,McCormack MC,Khan SI,et al.Photochemical Tissue Passivation Reduces Vein Graft Intimal Hyperplasia in a Swine Model of Arteriovenous Bypass Grafting.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5(8). pii: e003856. doi:10.1161/JAHA.116.003856.[8] Chandran PL,Paik DC,Holmes JW.Structural mechanism for alteration of collagen gel mechanics by glutaraldehyde crosslinking.Connect Tissue Res.2012;53(4):285-297.[9] Van de Walle AB,Uzarski JS, McFetridge PS.The consequence of biologic graft processing on blood interface biocompatibility and mechanics.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2015;6(3):303-313.[10] Authors/Task Force members,Windecker S,Kolh P,et al.2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI).Eur Heart J. 2014;35(37):2541-2619.[11] Hamedani BA,Navidbakhsh M,Tafti HA.Comparison between mechanical properties of human saphenous vein and umbilical vein.Biomed Eng Online.2012;11:59.[12] Leask RL,Butany J,Johnston KW,et al.Human saphenous vein coronary artery bypass graft morphology, geometry and hemodynamics.Ann Biomed Eng.2005;33(3):301-309.[13] Teng ZZ,Ji GY,Chu HJ,et al.Does PGA external stenting reduce compliance mismatch in venous grafts? Biomed Eng Online. 2007;6:12.[14] Ishiwata S,Tukada T,Nakanishi S,et al.Postangioplasty restenosis: platelet activation and the coagulation-fibrinolysis system as possible factors in the pathogenesis of restenosis. Am Heart J. 1997;133(4):387-392.[15] Nguyen HC,Grossi EA,LeBoutillier M,3rd,et al.Mammary artery versus saphenous vein grafts: assessment of basic fibroblast growth factor receptors.Ann Thorac Surg.1994; 58(2):308-310.[16] Turner NA,Hall KT,Ball SG,et al.Selective gene silencing of either MMP-2 or MMP-9 inhibits invasion of human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 2007; 193(1):36-43.[17] Kim FY,Marhefka G,Ruggiero NJ,et al.Saphenous vein graft disease: review of pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment. Cardiol Rev.2013;21(2):101-109.[18] Goissis G,Yoshioka SA,Braile DM,et al.The chemical protecting group concept applied in crosslinking of natural tissues with glutaraldehyde acetals.Artif Organs. 1998;22(3): 210-214.[19] Zilla P,Bezuidenhout D,Weissenstein C,et al.Diamine extension of glutaraldehyde crosslinks mitigates bioprosthetic aortic wall calcification in the sheep model.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;56(1):56-64.[20] Kim KM,Herrera GA,Battarbee HD.Role of glutaraldehyde in calcification of porcine aortic valve fibroblasts.Am J Pathol. 1999;154(3):843-852.[21] Wine Y,Cohen-Hadar N,Freeman A,et al.Elucidation of the mechanism and end products of glutaraldehyde crosslinking reaction by X-ray structure analysis.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007; 98(3):711-718.[22] Cheung DT,Perelman N,Ko EC,et al.Mechanism of crosslinking of proteins by glutaraldehyde III. Reaction with collagen in tissues. Connect Tissue Res.1985;13(2):109-115.[23] Angelini GD,Breckenridge IM,Butchart EG,et al.Metabolic damage to human saphenous vein during preparation for coronary artery bypass grafting.Cardiovasc Res. 1985;19(6): 326-334.[24] Angelini GD,Soyombo AA,Newby AC.Winner of the ESVS prize 1990.Smooth muscle cell proliferation in response to injury in an organ culture of human saphenous vein.Eur J Vasc Surg. 1991;5(1):5-12. |