中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (45): 7312-7319.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.45.018
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
促红细胞生成素促进内皮祖细胞增殖依赖于PI3K/Akt信号通路
吴海卫1,张 雷1,胡若愚2,李 好3,景 华1,董国华1,许 飚1,李德闽1
- 1南京大学临床学院解放军南京军区南京总医院心胸外科,江苏省南京市 210002;2东南大学附属中大医院心胸外科,江苏省南京市 210009;3上海市肺科医院胸外科,上海市 200433
Erythropoietin promotes endothelial progenitor cells proliferation depending on PI3k/Akt pathway
Wu Hai-wei1, Zhang Lei1, Hu Ruo-yu2, Li Hao3, Jing Hua1, Dong Guo-hua1, Xu Biao1, Li De-min1
- 1Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Command, Clinical Medicine School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China
摘要:
背景:促红细胞生成素能促进组织损伤部位血管生成,与其促进内皮祖细胞增殖、分化密切相关,但促红细胞生成素促进内皮祖细胞增殖、分化的机制尚不清楚。
目的:观察促红细胞生成素对小鼠骨髓来源内皮祖细胞功能活性的影响,并初步阐明其信号机制。
方法:密度梯度离心法分离获取小鼠骨髓内皮祖细胞,鉴定后传代培养,以PI3K特异性抑制剂LY294002作干预处理,实验细胞分为EGM-2组、促红细胞生成素处理组(培养液中促红细胞生成素浓度分别为1,5,10 U/mL)、促红细胞生成素+LY组(培养液中分别含有10 U/mL促红细胞生成素及10 mmol/L LY294002)、LY组(培养液中含10 mmol/L LY294002)、二甲基亚砜组(培养液中含1 mL/L二甲基亚砜),分别采用CCK8试剂盒、流式细胞法检测细胞增殖和凋亡,采用ELISA法检测细胞裂解液内皮型一氧化氮合酶、血管内皮生长因子含量,Western blot法测定细胞裂解液中Akt及p-Akt表达。
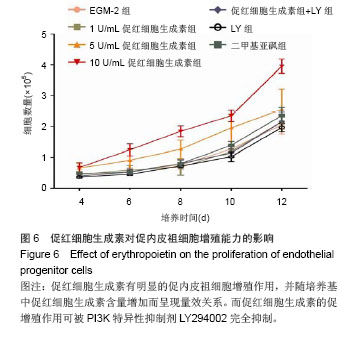
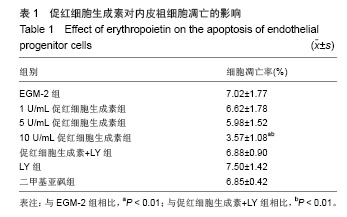
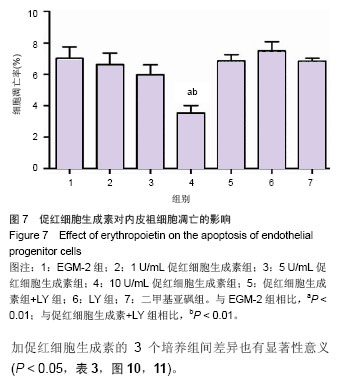
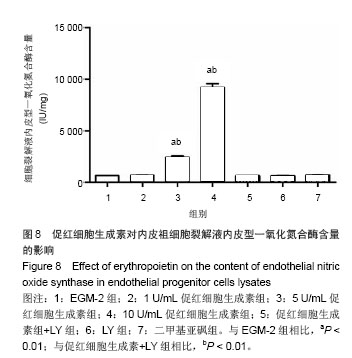
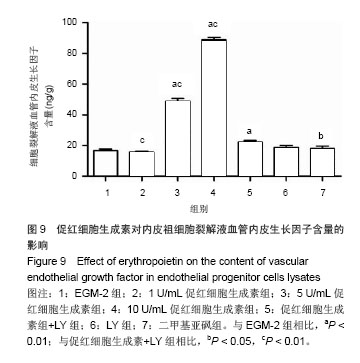
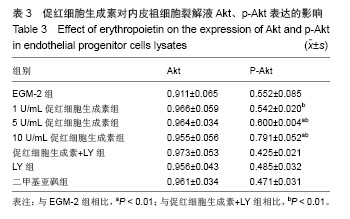
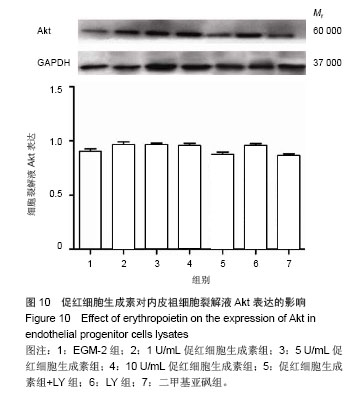
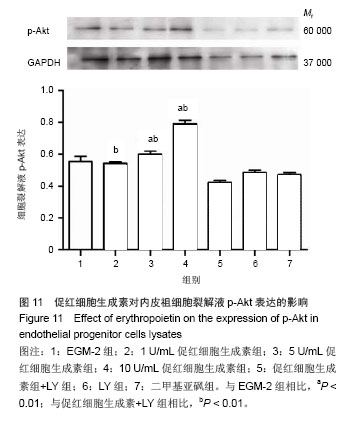
结果与结论:促红细胞生成素能显著促进内皮祖细胞增殖,并随培养基中促红细胞生成素含量增加而呈现量效关系,而促红细胞生成素的促增殖作用可被LY294002完全抑制。促红细胞生成素处理组细胞凋亡率明显低于促红细胞生成素+LY组。LY组、促红细胞生成素+LY组细胞裂解液中内皮型一氧化氮合酶、血管内皮生长因子含量显著低于促红细胞生成素处理各组。各组Akt表达无明显差异,而促红细胞生成素+LY组p-Akt表达显著低于促红细胞生成素各组。上述结果提示,促红细胞生成素能显著促进体外培养的内皮祖细胞的增殖、降低内皮祖细胞的凋亡率,其作用依赖于PI3K/Akt信号通路。
中图分类号:
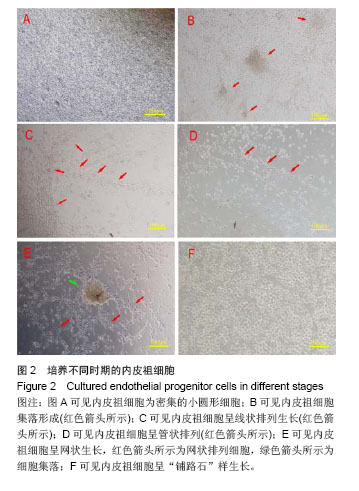
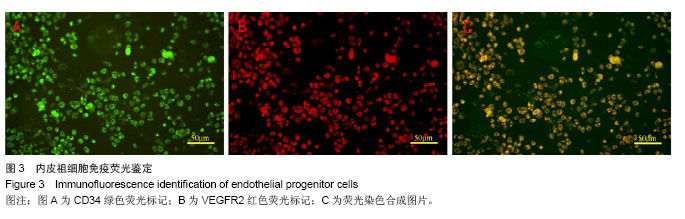
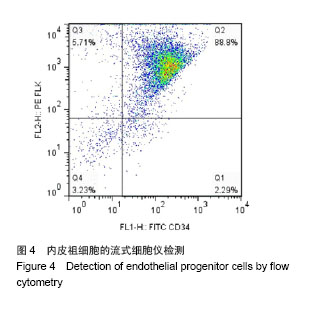
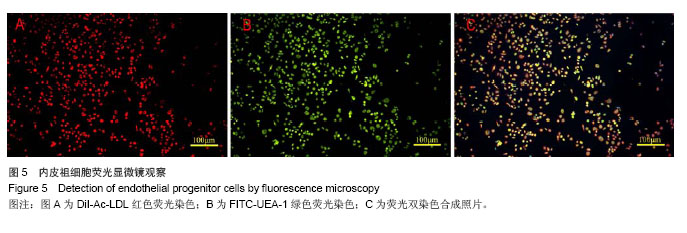

.jpg)
.jpg)