| [1]Patterson JL, Stull-Lane A, Girerd PH, et al. Analysis of adherence, biofilm formation and cytotoxicity suggests a greater virulence potential of Gardnerella vaginalis relative to other bacterialvaginosis-associated anaerobes. Microbiology. 2010;156(2):392-399.
[2]Kjelleberg S, Molin S. Is there a role for quorom sensing signals in bacterial biofilm? Current Opin Microb 2002;5: 254-258.
[3]Dunne WM. Bacterial adhesion: seen any good biofilms lately? Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15:55-66.
[4]Gov Y, Bitler A, Dell'Acqua G, et al. RNAⅢ inhibiting peptide (RIP), a global inhibitor of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis: strucure and function analysis. Peptides. 2001; 22(10): 1609-1620.
[5]Balaban N, Giacometti A, Cirioni O. Use of the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAⅢ-inhibiting peptide to prevent biofilm formation in vivo by drug-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 2003;187(4):625-630.
[6]邢庆昌,郝立波,王继芳.固相合成法合成葡萄球菌RNAⅢ抑制肽的鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(13): 2419-2422.
[7]Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520-532.
[8]Giacometti A, Cirioni O, Gov Y, et al. RNA Ⅲ inhibiting peptide inhibits in vivo biofilm formation by drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47(6):1979-1983.
[9]Balaban N, Giacometti A, Cirioni O. Use of the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAⅢ-inhibiting peptide to prevent biofilm formation in vivo by drug-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 2003;187(4):625-630.
[10]Vieira-da-Motta O, Ribeiro PD, Dias da Silva W, et al. RNAⅢ inhibiting peptide (RIP) inhibits agr-regulated toxin production. Peptides. 2001;22(10):1621-1627.
[11]邢庆昌,郝立波,王继芳.应用RNAⅢ抑制肽( RIP)抑制葡萄球菌毒素产生的实验研究[J].科学技术与工程,2011,11(2):317- 320.
[12]Yang G, Cheng H, Liu C, et al. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo by RAP-binding peptides. Peptides. 2003;24(11):1823-1828.
[13]Dell'Acqua G, Giacometti A, Cirioni O, et al. Suppression of drug-resistant Staphylococcal Infections by the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAⅢ-inhibiting peptide. J Infect Dis. 2004;190(2):318-320.
[14]Balaban N, Gov Y, Giacometti A, et al. A chimeric peptide composed of a dermaseptin derivative and an RNA Ⅲ-inhibiting peptide prevents graft-associated infections by antibiotic-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48(7):2544-2550.
[15]郝立波,邢庆昌,王继芳,等.RNAⅢ抑制肽抑制葡萄球菌在人工关节材料表面黏附的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(23): 1814-1817.
[16]Balaban N, Singh B, Goldkorn RT, et al. Activation and inhibition of the staphylococcal agr system. Technical comment: Response. Science. 2000;287-391.
[17]Gustafsson E, Nilsson P, Karlsson S, et al. Characterizing the Dynamics of the Quorum-Sensing System in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004; 8(4):232-242.
[18]Park MK, Park JS, Park EM, et al. Halofuginone ameliorates autoimmune arthritis in mice by regulating the balance between Th17 and Treg cells and inhibiting osteoclastogenesis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(5): 1195-207.
[19]Lee J, Park DY, Park do Y, et al. Angiopoietin-1 suppresses choroidal neovascularization and vascular leakage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(4):2191-2199.
[20]Ariyoshi W, Okinaga T, Knudson CB, et al. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid regulates osteoclast formation by inhibiting receptor activator of NF-κB ligand through Rho kinase. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):111-120.
[21]Hamm A, Veschini L, Takeda Y, et al. PHD2 regulates arteriogenic macrophages through TIE2 signalling. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(6):843-857.
[22]Naidu VG, Dinesh Babu KR, et al. RANKL targeted peptides inhibit osteoclastogenesis and attenuate adjuvant induced arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB activation and down regulating inflammatory cytokines. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203(2): 467-479.
[23]Rodrigues WF, Madeira MF, da Silva TA, et al. Low dose of propranolol down-modulates bone resorption by inhibiting inflammation and osteoclast differentiation. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165(7):2140-2151.
[24]Campa C, Harding SP. Anti-VEGF compounds in the treatment of neovascular age related macular degeneration. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12(2):173-181.
[25]Lee YS, Kim YS, Lee SY, et al. AMP kinase acts as a negative regulator of RANKL in the differentiation of osteoclasts. Bone. 2010;47(5):926-937.
[26]Levitin A, Yanofsky C. Positions of Trp codons in the leader peptide-coding region of the at operon influence anti-trap synthesis and trp operon expression in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 2010;192(6):1518-1526.
[27]Bandhakavi S, Kim YM, Ro SH, et al. Quantitative nuclear proteomics identifies mTOR regulation of DNA damage response. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(2):403-414.
[28]Yu M, Moreno JL, Stains JP, et al. Complex regulation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) expression by interleukin 4 (IL-4): IL-4 indirectly suppresses receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-mediated TRAP expression but modestly induces its expression directly. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(47):32968-32979.
[29]Barakat MR, Kaiser PK. VEGF inhibitors for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;18(5):637-646.
[30]Geng W, Hill K, Zerwekh JE, et al. Inhibition of osteoclast formation and function by bicarbonate: role of soluble adenylyl cyclase. J Cell Physiol. 2009;220(2):332-240.
[31]Burton JB, Priceman SJ, Sung JL, et al. Suppression of prostate cancer nodal and systemic metastasis by blockade of the lymphangiogenic axis. Cancer Res. 2008;68(19): 7828-7837.
[32]Ma WW, Jimeno A. Strategies for suppressing angiogenesis in gynecological cancers.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007;43(4): 259-273.
[33]Balaban N, Cirioni O, Giacometti A, et al. Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection by the quorum-sensing inhibitor RIP. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(6):2226-2229.
[34]Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, et al. MafB negatively regulates RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Blood. 2007; 109(8):3253-3259.
[35]Christensen EN, Mendelsohn ME. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha inhibits thrombin receptor-mediated calcium mobilization in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2006;281(13):8409-8416.
[36]Bundschu K, Gattenlöhner S, Knobeloch KP, et al. Tissue-specific Spred-2 promoter activity characterized by a gene trap approach. Gene Expr Patterns. 2006;6(3):247-255.
[37]Murray JL, Mavrakis M, McDonald NJ, et al. Rab9 GTPase is required for replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, filoviruses, and measles virus. J Virol. 2005;79(18): 11742-11751.
[38]Mangashetti LS, Khapli SM, Wani MR. IL-4 inhibits bone-resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts by affecting NF-kappa B and Ca2+ signaling. J Immunol. 2005;175(2): 917-925.
[39]Mei ZZ, Zheng XF, Dong Y, et al. Inhibiting expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase promotes degradation of survivin protein. Ai Zheng. 2005;24(5): 525-530.
[40]Hu ZW, Shen ZY, Huang JH. Experimental study on effect of epimedium flavonoids in protecting telomere length of senescence cells HU. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004;24(12):1094-1097.
[41]Biswas SK, McClure D, Jimenez LA, et al. Curcumin induces glutathione biosynthesis and inhibits NF-kappaB activation and interleukin-8 release in alveolar epithelial cells: mechanism of free radical scavenging activity. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(1-2):32-41.
[42]Yanofsky C. The different roles of tryptophan transfer RNA in regulating trp operon expression in E. coli versus B. subtilis. Trends Genet. 2004;20(8):367-374.
[43]Chen G, Yanofsky C. Features of a leader peptide coding region that regulate translation initiation for the anti-TRAP protein of B. subtilis. Mol Cell. 2004;13(5):703-711.
[44]Oh KO, Kim SW, Kim JY, et al. Effect of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch extracts on bone metabolism. Clin Chim Acta. 2003; 334(1-2):185-195.
[45]Wulff C, Wilson H, Rudge JS, et al. Luteal angiogenesis: prevention and intervention by treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor trap (A40). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(7):3377-3386.
[46]Balaban N, Goldkorn T, Gov Y, et al. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating Protein (TRAP). J Biol Chem. 2001;276(4): 2658-2667.
[47]Laitala-Leinonen T, Löwik C, Papapoulos S, et al. Inhibition of intravacuolar acidification by antisense RNA decreases osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1999;112( Pt 21):3657-3666. |

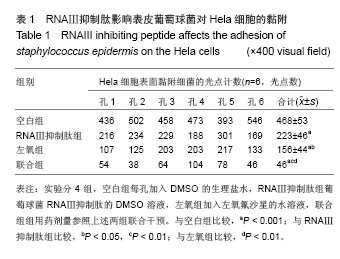
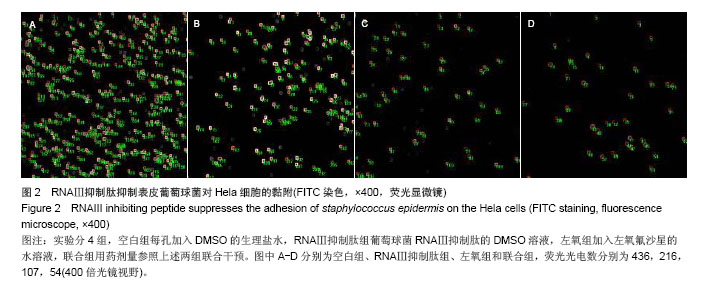
.jpg)