| [1] Peck WA, Birge SJ, Fedak SA. Bone cells: biochemical and biological studies after enzymatic isolation. Science.1964; 146(3650): 1476-1477.
[2] Yin M, Dai H, Yin Y. A new method of isolating and culturing rabbit osteoblasts in vitro. Sheng wu yi xue gong cheng xue za zhi.2013;30(5):1063-1066.
[3] Jonason JH, O’Keefe RJ. Isolation and Culture of Neonatal Mouse Calvarial Osteoblasts. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1130: 295-305.
[4] Gartland A, Rumney RM, Dillon JP, et al. Isolation and culture of human osteoblasts. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;806:337-355.
[5] 芮钢,金旭红,郭元利,等.成骨细胞的体外培养:来自SCI及NIH 基金和德温特专利数据库2008/2010相关文献及数据分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012,16(2):191-200.
[6] Thiele F, Cohrs CM, Przemeck GK, et al.In vitro analysis of bone phenotypes in Col1a1 and Jagged1 mutant mice using a standardized osteoblast cell culture system. J bone and miner metab.2013;31(3): 293-303.
[7] Gallet M,Saïdi S,Haÿ E,et al.Repression of osteoblast maturation by ERRαlpha accounts for bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. PloS one. 2013;8(1): e54837.
[8] Costa R,Ribeiro C,Lopes AC,et al.Osteoblast, fibroblast and in vivo biological response to poly (vinylidene fluoride) based composite materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013;24(2): 395-403.
[9] Rausch-fan X,Qu Z, Wieland M, et al. Differentiation and cytokine synthesis of human alveolar osteoblasts compared to osteoblast-like cells (MG63) in response to titanium surfaces. Dent Mter.2008;24(1):102-110.
[10] 练克俭,陈长青,黄立羡,等.皮质骨和其他不同来源兔成骨细胞的体外培养和生物学特性比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(3):218-220.
[11] 王勇平,廖燚,蒋垚.成骨细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(33):6231-6234.
[12] 李玲慧,丁道芳,杜国庆,等.不同胶原酶消化对原代成骨细胞获得率及活性的比较[J].中国骨伤,2013 (4):328-331.
[13] 程浩,张延芳,许巍.新生大鼠成骨细胞原代培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(41):7199-7204.
[14] 孙玲,侯建明.混合酶消化法大鼠颅盖骨细胞的原代培养和鉴定[J].中国医学创新,2011,8(19):17-19.
[15] Masquelier D,Herbert B,Hauser N,et al.Morphologic characterization of osteoblast-like cell cultures isolated from newborn rat calvaria.Calcif Tissue Int.1990;47(2): 92-104.
[16] Lian JB,Stein GS. Concepts of osteoblast growth and differentiation: basis for modulation of bone cell .development and tissue formation. Crit Rev in Oral Bio Med .1992;3(3): 269-305.
[17] Linsley C,Wu B,Tawil B.The effect of fibrinogen, collagen type I, and fibronectin on mesenchymal stem cell growth and differentiation into osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A.2013;19 (11-12): 1416-1423.
[18] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].西安:世界图书出版公司:1996, 83-84.
[19] 陈强,夏天,叶哲伟,等.优化组织块法体外培养新生SD大鼠原代成骨细胞与鉴定[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2012,47(9):1124-1127.
[20] Suzuki A,Takayama T,Suzuki N,et al.Daily low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-mediated osteogenic differentiation in rat osteoblasts.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin(Shanghai).2009;41(2): 108-115.
[21] 那键,马超,霍维玲,等.雌性乳鼠颅骨来源的成骨细胞培养方法的建立及其评价[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2013,39(1):057.
[22] Stein GS, Lian JB.Molecular mechanisms mediating proliferation/differentiation interrelationships during progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocr Rev.1993;14(4):424-442.
[23] 裴国献.组织工程学实验技术[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2006: 61.
[24] Lo KW,Kan HM, Ashe KM,et al. The small molecule PKA‐specific cyclic AMP analogue as an inducer of osteoblast‐like cells differentiation and mineralization. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(1):40-48.
[25] Uchihashi K,Aoki S, Matsunobu A, et al. Osteoblast migration into type I collagen gel and differentiation to osteocyte-like cells within a self-produced mineralized matrix:A novel system for analyzing differentiation from osteoblast to osteocyte. Bone. 2013;52(1):102-110.
[26] Warner GP, Hubbard HL,Lioyd GC, et al.32 Pi-and 45 Ca-metabolism by matrix vesicle –enriched micrsomes prepared from chicken epiphyseal cartiliage by isosmotic Percoll density- gradient fractionation.Calcif Tssue Int.1983; 35(3):327-338.
[27] Wong MM, Rao LG,Ly H,et al.Long‐term effects of physiologic concentrations of dexamethasone on human bone‐derived cells.J Bone Miner Res.1990;5(8):803-813.
[28] 尹美珍,戴红莲,殷义霞.体外分离培养成骨细胞的一种新方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2013,30(005):1063-1066.
[29] Hayashi O, Katsube Y, Hirose M, et al.Comparison of osteogenic ability of rat mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, periosteum, and adipose tissue. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;82(3):238-247.
[30] Swaminathan R. Biochemical markers of bone turnover. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2001;313(1):95-105.
[31] Ducy P,Desbois C,Boyce B,et al.Increased bone formation in osteocalcin-deficient mice. Nature.1996;382:448-452.
[32] 汤小康,程婉,许兵,等.骨细胞分离培养及其与成骨细胞鉴别比较的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(3):227-231. |
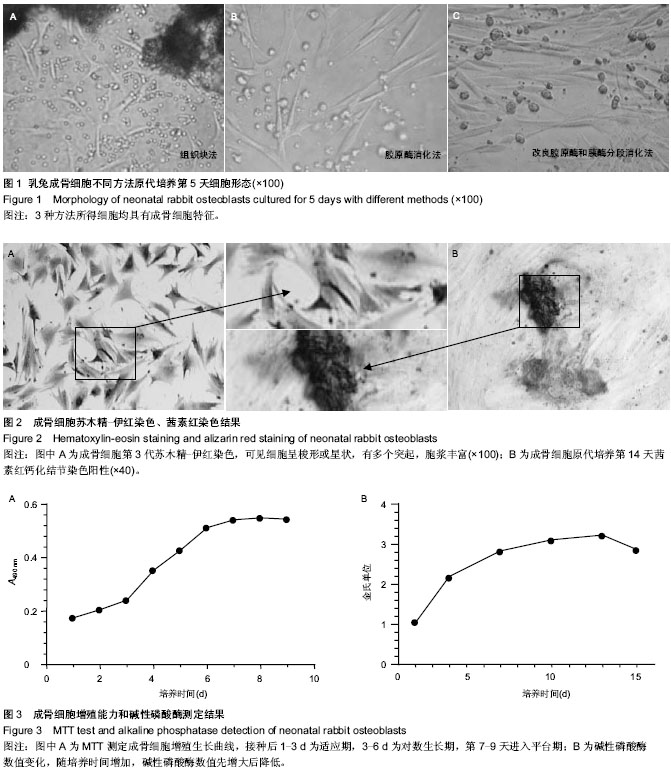
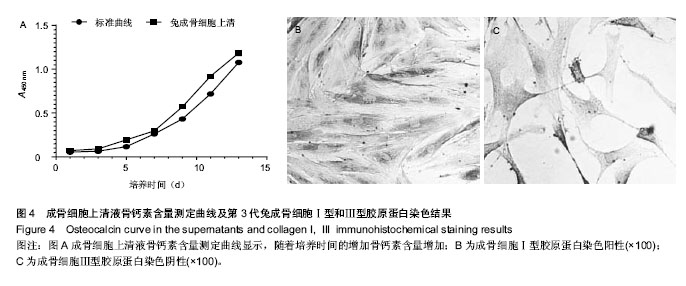
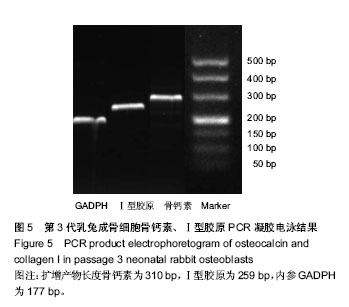
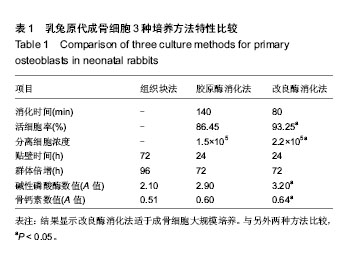
.jpg)
.jpg)