中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (34): 5441-5448.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.34.006
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
珊瑚羟基磷灰石与异体脱细胞真皮基质联合修复牙根尖周组织缺损
徐 隽1,王进涛2,李 刚1,史芳川2,钟良军2
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔医学中心牙周粘膜科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2杭州师范大学附属医院口腔科,浙江省杭州市 310015
-
修回日期:2014-06-05出版日期:2014-08-20发布日期:2014-08-20 -
通讯作者:钟良军,博士,教授,主任医师,杭州师范大学附属医院口腔科,浙江省杭州市 310015 -
作者简介:徐隽,女,1974年生,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市人,汉族,2009年新疆医科大学毕业,硕士,讲师,主治医师,主要从事口腔内科学方面的研究。 -
基金资助:新疆维吾尔自治区科技支疆项目(201091144)
Acellular dermal matrix allograft combined with coralline hydroxyapatite repair periapical tissue defects
Xu Jun1, Wang Jin-tao2, Li Gang1, Shi Fang-chuan2, Zhong Liang-jun2
- 1 Periodontal & Mucosal Department, Center of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2 Department of Stomatology, the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-06-05Online:2014-08-20Published:2014-08-20 -
Contact:Zhong Liang-jun, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Department of Stomatology, the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Xu Jun, Master, Lecturer, Attending physician, Periodontal & Mucosal Department, Center of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:a grant from Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 201091144
摘要:
背景:慢性根尖周炎症导致根尖周骨质破坏及缺损并不少见,若不能及时消除炎症终止骨吸收和牙龈组织的破坏,修复根尖周组织缺损,最终将导致牙丧失。脱细胞真皮基质和珊瑚羟基磷灰石在动物实验中常用于修复牙周损伤。
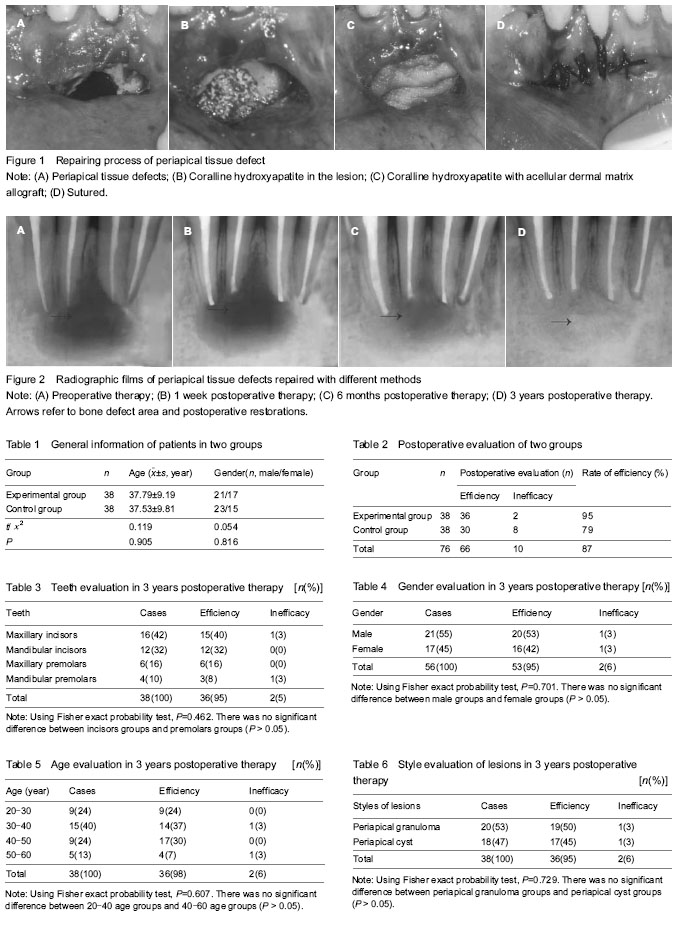
结果与结论:修复1个月后,实验组患者异体脱细胞真皮基质全部存活,因修整瘘管口周围炎性的肉芽组织导致的牙龈组织缺损已经愈合。在修复12个月后,实验组患者的修复有效率明显高于对照组(P < 0.05)。实验组患者修复6个月后骨缺损区阴影基本消失,珊瑚羟基磷灰石颗粒间的透射影减小,出现有一定致密度的影像,提示有新骨长入;12个月后珊瑚羟基磷灰石颗粒密度已接近正常的骨组织密度,与正常骨组织之间有密度移行改变,逐渐与牙槽骨形成骨融合。异体脱细胞基质与珊瑚羟基磷灰石的生物相容性良好。提示异体脱细胞真皮基质与珊瑚羟基磷灰石联合修复根尖周组织缺损具有良好的临床疗效。
中图分类号:
引用本文
徐 隽,王进涛,李 刚,史芳川,钟良军. 珊瑚羟基磷灰石与异体脱细胞真皮基质联合修复牙根尖周组织缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(34): 5441-5448.
Xu Jun, Wang Jin-tao, Li Gang, Shi Fang-chuan, Zhong Liang-jun. Acellular dermal matrix allograft combined with coralline hydroxyapatite repair periapical tissue defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5441-5448.
Biocompatibility of different methods for repairing periapical tissue defects

| [1] Tronstad L, Barnett F, Cervone F. Periapical bacterial plaque in teeth refractory to endodontic treatment. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990;6(2):73-77. [2] Sen BH, Piskin B, Demirci T. Observation of bacteria and fungi in infected root canals and dentinal tubules by SEM. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1995;11(1):6-9. [3] Ng YL, Mann V, Gulabivala K. Tooth survival following non-surgical root canal treatment: a systematic review of the literature. Int Endod J. 2010;43(3):171-189. [4] Tsesis I, Rosen E, Tamse A, et al. Effect of guided tissue regeneration on the outcome of surgical endodontic treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endod. 2011;37(8):1039-1045. [5] Goyal B, Tewari S, Duhan J, et al. Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich plasma and guided tissue regeneration membrane in the healing of apicomarginal defects: a clinical study. J Endod. 2011;37(6):773-780. [6] Kovác J, Kovác D. Histopathology and etiopathogenesis of chronic apical periodontitis--periapical granuloma. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2011;60(2):77-86. [7] Nair PN. Pathogenesis of apical periodontitis and the causes of endodontic failures. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004; 15(6):348-381. [8] Kawaguchi H, Kurihara H. Clinical trial of periodontal tissue regeneration. Nihon Rinsho. 2008;66(5):948-954. [9] Ng YL, Mann V, Gulabivala K. A prospective study of the factors affecting outcomes of non-surgical root canal treatment: part 2: tooth survival. Int Endod J. 2011;44(7): 610-625. [10] Ma J, Al-Ashaw AJ, Shen Y, et al. Efficacy of ProTaper Universal Rotary Retreatment system for gutta-percha removal from oval root canals: a micro-computed tomography study. J Endod. 2012;38(11):1516-1520. [11] García CC, Sempere FV, Diago MP, et al. The post-endodontic periapical lesion: histologic and etiopathogenic aspects. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007;12(8):E585-590. [12] Maddalone M, Gagliani M. Periapical endodontic surgery: a 3-year follow-up study. Int Endod J. 2003;36(3):193-198. [13] von Arx T. Apical surgery: A review of current techniques and outcome. Saudi Dent J. 2011;23(1):9-15. [14] Lindeboom JA. Apical endodontic surgery. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2004;111(4):146-151. [15] Pawar AM, Kokate SR, Shah RA. Management of a large periapical lesion using Biodentine(™) as retrograde restoration with eighteen months evident follow up. J Conserv Dent. 2013;16(6):573-575. [16] Bashutski JD, Wang HL. Periodontal and endodontic regeneration. J Endod. 2009;35(3):321-328. [17] Kinaia BM, Chogle SM, Kinaia AM, et al. Regenerative therapy: a periodontal-endodontic perspective. Dent Clin North Am. 2012;56(3): 537-547. [18] Pecora G, De Leonardis D, Ibrahim N, et al. The use of calcium sulphate in the surgical treatment of a 'through and through' periradicular lesion. Int Endod J. 2001;34(3): 189-197. [19] Lin L, Chen MY, Ricucci D, et al. Guided tissue regeneration in periapical surgery. J Endod. 2010;36(4): 618-625. [20] Naylor J, Mines P, Anderson A, et al. The use of guided tissue regeneration techniques among endodontists: a web-based survey. J Endod. 2011;37(11):1495-1498. [21] Tobón SI, Arismendi JA, Marín ML, et al. Comparison between a conventional technique and two bone regeneration techniques in periradicular surgery. Int Endod J. 2002;35(7):635-641. [22] von Arx T, Cochran DL. Rationale for the application of the GTR principle using a barrier membrane in endodontic surgery: a proposal of classification and literature review. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2001;21(2):127-139. [23] Taschieri S, Corbella S, Tsesis I, et al. Effect of guided tissue regeneration on the outcome of surgical endodontic treatment of through-and-through lesions: a retrospective study at 4-year follow-up. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 15(3): 153-159. [24] Marín-Botero ML, Domínguez-Mejía JS, Arismendi-Echavarría JA, et al. Healing response of apicomarginal defects to two guided tissue regeneration techniques in periradicular surgery: a double-blind, randomized-clinical trial. Int Endod J. 2006;39(5):368-377. [25] Sánchez-Torres A, Sánchez-Garcés MA, Gay-Escoda C. Materials and prognostic factors of bone regeneration in periapical surgery: A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2014. in press. [26] Baran ET, Tuzlakoglu K, Salgado AJ, et al. Multichannel mould processing of 3D structures from microporous coralline hydroxyapatite granules and chitosan support materials for guided tissue regeneration/engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15(2):161-165. [27] Swetha M, Sahithi K, Moorthi A, et al. Biocomposites containing natural polymers and hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;47(1):1-4. [28] Zhang L, Tang P, Zhang W, et al. Effect of chitosan as a dispersant on collagen-hydroxyapatite composite matrices. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(1):71-79. [29] Venkatesan J, Kim SK. Chitosan composites for bone tissue engineering--an overview. Mar Drugs. 2010;8(8):2252-2266. [30] Chen L, Hu J, Shen X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-multiwalled carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(8):1843-1851. [31] Pighinelli L, Kucharska M. Chitosan-hydroxyapatite composites. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;93(1):256-262. [32] Zigdon H, Horwitz J. Using acellular dermal matrix (ADM) allograft in periodontal surgery--a literature review and case reports. Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim. 2006;24(3):19-29, 92. [33] Tal H. Subgingival acellular dermal matrix allograft for the treatment of gingival recession: a case report. J Periodontol. 1999;70(9):1118-1124. [34] de Souza SL, Novaes AB Jr, Grisi DC, et al. Comparative clinical study of a subepithelial connective tissue graft and acellular dermal matrix graft for the treatment of gingival recessions: six- to 12-month changes. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2008;10(3):87-94. [35] Rahmani ME, Lades MA. Comparative clinical evaluation of acellular dermal matrix allograft and connective tissue graft for the treatment of gingival recession. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2006;7(2):63-70. [36] Novaes AB Jr, de Barros RR. Acellular dermal matrix allograft. The results of controlled randomized clinical studies. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2008;10(4):123-129. [37] Moslemi N, Mousavi Jazi M, Haghighati F, et al. Acellular dermal matrix allograft versus subepithelial connective tissue graft in treatment of gingival recessions: a 5-year randomized clinical study. J Clin Periodontol. 2011; 38(12): 1122-1129. [38] Fotek PD, Neiva RF, Wang HL. Comparison of dermal matrix and polytetrafluoroethylene membrane for socket bone augmentation: a clinical and histologic study. J Periodontol. 2009;80(5):776-785. [39] Froum S, Cho SC, Elian N, et al. Extraction sockets and implantation of hydroxyapatites with membrane barriers: a histologic study. Implant Dent. 2004;13(2):153-164. [40] Terino EO. Alloderm acellular dermal graft: applications in aesthetic soft-tissue augmentation. Clin Plast Surg. 2001; 28(1):83-99. [41] Barros RR, Novaes AB, Grisi MF, et al. A 6-month comparative clinical study of a conventional and a new surgical approach for root coverage with acellular dermal matrix. J Periodontol. 2004;75(10):1350-1356. [42] Sclafani AP, Romo T 3rd, Jacono AA, et al. Evaluation of acellular dermal graft (AlloDerm) sheet for soft tissue augmentation: a 1-year follow-up of clinical observations and histological findings. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001;3(2): 101-103. [43] Orstavik D, Kerekes K, Eriksen HM. The periapical index: a scoring system for radiographic assessment of apical periodontitis. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1986;2(1):20-34. [44] Friedman S, Abitbol S, Lawrence HP. Treatment outcome in endodontics: the Toronto Study. Phase 1: initial treatment. J Endod. 2003;29(12):787-793. [45] Lin L, Chen MY, Ricucci D, et al. Guided tissue regeneration in periapical surgery. J Endod. 2010;36(4): 618-625. [46] Moreira-Gonzalez A, Jackson IT, Miyawaki T, et al. Augmentation of the craniomaxillofacial region using porous hydroxyapatite granules. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(6):1808-1817. [47] Damien E, Revell PA. Coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitute: A review of experimental studies and biomedical applications. J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2004;2(2):65-73. [48] Ducheyne P, Qiu Q. Bioactive ceramics: the effect of surface reactivity on bone formation and bone cell function. Biomaterials. 1999;20(23-24):2287-2303. [49] Luo ZB, Zhang QB, Zhang ZQ, et al. Performance of coralline hydroxyapatite in sinus floor augmentation: a retrospective study. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17(9): 2003-2010. [50] Fu K, Xu Q, Czernuszka J, et al. Characterization of a biodegradable coralline hydroxyapatite/calcium carbonate composite and its clinical implementation. Biomed Mater. 2013;8(6):065007. [51] Markel DC, Guthrie ST, Wu B, et al. Characterization of the inflammatory response to four commercial bone graft substitutes using a murine biocompatibility model. J Inflamm Res. 2012;5:13-18. [52] Moslemi N, Mousavi Jazi M, Haghighati F, et al. Acellular dermal matrix allograft versus subepithelial connective tissue graft in treatment of gingival recessions: a 5-year randomized clinical study. J Clin Periodontol. 2011;38(12): 1122-1129. [53] Thombre V, Koudale SB, Bhongade ML. Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of coronally positioned flap with or without acellular dermal matrix allograft in the treatment of multiple marginal gingival recession defects. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(3):e88-94. [54] Wagshall E, Lewis Z, Babich SB, et al. Acellular dermal matrix allograft in the treatment of mucogingival defects in children: illustrative case report. ASDC J Dent Child. 2002; 69(1):39-43, 11. [55] Batista EL Jr, Batista FC. Managing soft tissue fenestrations in bone grafting surgery with an acellular dermal matrix: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001;16(6):875-879. [56] Koudale SB, Charde PA, Bhongade ML. A comparative clinical evaluation of acellular dermal matrix allograft and sub-epithelial connective tissue graft for the treatment of multiple gingival recessions. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012; 16(3):411-416. [57] Zuolo ML, Ferreira MO, Gutmann JL. Prognosis in periradicular surgery: a clinical prospective study. Int Endod J. 2000;33(2):91-98. [58] Luczyszyn SM, Papalexiou V, Novaes AB Jr, et al. Acellular dermal matrix and hydroxyapatite in prevention of ridge deformities after tooth extraction. Implant Dent. 2005;14(2): 176-184. [59] Sàndor GK, Kainulainen VT, Queiroz JO, et al. Preservation of ridge dimensions following grafting with coral granules of 48 post-traumatic and post-extraction dento-alveolar defects. Dent Traumatol. 2003;19(4):221-227. [60] Fowler EB, Breault LG. Ridge augmentation with a folded acellular dermal matrix allograft: a case report. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2001;2(3):31-40. [61] Sadat Mansouri S, Ayoubian N, Eslami Manouchehri M. A comparative 6-month clinical study of acellular dermal matrix allograft and subepithelial connective tissue graft for root coverage. J Dent (Tehran). 2010;7(3):156-164. [62] Artzi Z, Wasersprung N, Weinreb M, et al. Effect of guided tissue regeneration on newly formed bone and cementum in periapical tissue healing after endodontic surgery: an in vivo study in the cat. J Endod. 2012;38(2):163-169. [63] Steele MH, Seagle MB. Palatal fistula repair using acellular dermal matrix: the University of Florida experience. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56(1):50-53. [64] de Souza SL, Novaes AB Jr, Grisi DC, et al. Comparative clinical study of a subepithelial connective tissue graft and acellular dermal matrix graft for the treatment of gingival recessions: six- to 12-month changes. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2008;10(3):87-94. [65] Thomas LJ, Emmadi P, Thyagarajan R, et al. A comparative clinical study of the efficacy of subepithelial connective tissue graft and acellular dermal matrix graft in root coverage: 6-month follow-up observation. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013;17(4):478-483. |
| [1] | 李 黎, 马 力. 磁性壳聚糖微球固定化乳糖酶及其酶学性质[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [2] | 刘 鋆, 杨 龙, 王伟宇, 周玉虎, 吴 颖, 卢 涛, 舒莉萍, 马敏先, 叶 川. 聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [3] | 周安琪, 唐渝菲, 吴秉峰, 向 琳. 骨膜组织工程设计:共性与个性的结合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [4] | 郎丽敏, 何 生, 姜增誉, 胡奕奕, 张智星, 梁敏茜. 导电复合材料在心肌梗死组织工程治疗领域的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [5] | 解 健, 苏俭生. 静电纺丝取向纳米纤维作为组织工程生物支架的优势与特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [6] | 纪 琦, 喻正文, 张 剑. 3D打印金属基生物材料工艺和临床应用的问题与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [7] | 宋涯含, 吴云霞, 范道洋. 基于VOSviewer生物医学领域3D打印的知识图谱分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(15): 2385-2393. |
| [8] | 钱楠楠, 张 潜, 杨 睿, 敖 俊, 章 涛. 间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤:细胞治疗及联合新药和生物材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [9] | 罗雅馨, 毕浩然, 陈晓旭, 杨 琨. 细胞外基质与组织的再生与修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(11): 1785-1790. |
| [10] | 贾 巍, 张满栋, 陈维毅, 王晨艳, 郭 媛. 股骨假体材料对人工膝关节置换性能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [11] | 王 倩, 李 璐, 舒静媛, 董志恒, 靳友士, 王青山. 氧化锆基纳米羟基磷灰石功能梯度生物材料的微观形貌和物相分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| [12] | 杨亚楠, 李峻峰, 王 立, 刘恒全, 赖雪飞. 柠檬酸钙:一种有趣的有机钙生物医用材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1609-1615. |
| [13] | 樊雪敏, 方善宝, 陈志兴, 莫水学. 纳米粘土锂皂石的研究现状与应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1622-1627. |
| [14] | 王 刚, 李东辉, 白志明. 长段输尿管损伤替代治疗的方法、材料及修复重建的演变历程[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1299-1305. |
| [15] | 任春梅, 刘玉芳, 许 诺, 邵苗苗, 何建亚, 李晓杰.
非编码RNAs在人牙髓干细胞中的调控作用及机制 |
Design
1 在临床上,由于牙齿的慢性根尖周炎症所导致的根尖周骨质破坏及缺损并不少见,若不能及时消除炎症终止骨吸收和牙龈组织的破坏,修复根尖周组织缺损,最终将导致牙丧失。临床治疗的最终目的是使被破坏的组织获得修复和再生,有新附着形成和骨重建,不仅在于强调消除炎症,防止感染及复发,更重要的还在于重建缺损组织的正常结构和功能。 2 文章的特点在于证实在骨缺损处植入珊瑚羟基磷灰石后对骨的生长有诱导作用,而植入异体脱细胞真皮基质能够诱导上皮细胞生长,加快骨缺损修复,两者结合能够显著提高根尖周组织缺损的治疗效果。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||