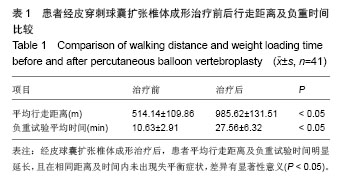
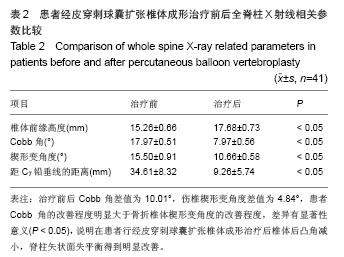
| [1]Ettinger MP. Aging bone and osteoporosis: strategies for preventing fractures in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163(18):2237-2246.
[2]安珍,杨定焯,张祖君,等.骨质疏松性脊椎压缩性骨折流行病学调查分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2002,8(1):82-83.
[3]李宁华,区品中,朱汉民,等.中国部分地区中老年人群原发性骨质疏松患病率的研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(5):275-278.
[4]谢晓勇,李平生,李玉茂,等.骨质疏松性脊柱多发性骨折后凸成形术近期疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(7): 467-468.
[5]Schofer MD,Efe T,Timmesfeld N,et al.Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the treatment of fresh vertebral compression fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10):1391-1399.
[6]Legaye J,Duval-Beaupre G,Hecquet J,et al. Pelvic incidence:A fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(2):99-103.
[7]Vaz G,Roussouly P,Berthonnaud E,et al. Sagittal morphology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(1): 80-87.
[8]Voutsinas SA,MacEwen GD.Sagittal profiles of the spine.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;210:235-242.
[9]Kouwenhoven JM,Castelein RM. The pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:review of the literature. Spine. 2008;33(26):2898-908.
[10]Cho KJ,Suk SI,Park SR,et al. Risk factors of sagittal decompensation after long posterior instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 2010;35(17): 1595-1601.
[11]Barrey C,Roussouly P,Perrin G,et al. Sagittal balance disorders in severe degenerative spine:Can we identify the compensatory mechanisms. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(Suppl 5):626-633.
[12]Le Huec JC,Charosky S,Barrey C,et al. Sagittal imbalance cascade for simple degenerative spine and consequences: algorithm of decision for appropriate treatment. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(Suppl 5):699-703.
[13]Schwab FJ,Smith VA,Biserni M,et al. Adult scoliosis:a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(4):387-392.
[14]Shipp KM, Purser JL, Gold DT, et al.Timed Loaded Standing: A Measure of Combined Trunk and Arm Endurance Suitable for People with Vertebral Osteoporosis.Osteoporos Int. 2000; 11:914-922.
[15]Alanay A, Pekmezci M, Karaeminogullari O, et al. Radiographic measurement of the sagittal plane deformity in patients with osteoporotic spinal fractures evaluation of intrinsic error. Eur Spine J. 2007;16:2126-2132.
[16]韦以宗.脊柱机能解剖学研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2003, 11(1): 1-9.
[17]Naylor A. Intervertabral disk prolapse and degeneration. Spine.1976;1:108.
[18]Kanis J A. Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. Lancet.2002;359(9321): 1929-1936.
[19]Cummings SR, Melton LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1761-1767.
[20]Kado DM, Browner WS, Palermo L, et al. Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Arch Int Med.1999; 159(11):1215-1220.
[21]Beahonnaud E,Labelle H,Roussouly P,et al.A variability study of computerized sagittal spinopelvie radiologic measurements of trunk balance. Spine Disord Tech. 2005;1:66-71.
[22]Min K,Hahn F,Ziebarth K. Short anterior correction of the thoracolumbar/lumber curve in King 1 idiopathic scoliosis:the behaviour of the instrumented and non-instrumented curves and the trunk balance. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(1):65-72.
[23]Yin G, Qiu Y,Sun X, et al. The influence of different arm position on the spinal sagittal profile in normal adolescents and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin J Orthop. 2008; 28(9): 726-730.
[24]Debarge R,Demey G,Roussouly P.Sagittal balance analysis after pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine. 2009;34(8):785-791.
[25]Roussouly P, Nnadi C. Sagittal plane deformity:an overview of interpretation and management.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(1): 1824-1836.
[26]Lee C, Chung S, Kang K, et al. Normal patterns of sagittal alignment of the spine in young adults radiological analysis in a korean population.Spine. 2011;36(25):E1648-1654.
[27]Cotton A,Boutry N,Cortet B,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty state of the art.Radiographics. 1998;18:311-320.
[28]Tohmeh A,Dewatre F,Cortet B,et al.Biomechanical efficacy of osteoporotic compression fractures.Spine. 1999;24: 1772-1776.
[29]Deramond H,Wright NT,Belkoff SM.Temperature elevation caused by bone cement polymerization during vertebroplasty. Bone. 1999;25(2):17-21S.
[30]Miyazaki M,Hymanson HJ,Morshita Y,et al.Kinematic analysis of the relationship between sagittal alignment and disc degeneration in the cervical spine.Spine. 2008;23:870-876. |