| [1] Kotwal S,Pumberger M,Hughes A,et al. Degenerative scoliosis: a review. HSS J.2011;7(3):257-264.[2] Chin KR,Furey C,Bohlman HH. Risk of progression in de novo low-magnitude degenerative lumbar curves:natural history and literature review. Am J Orthop(Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(8):404-409[3] 孟庆华,鲍春雨,刘晋浩.人体脊柱全颈椎三维有限元模型研究与应用[J].医用生物力学,2009,24(3):178-182.[4] Aebi M. The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(10): 925-948. [5] Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(9): 1082-1085.[6] 王加谋,陈超,李前龙,等.退变椎间盘在骨质疏松椎体应力分布中作用的有限元方法研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007,15(7): 41-44.[7] Wang X, Dumas GA. Evaluation of effects of selected factors on inter-vertebral fusion-a simulation study. Med Eng Phys. 2005;27(3):197-207.[8] 谌宏军,刘仲前.椎间盘退变与分子生物学研究治疗进展[J].实用医院临床杂志,2010,7(1):119-112.[9] Itoh H,Asou Y,Hara Y, et al .Enhanced type X collagen expression in the extruded nucleus pulposus of the chondrody strophoid dog. Vet Med Sci.2008;70(1):37-42.[10] 杜文丙,刘维钢.腰椎间盘退变的影响因素研究进展[J].农垦医学, 2010,32(1):71-74.[11] 张小海,徐宏光,吴天亮.椎间盘退变与生物力学[J].国际骨科学杂志,2010,31(3):137-138.[12] 唐小君.椎间盘退变对腰椎生物力学影响的有限元研究[D].浙江大学,2007.[13] 高飞,赵斌.腰椎关节突关节基础研究新进展[J].国际影像学杂志, 2009,19(7):925-927.[14] 李海侠,邹德威,陆明. 人工髓核假体的研究进展及其发展方向[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2429-2433.[15] 闫广辉,张庆胜,靳宪辉,等.经腰椎椎弓根动态内固定研究进展[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(6):31-34.[16] Ploumis A, Transfledt EE, Denis F. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2007; 7(4):428-436.[17] 顾韬,阮狄克. 生物力学因素对椎间盘退变的影响及机理[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(6):523-526. [18] Reutlinger C, Hasler C, Scheffler K, et al. Intraoperative determination of the load–displacement behavior of scoliotic spinal motion segments: preliminary clinical results. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl 6:S860-867.[19] Ohtori S, Yamashita M, Inoue G, et al. Rotational hypermobility of disc wedging using kinematic CT: preliminary study to investigate the instability of discs in degenerated scoliosis in the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(6): 989-994. [20] Bess S, Boachie-Adjei O, Burton D, et al. Pain and disability determine treatment modality for older patients with adult scoliosis, while deformity guides treatment for younger patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(20):2186-2190.[21] 李庆兵,冯跃,罗建,等. 有限元分析在手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症中的研究进展[J].南京中医药大学学报,2013,29(1):94-96.[22] 刘仕友,路青林,郑伟,等. 椎体后凸成形椎间盘骨水泥渗漏时行相邻椎体预防性强化的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(22):4001-4005.[23] 黄菊英,李海云,菅凤增,等. 腰椎间盘突出症有限元模型的建立与分析[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2012,12(4):394-398.[24] 徐海涛,李松,刘澜,等. 腰椎斜扳手法时椎间盘的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2335-2338.[25] 张明才,吕思哲,程英武,等. 基于有限元模型研究椎骨错缝对颈椎病患者关节应力的影响[J]. 中国骨伤,2011,24(2):128-131. |
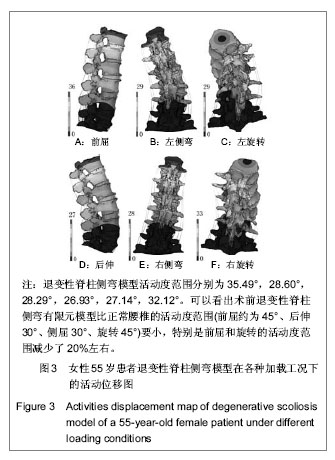
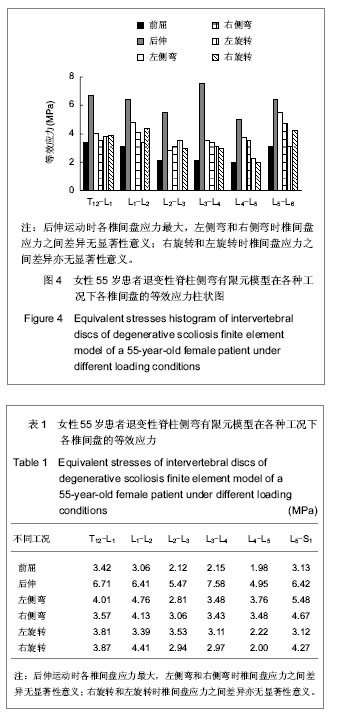

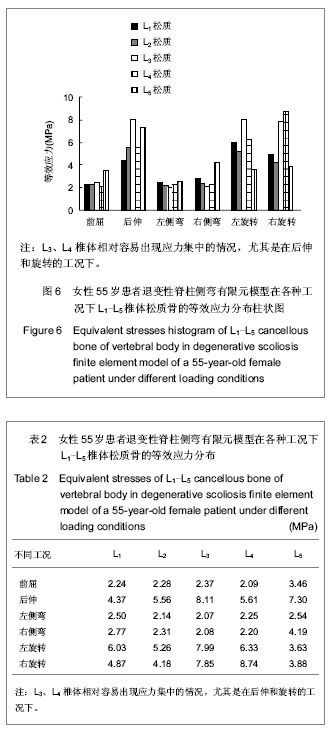
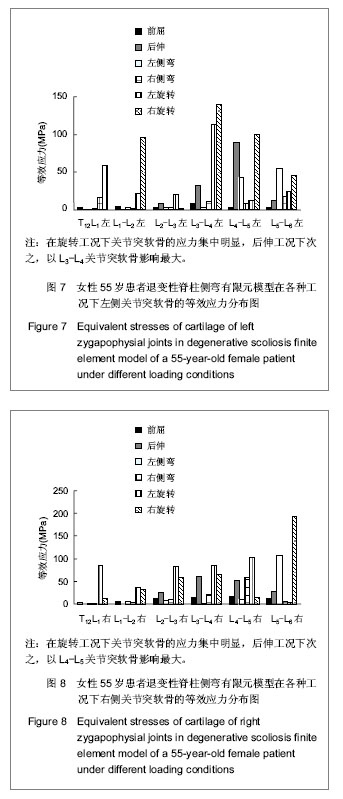
.jpg)
.jpg)