| [1] Capla JM, Grogan RH, Callaghan MJ, et al. Diabetes impairs endothelial progenitor cell-mediated blood vessel formation in response to hypoxia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(1):59-70.[2] Danet GH, Luongo JL, Butler G, et al. C1qRp defines a new human stem cell population with hematopoietic and hepatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(16):10441- 10445.[3] Hong SH, Gang EJ, Jeong JA, et al. In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330(4):1153-1161.[4] 陈海鸥,胡小宣,刘红娟,等.脐血干细胞移植治疗肝硬化的疗效观察[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2010,18(7):537-538.[5] Jung KH, Shin HP, Lee S, et al. Effect of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a cirrhotic rat model. Liver Int. 2009;29(6):898-909. [6] 金光鑫,吴德全.脐带血间充质干细胞研究进展[J].国际移植与血液净化杂志,2006,4(5):45-48.[7] Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110.[8] Jonker AM, Dijkhuis FW, Boes A, et al. Immunohistochemical study of extracellular matrix in acute galactosamine hepatitis in rats. Hepatology. 1992;15(3):423-431.[9] Jonker AM, Dijkhuis FW, Kroese FG, et al. Immunopathology of acute galactosamine hepatitis in rats. Hepatology. 1990; 11(4):622-627. [10] Yan L, Xu SP, Wang SZ, et al. G-CSF mobilized PBMCs contribute to the liver function of cirrhotic rats. Excli J. 2010; 9:67-75.[11] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells.The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[12] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.[13] Yang CC, Shih YH, Ko MH, et al. Transplantation of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly after complete transection of the rat spinal cord. PLoS One. 2008; 3(10):e3336.[14] Chao KC, Chao KF, Fu YS, et al. Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to control type 1 diabetes. PLoS One.2008;3(1):e1451.[15] Moodley Y, Atienza D, Manuelpillai U, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce fibrosis of bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Pathol. 2009;175(1): 303-313. [16] Prasanna SJ, Gopalakrishnan D, Shankar SR, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, IFNgamma and TNFalpha, influence immune properties of human bone marrow and Wharton jelly mesenchymal stem cells differentially. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9016.[17] Liu Y, Mu R, Wang S, et al. Therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):R210.[18] Zhao L, Weir MD, Xu HH. Human umbilical cord stem cell encapsulation in calcium phosphate scaffolds for bone engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3848-3857.[19] Struys T, Moreels M, Martens W, et al. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical analysis of multilineage differentiated human dental pulp- and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;193(6):366-378.[20] Chang SJ, Weng SL, Hsieh JY, et al. MicroRNA-34a modulates genes involved in cellular motility and oxidative phosphorylation in neural precursors derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Med Genomics. 2011;4:65.[21] Zhao Z, Chen Z, Zhao X, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes the differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes under the designated culturing conditions. J Biomed Sci. 2011;18:37.[22] Tse W, Laughlin MJ. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: a new alternative option. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2005:377-383.[23] 胡荣昕,缪伟峰.肝纤维化动物模型的研究概况[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2007,10(2):133-135.[24] Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(6):1655-1669.[25] Serrano AL, Mann CJ, Vidal B, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating fibrosis in skeletal muscle repair and disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;96:167-201.[26] 覃慧敏,田卫群.骨髓间充质干细胞经不同移植途径治疗终末期肝病[J].中华临床医师杂志,2011,5(21):6416-6418.[27] Kim WH, Matsumoto K, Bessho K, et al. Growth inhibition and apoptosis in liver myofibroblasts promoted by hepatocyte growth factor leads to resolution from liver cirrhosis. Am J Pathol. 2005;166(4):1017-1028.[28] Kakinuma S, Tanaka Y, Chinzei R, et al. Human umbilical cord blood as a source of transplantable hepatic progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2003;21(2):217-227. |
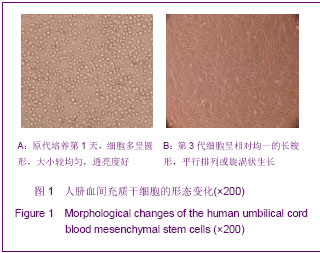
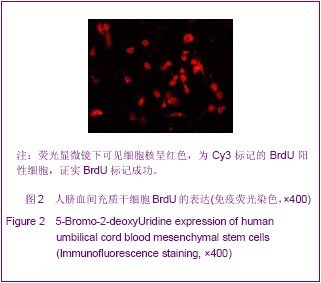
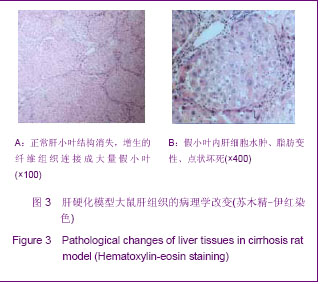
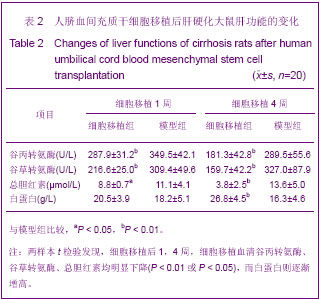
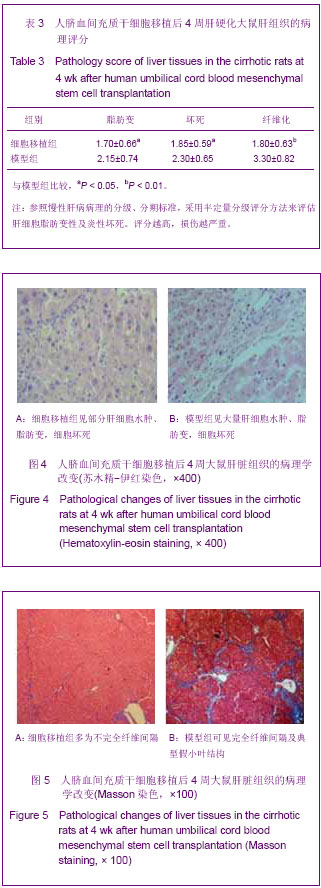

.jpg)
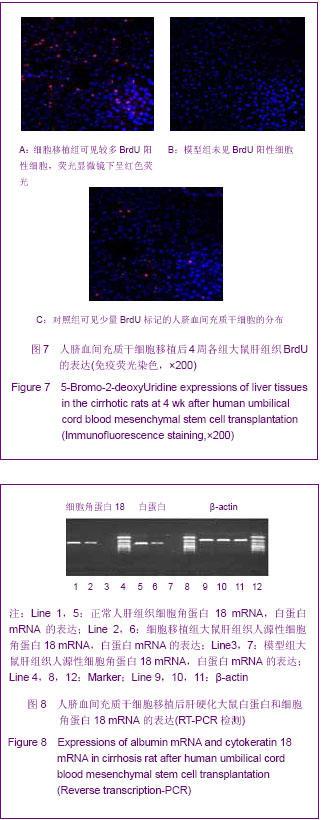
.jpg)