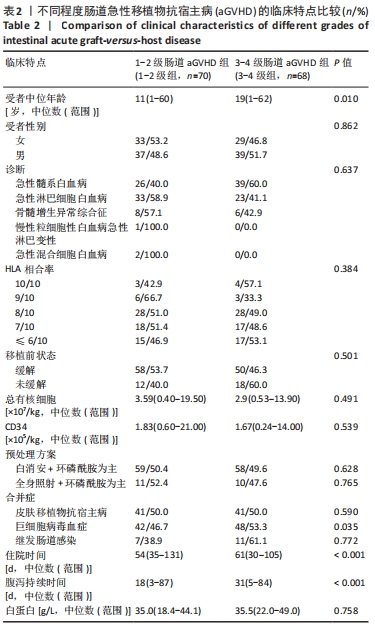
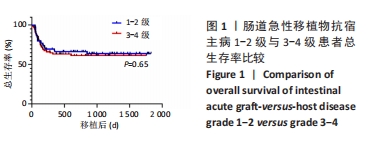
[1] YUN HD, VARMA A, HUSSAIN MJ, et al. Clinical Relevance of Immunobiology in Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation. J Clin Med. 2019;8(11):1968.
[2] HORWITZ ME, STIFF PJ, CUTLER C, et al. Omidubicel vs standard myeloablative umbilical cord blood transplantation: results of a phase 3 randomized study. Blood. 2021;138(16):1429-1440.
[3] KANDA J, HAYASHI H, RUGGERI A, et al. The impact of GVHD on outcomes after adult single cord blood transplantation in European and Japanese populations. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57(1):57-64.
[4] VAN HALTEREN AGS, SUWANDI JS, TUIT S, et al. A unique immune signature in blood separates therapy-refractory from therapy-responsive acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2023;141(11):1277-1292.
[5] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组.中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅲ)——急性移植物抗宿主病(2020年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2020,41(7):529-536.
[6] BURGOS DA SILVA M, PONCE DM, DAI A, et al. Preservation of the fecal microbiome is associated with reduced severity of graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2022;140(22):2385-2397.
[7] PONCE DM, POLITIKOS I, ALOUSI A, et al. Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Graft-versus-Host Disease after Cord Blood Transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(7):540-544.
[8] TAKAHASHI T, ARORA M, OKOEV G, et al. Late-Onset Acute and Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children: Clinical Features and Response to Therapy. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(8):667.e1-667.e5.
[9] JIN L, SUN Z, LIU H, et al. Inflammatory monocytes promote pre-engraftment syndrome and tocilizumab can therapeutically limit pathology in patients. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4137.
[10] 中华医学会血液学分会造血干细胞应用学组.造血干细胞移植相关血栓性微血管病诊断和治疗中国专家共识(2021年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2021,42(3):177-184.
[11] 安徽省肿瘤质量控制中心癌痛专家组.安徽省癌症疼痛诊疗专家共识(2019年版)[J].安徽医药,2020,24(5):1041-1047.
[12] ZHANG P, FENG K, XUE Y, et al. Clinical applications of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(1):155-161.
[13] ALADAĞ E, KELKITLI E, GÖKER H. Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease: A Brief Review. Turk J Haematol. 2020;37(1):1-4.
[14] STIKVOORT A, GABALLA A, SOLDERS M, et al. Risk Factors for Severe Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in Donor Graft Composition. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24(3):467-477.
[15] YANG R, ZHANG R, ZHANG Y, et al. Risk Factors Analysis for Human Cytomegalovirus Viremia in Donor+/Recipient+ Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Lab Med. 2020;51(1):74-79.
[16] PHAN M, CHAVAN R, BEUTTLER R, et al. Evaluating risk factors for acute graft versus host disease in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients receiving tacrolimus. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(4):1303-1313.
[17] SCHUTT SD, WU Y, KHAREL A, et al. The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(21):e143950.
[18] MARIOTTI J, PENACK O, CASTAGNA L. Acute Graft-versus-Host-Disease Other Than Typical Targets: Between Myths and Facts. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(2):115-124.
[19] JABR R, EL ATROUNI W, SHUNE L, et al. Clostridioides difficile Infection and Risk of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease among Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(2):176.e1-176.e8.
[20] YAN FH, WANG M, YAO JF, et al. Impact of Human Leukocyte Antigen Loci and Haplotypes on Intestinal Acute Graft-versus-host Disease after Human Leukocyte Antigen-matched Sibling Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(11):1290-1295.
[21] LIU Y, ZHAO Y, QI J, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation combined with ruxolitinib as a salvage treatment for intestinal steroid-refractory acute GVHD. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11(1):96.
[22] SUN X, PISANO M, XU L, et al. Baicalin regulates autophagy to interfere with small intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6551.
[23] SONG A, SHEN N, GAN C, et al. Exploration of the relationship between intestinal flora changes and gut acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transl Pediatr. 2021;10(2): 283-295.
[24] 孙元利,桂瑞丰,王科,等.急性白血病并发革兰阴性菌血流感染病原菌及其危险因素[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2023,33(7):996-1000.
[25] 刘明红,王海慧,周爱萍,等.造血干细胞移植患者移植早期肛周感染的影响因素[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2021,31(24):3782-3786.
[26] YANG LP, ZHAO P, WU YJ, et al. Treatment outcome and efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in a large real-world cohort study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57(4):554-561.
[27] KUBA A, RAIDA L, BRYCHTOVA S, et al. Cellular senescence marker p16INK4a and NFKB1 gene polymorphisms in lower gastro-intestinal acute graft versus host disease. Transpl Immunol. 2023;76:101768.
[28] 李娇霞,杨琴,冯素丽.健康教育联合针对性护理对干细胞移植后的肠道排异患者依从性的影响[J].北京医学,2019,41(2):170-172.
[29] 侯玉洁.白血病异基因造血干细胞移植后并发肠道移植物抗宿主病的观察及护理[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(22):216-217.
[30] RASHIDI A, HERMAN A, GOMES ALC, et al. An alpha-defensin gene single nucleotide polymorphism modulates the gut microbiota and may alter the risk of acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2020;189(5):926-930.
|