中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2042-2046.doi: 10.12307/2024.170
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
脐带间充质干细胞替代供者骨髓细胞在单倍体相合造血干细胞移植中的作用
张文荟,裴晓杭,孔 黛,刘忠文
- 河南省人民医院血液内科,郑州大学人民医院,河南省郑州市 450002
Efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells replacing donor bone marrow cells in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Zhang Wenhui, Pei Xiaohang, Kong Dai, Liu Zhongwen
- Department of Hematology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
脐带间充质干细胞:间充质干细胞可以调节T和B淋巴细胞增殖、激活、成熟,以诱导调节性T淋巴细胞的形成。动物研究显示,在体外扩增的间充质干细胞和造血干细胞共同移植后,造血干细胞的植入得到改善,移植物抗宿主病风险降低。造血干细胞移植分类:①按造血干细胞的来源部位可分为骨髓移植、外周血干细胞移植和脐血干细胞移植;②按照供者与受者的关系分为自体移植、同基因移植和异基因移植,其中同基因移植是指患者与移植供者为同卵孪生兄弟或姐妹;③根据供者与受者 HLA 配型相合程度分为 HLA 全相合移植、不全相合移植、单倍体相合移植;④根据移植前的预处理方案强度可分为:清髓性造血干细胞移植和非清髓性造血干细胞移植(减低预处理剂量的造血干细胞移植)。
背景:HLA单倍体相合异基因造血干细胞移植为高危恶性血液病患者提供了生存的机会。近年来,对单倍体相合移植的移植模式及移植物选择的探究仍在进行。目前国内逐渐流行以北京大学血液病研究中心建立的非体外去除T细胞骨髓和外周血干细胞混合移植模式,但此模式需采集供者骨髓液而增加了供者的痛苦和风险。
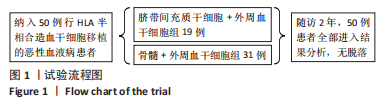
目的:探讨脐带间充质干细胞替代供者骨髓细胞联合单倍体相合外周血造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的疗效。方法:入组2019年1月至2022年5月接受单倍体相合造血干细胞移植的恶性血液病患者50例,按2∶3比例随机分配到2个研究组,其中脐带间充质干细胞+外周血干细胞移植的受者19例,骨髓细胞+外周血干细胞移植的受者31例。该研究经河南省人民医院伦理委员会审批。脐带间充质干细胞的受者于移植当天,首先输注1份第三方脐带间充质干细胞(1×106/kg),6 h后输注外周血造血干细胞。骨髓细胞的受者于移植+1 d输注供者骨髓细胞,于+2 d输注外周血干细胞。移植后所有受者均采用兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白+环孢素A+吗替麦考酚酯+短疗程甲氨喋呤预防移植物抗宿主病。
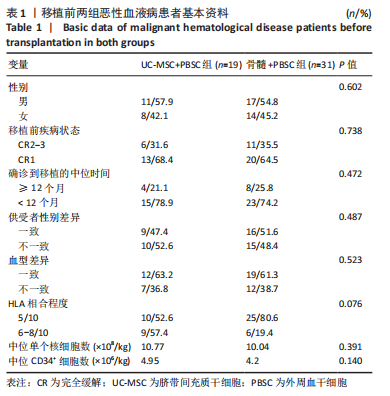
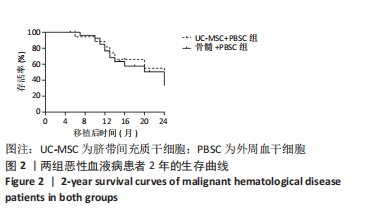
结果与结论:脐带间充质干细胞回输无不良事件发生,脐带间充质干细胞组和骨髓组的植入成功率分别为 100%(19/19)和 96.8%(30/31),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组的粒系植入中位时间分别为14 d和15 d,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组的血小板植入中位时间分别为20 d和19 d,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组Ⅱ-Ⅳ度急性移植物抗宿主病发生率分别为21.1%(4/19)和58.1%(18/31),差异有显著性意义(P=0.01);两组慢性移植物抗宿主病发生率分别为21.1%(4/19)和25.8%(8/31),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。两组复发率分别为15.8%(3/19)和16.1%(5/31),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。两组早期巨细胞病毒血症发生率分别为42.1%(8/19)和35.5%(11/31),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组移植后2年总存活率分别为68.4%(10/19)和70.9%(16/31),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。结果表明:脐带间充质干细胞替代供者骨髓细胞在单倍体相合外周血造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病中的疗效良好,降低了移植后急性移植物抗宿主病发生率,并未增加慢性移植物抗宿主病、复发率和早期巨细胞病毒血症的发生率,同时减少了供者采集骨髓的痛苦和风险。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1349-3644 (张文荟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: