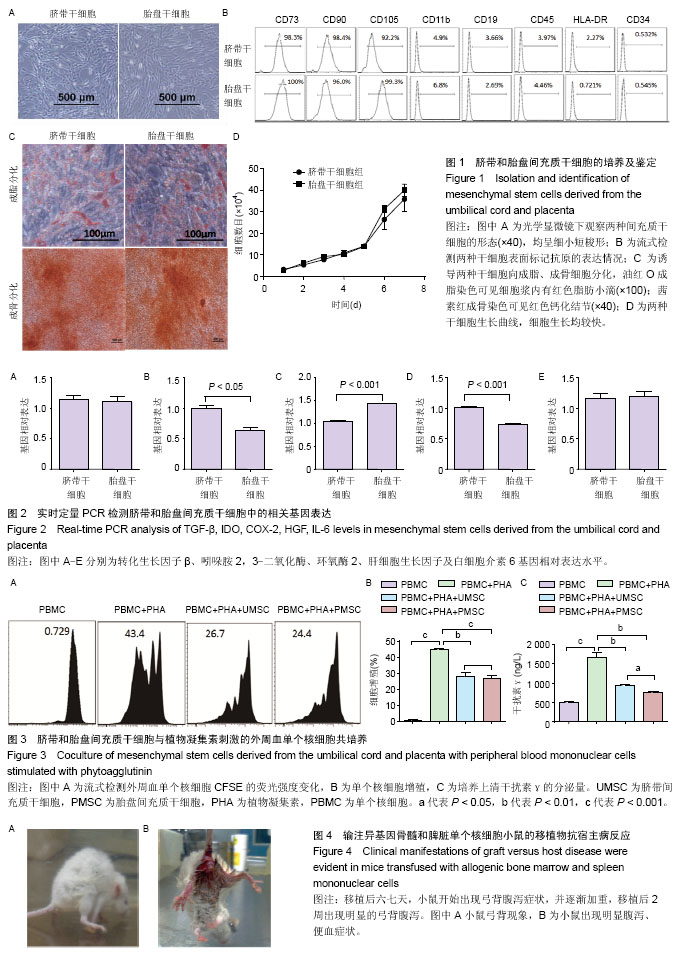
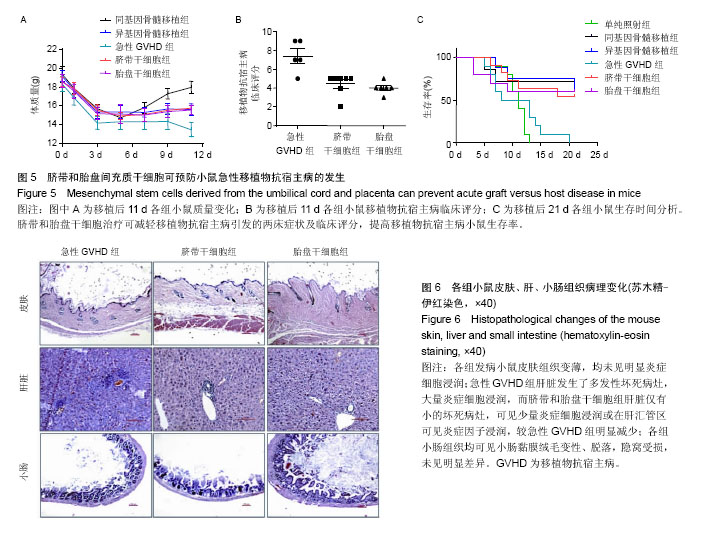
| [1] Baron F,Storb R.Mesenchymal stromal cells: a new tool against graft-versus-host disease? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(6):822-840.[2] Dominici M,Le Blanc K,Mueller I,et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells.The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8:315-317.[3] Lu LL,Liu YJ,Yang SG, et al.Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica.2006;91:1017-1026.[4] Yen BL,Huang HI,Chien CC,et al.Isolation of multipotent cells from human term placenta.Stem Cells.2005;23:3-9.[5] Tondreau T,Lagneaux L,Dejeneffe M,et al.Isolation of BM mesenchymal stem cells by plastic adhesion or negative selection: phenotype, proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential.Cytotherapy.2004;6:372-379.[6] Le Blanc K,Rasmusson I,Sundberg B,et al.Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells.Lancet.2004; 363: 1439-1441.[7] Muroi K,Miyamura K,Okada M,et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (JR-031) for steroid-refractory grade III or IV acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II/III study. Int J Hematol.2016;103:243-250.[8] Galipeau J.The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy. 2013;15:2-8.[9] Wu Y,Wang Z,Cao Y,et al.Cotransplantation of haploidentical hematopoietic and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with a myeloablative regimen for refractory/relapsed hematologic malignancy.Ann Hematol.2013;92:1675-1684.[10] Jang MJ,Kim HS,Lee HG,et al.Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells have an immunomodulatory effect that can control acute graft-versus-host disease in mice.Acta Haematol.2013;129(4):197-206.[11] Cooke KR,Kobzik L,Martin TR,et al.An experimental model of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: I. The roles of minor H antigens and endotoxin. Blood.1996;88:3230-3239.[12] Yang ZX,Han ZB,Ji YR,et al.CD106 identifies a subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells with unique immunomodulatory properties.PloS One.2013;8:e59354.[13] Manochantr S,U-pratya Y,Kheolamai P,et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from amnion, placenta, Wharton's jelly and umbilical cord.Intern Med J.2013;43(4):430-439.[14] Ferrara JL,Levine JE,Reddy P,et al.Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009;373:1550-1561.[15] Ferrara JL,Reddy P.Pathophysiology of graft-versus-host disease.Semin Hematol.2006;43:3-10.[16] Teshima T,Ferrara JL.Understanding the alloresponse: New approaches to graft-versus-host disease prevention.Semin Hematol.2002;39(1):15-22.[17] Murphy WJ,Welniak LA,Taub DD,et al.Differential effects of the absence of interferon-gamma and IL-4 in acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mice.J Clin Invest.1998;102:1742-1748.[18] Soleymaninejadian E,Pramanik K,Samadian E.Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: cytokines and factors.Am J Reprod Immunol.2012;67:1-8.[19] Yagi H,Soto-Gutierrez A,Parekkadan B,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms of immunomodulation and homing. Cell Transplant.2010;19:667-679.[20] Arnberg F,Lundberg J,Olsson A,et al.Intra-arterial Administration of Placenta-Derived Decidual Stromal Cells to the Superior Mesenteric Artery in the Rabbit: Distribution of Cells, Feasibility, and Safety.Cell Transplant.2016;25(2): 401-410.[21] Kean TJ,Lin P,Caplan AI,et al.MSCs: Delivery Routes and Engraftment, Cell-Targeting Strategies, and Immune Modulation.Stem Cells Int.2013;2013:732742.[22] Aggarwal S,Pittenger MF.Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses.Blood.2005; 105:1815-1822.[23] Waterman RS,Tomchuck SL,Henkle SL,et al.A new mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) paradigm: polarization into a pro-inflammatory MSC1 or an Immunosuppressive MSC2 phenotype. PloS One.2010;5:e10088. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)