[1] SARROPOULOS I, MARIN R, CARDOSO-MOREIRA M, et al. Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species. Nature. 2019;571(7766):510-514.
[2] DÍAZ-VESGA MC, ZÚÑIGA-CUEVAS Ú, RAMÍREZ-REYES A, et al. Potential Therapies to Protect the Aging Heart Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:770421.
[3] LIU D, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Snapshot: Implications for mTOR in Aging-related Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Aging Dis. 2019;10(1):116-133.
[4] MA W, ZHU K, YIN L, et al. Effects of ischemic postconditioning and long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Bioengineered. 2022;13(6): 14799-14814.
[5] BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, KROEMER G, GALLUZZI L. Autophagy and Mitophagy in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2017;120(11):1812-1824.
[6] DONG Y, CHEN H, GAO J, et al. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;136:27-41.
[7] WANG Y, ZHOU L, SU W, et al. Selective Inhibition of PKCβ2 Restores Ischemic Postconditioning-Mediated Cardioprotection by Modulating Autophagy in Diabetic Rats. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:2408240.
[8] CHEN Z, HU Z, LU Z, et al. Differential microRNA profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy signaling network. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:378484.
[9] ZHANG J, CHEN S, LIU K. Structural insights into piRNA biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2022;1865(2):194799.
[10] ANZELON TA, CHOWDHURY S, HUGHES SM, et al. Structural basis for piRNA targeting. Nature. 2021;597(7875):285-289.
[11] CZECH B, MUNAFÒ M, CIABRELLI F, et al. piRNA-Guided Genome Defense: From Biogenesis to Silencing. Annu Rev Genet. 2018;52: 131-157.
[12] YANG Q, LI R, LYU Q, et al. Single-cell CAS-seq reveals a class of short PIWI-interacting RNAs in human oocytes. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):3389.
[13] WANG K, ZHOU LY, LIU F, et al. PIWI-Interacting RNA HAAPIR Regulates Cardiomyocyte Death After Myocardial Infarction by Promoting NAT10-Mediated ac4 C Acetylation of Tfec mRNA. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(8):e2106058.
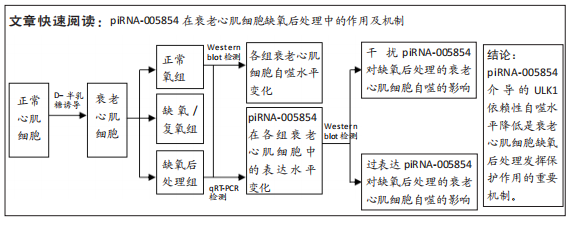
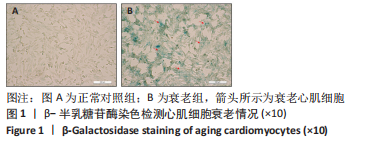
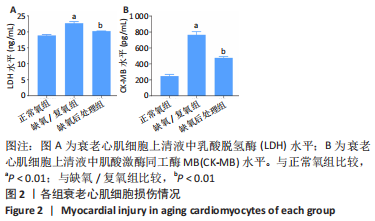
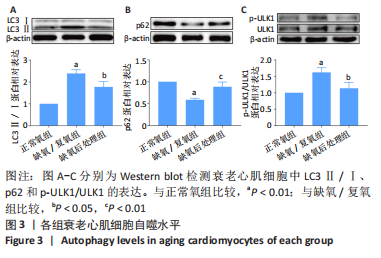
[14] 王琳,丁秀云,刘谟焓,等.D-半乳糖对幼鼠心肌细胞拟衰老作用的实验 [J].中国临床康复,2005,9(39):25-27,193.
[15] 徐灵博,郝银菊,丁宁,等.衰老心肌细胞缺氧后处理中miR-204的作用 [J].广东医学,2017,38(18):2764-2767.
[16] 胡大一,韩雅玲,宁光,等. 中国心血管病一级预防指南 [J].中华心血管病杂志,2020,48(12):1000-1038.
[17] IBÁÑEZ B, HEUSCH G, OVIZE M, et al. Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(14):1454-1471.
[18] BIRNBACH B, HÖPNER J, MIKOLAJCZYK R. Cardiac symptom attribution and knowledge of the symptoms of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20(1):445.
[19] 盛菽洋, 程江.生化标志物检测对急性心肌梗死再灌注的临床应用 [J]. 农垦医学,2021,43(3):248-251.
[20] PIRZEH L, BABAPOUR V, BADALZADEH R, et al. Pretreatment with vildagliptin boosts ischemic-postconditioning effects on cardioprotection and expression profile of genes regulating autophagy and mitochondrial fission/fusion in diabetic heart with reperfusion injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392(11): 1371-1382.
[21] HEUSCH G. Molecular basis of cardioprotection: signal transduction in ischemic pre-, post-, and remote conditioning. Circ Res. 2015;116(4): 674-699.
[22] HUMMITZSCH L, ZITTA K, BERNDT R, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning attenuates intestinal mucosal damage: insight from a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):136.
[23] BALLIN M, NORDSTRÖM P, NIKLASSON J, et al. Associations of Visceral Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Density With Incident Stroke, Myocardial Infarction, and All-Cause Mortality in Community-Dwelling 70-Year-Old Individuals: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(9):e020065.
[24] MA Y, MOUTON AJ, LINDSEY ML. Cardiac macrophage biology in the steady-state heart, the aging heart, and following myocardial infarction. Transl Res. 2018;191:15-28.
[25] AMAN Y, SCHMAUCK-MEDINA T, HANSEN M, et al. Autophagy in healthy aging and disease. Nat Aging. 2021;1(8):634-650.
[26] SU X, SHEN Y, JIN Y, et al. Aging-Associated Differences in Epitranscriptomic m6A Regulation in Response to Acute Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Female Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:654316.
[27] DE LUCIA C, PIEDEPALUMBO M, WANG L, et al. Effects of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury on plasma metabolomic profile during aging. Aging Cell. 2021;20(1):e13284.
[28] SAHA S, PANIGRAHI DP, PATIL S, et al. Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:485-495.
[29] WU X, LIU Z, YU XY, et al. Autophagy and cardiac diseases: Therapeutic potential of natural products. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(1):314-341.
[30] JUNG S, CHOE S, WOO H, et al. Autophagic death of neural stem cells mediates chronic stress-induced decline of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive deficits. Autophagy. 2020;16(3):512-530.
[31] WANG X, GUO Z, DING Z, et al. Inflammation, Autophagy, and Apoptosis After Myocardial Infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(9):e008024.
[32] HEUSCH G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12):773-789.
[33] DU J, LI Y, ZHAO W. Autophagy and Myocardial Ischemia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:217-222.
[34] LI G, DING N, XIONG J, et al. Ischemic Postconditioning Protects against Aged Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of miR-181a-2-3p. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:9635674.
[35] LI Y, CHEN Y. AMPK and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:85-108.
[36] TONG M, SAITO T, ZHAI P, et al. Alternative Mitophagy Protects the Heart Against Obesity-Associated Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2021; 129(12):1105-1121.
[37] KOBAYASHI S, XU X, CHEN K, et al. Suppression of autophagy is protective in high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Autophagy. 2012;8(4):577-592.
[38] SIOMI H, SIOMI MC. On the road to reading the RNA-interference code. Nature. 2009;457(7228):396-404.
[39] YANG J, XUE FT, LI YY, et al. Exosomal piRNA sequencing reveals differences between heart failure and healthy patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(22):7952-7961.
[41] PERERA BPU, TSAI ZT, COLWELL ML, et al. Somatic expression of piRNA and associated machinery in the mouse identifies short, tissue-specific piRNA. Epigenetics. 2019;14(5):504-521.
[41] RAJAN KS, VELMURUGAN G, GOPAL P, et al. Abundant and Altered Expression of PIWI-Interacting RNAs during Cardiac Hypertrophy. Heart Lung Circ. 2016;25(10):1013-1020.
[42] 滕增光. piRNA-DQ765261/Bcl-xL和AMPK/ULK在镉诱导生精细胞自噬中的作用 [D].武汉:武汉科技大学,2021. |