中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2481-2487.doi: 10.12307/2024.309
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
高氟干预成釉细胞钙稳态差异表达基因的筛选及分析
黄 婷1,刘 霞1,王 烛2,陈 霆2,陈 彬2,白国辉1,吴家媛1,田 源1
- 1遵义医科大学附属口腔医院,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563000
Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes for calcium homeostasis in ameloblasts with high fluoride intervention
Huang Ting1, Liu Xia1, Wang Zhu2, Chen Ting2, Chen Bin2, Bai Guohui1, Wu Jiayuan1, Tian Yuan1
- 1Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
氟斑牙:是长期摄入大量的氟所导致的牙釉质发育障碍。钙稳态:正常生理环境下细胞内和细胞外钙离子浓度保持动态平衡称为钙稳态,当机体受到有害因素的刺激时可出现钙稳态失衡,导致细胞内钙离子浓度异常增加,最终诱发疾病。
背景:氟牙症是长期摄入大量氟所导致的牙釉质发育障碍,病因复杂,其发病机制有待深入研究。
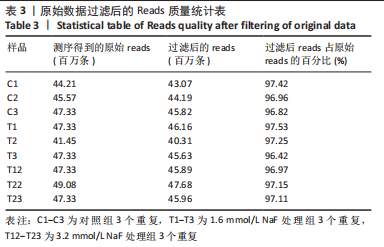
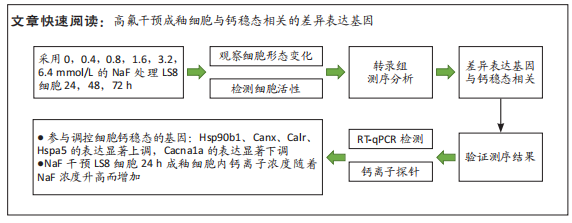
目的:通过转录组测序技术筛选高氟干预成釉细胞与钙稳态相关的差异表达基因,并进一步探索氟斑牙形成的分子机制。方法:分别用浓度为0,0.4,0.8,1.6,3.2,6.4 mmol/L的NaF处理成釉细胞LS8 24,48,72 h,检测细胞形态、细胞活性与细胞内钙离子浓度。分别用浓度为0,1.6,3.2 mmol/L的NaF处理成釉细胞LS8 24 h,通过转录组测序筛选差异表达基因,并对差异表达基因进行验证。
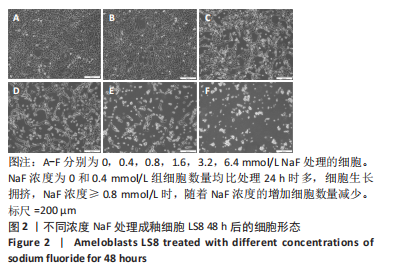
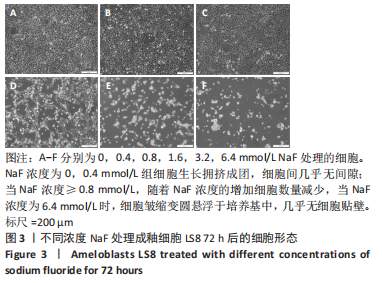
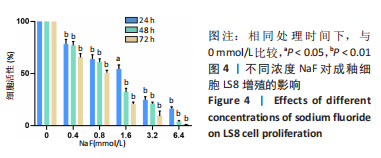
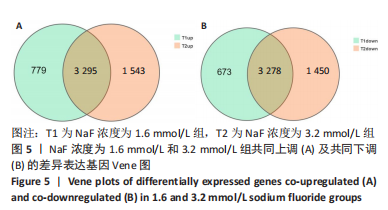
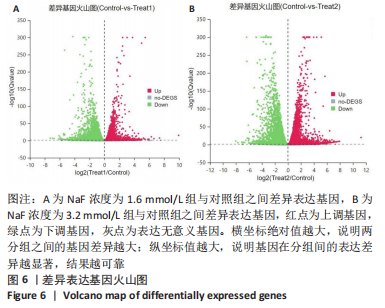
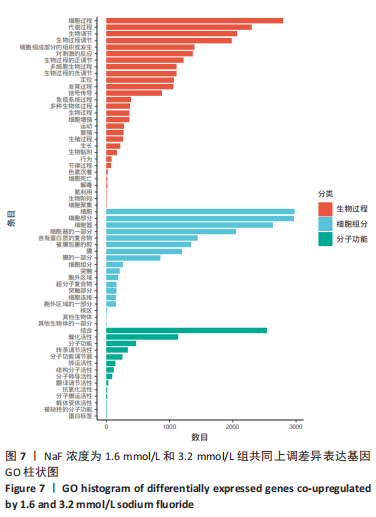
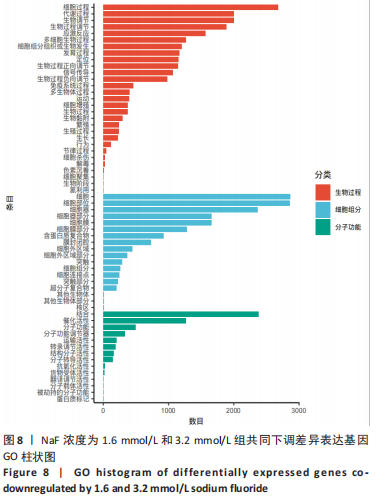
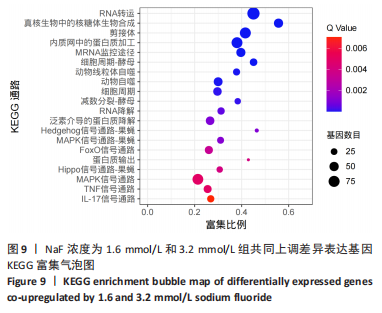
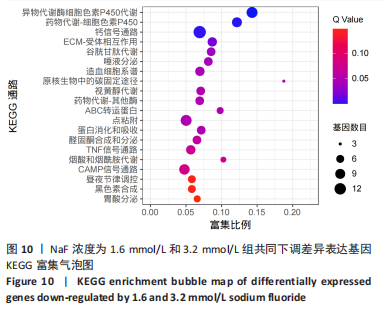
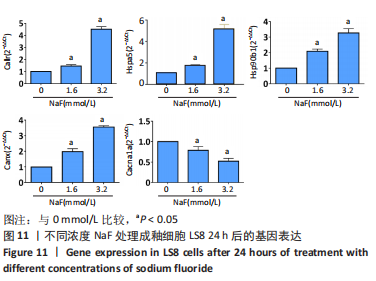
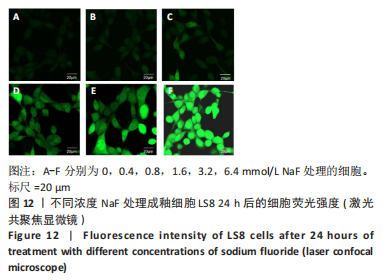
结果与结论:①处理24 h后,NaF浓度0,0.4,0.8 mmol/L组细胞生长状态良好,细胞的数量增多,细胞轮廓清晰;当NaF浓度≥1.6 mmol/L,随着NaF浓度的增加,细胞体积逐渐皱缩变小、细胞数量减少。处理48,72 h后,NaF浓度0,0.4 mmol/L组细胞数量增加,0.8,1.6,3.2 mmol/L组细胞数量逐渐减少,细胞形态变圆、变小,6.4 mmol/L组细胞皱缩变圆悬浮于培养基中,几乎无细胞贴壁。当NaF浓度相同时,处理24 h后LS8细胞的生长状态最佳。CCK-8检测结果显示,当NaF浓度相同时,随着处理时间的延长,细胞活性减弱;当处理时间相同时,随着NaF浓度的增加,细胞活性减弱。处理24 h后,随着NaF浓度的增加,细胞内钙离子浓度增加。②转录组测序分析发现参与调控细胞钙稳态的基因:Hsp90b1、Canx、Calr、Hspa5的表达显著上调(P < 0.05),Cacna1a的表达显著下调(P < 0.05),该结果得到了RT-qPCR检测的验证。③结果显示,NaF对LS8细胞增殖的抑制作用可能与细胞内Ca2+浓度异常增加有关,其机制可能由蛋白质加工合成通路Hsp90b1、Canx、Calr、Hspa5表达上调和钙信号通路Cacna1a表达下调所导致。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-8135-1744(黄婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: